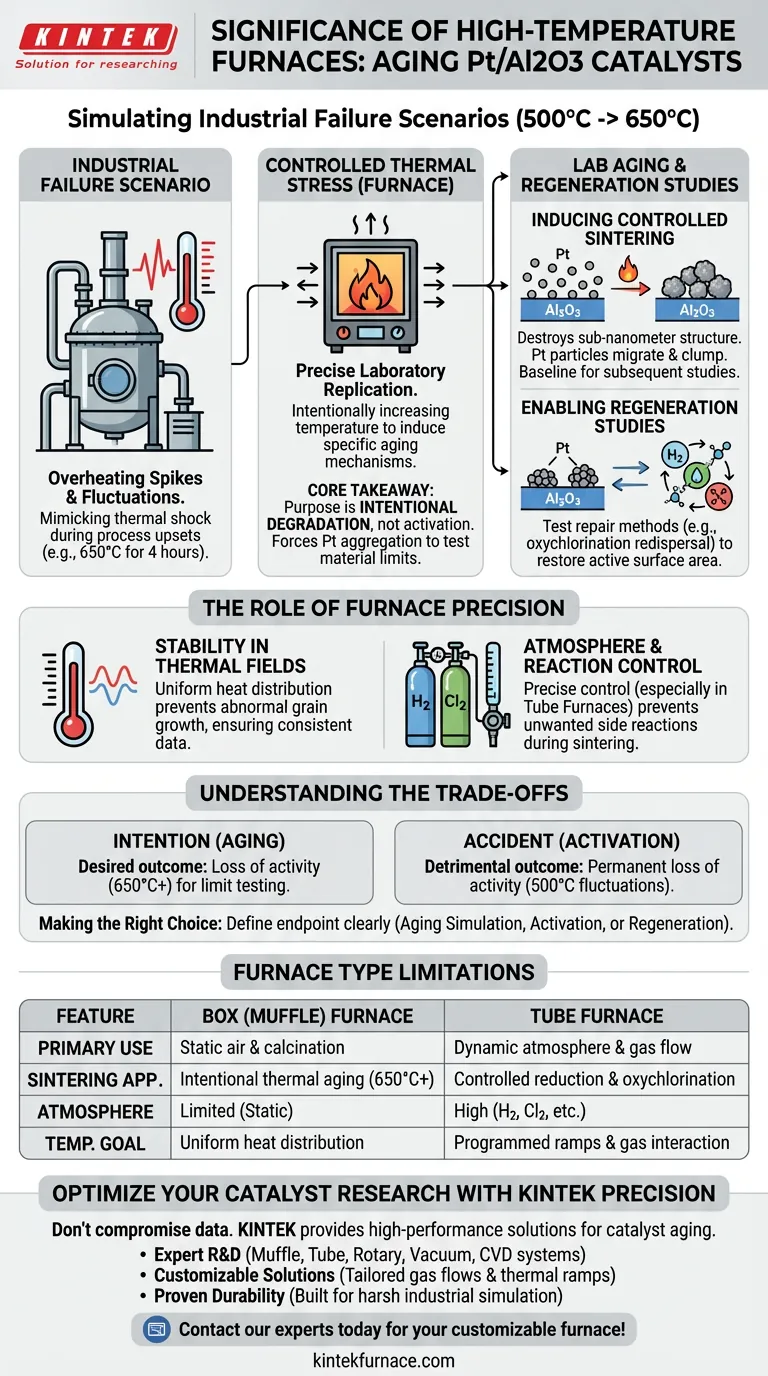
Simulating industrial failure scenarios is the primary significance of using high-temperature furnaces for Pt/Al2O3 catalysts. By intentionally increasing the temperature from 500 °C to 650 °C, researchers replicate the overheating conditions found in large-scale industrial reactors. This controlled thermal stress is necessary to induce specific aging mechanisms for study.
Core Takeaway The purpose of this high-temperature treatment is not catalyst activation, but intentional degradation. It forces the aggregation of platinum particles to test the limits of the material, creating a baseline for evaluating subsequent regeneration processes like oxychlorination redispersal.
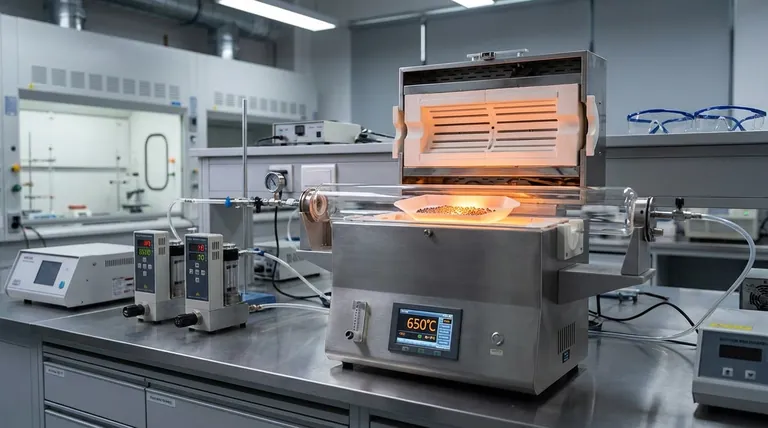

Replicating Real-World Stress Factors
Simulating Overheating Failure
In industrial operations, reactors are subject to temperature spikes and fluctuations. The furnace allows researchers to model these "overheating failure scenarios" precisely. By shifting the environment from a standard 500 °C to an elevated 650 °C for a sustained period (e.g., 4 hours), the equipment mimics the thermal shock a catalyst endures during process upsets.
Inducing Controlled Sintering
The primary physical outcome of this heat treatment is sintering. High temperatures cause the platinum (Pt) particles on the aluminum oxide (Al2O3) support to migrate and clump together. This aggregation destroys the desirable sub-nanometer structure of the catalyst, effectively aging it under laboratory conditions.
Enabling Regeneration Studies
The ultimate goal of inducing this damage is to verify repair methods. Once the platinum has aggregated, researchers can test "oxychlorination redispersal processes." The furnace provides the initial "broken" state required to prove that a regeneration technique can successfully restore the active surface area of the catalyst.
The Role of Furnace Precision
Stability in Thermal Fields
While the goal is degradation, the application of heat must be uniform. A stable temperature field prevents random, abnormal grain growth that leads to inconsistent data. Whether using a box or tube furnace, the equipment must ensure that the thermal exposure is consistent across the entire sample batch.
Atmosphere and Reaction Control
The choice between a tube and box furnace often comes down to atmospheric requirements. A tube furnace is typically required when specific gas flows (like hydrogen for reduction or specialized oxidizing atmospheres) are needed during the heating ramp. Precise control over the environment prevents unwanted chemical side reactions while the physical sintering occurs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Intention vs. Accident
It is critical to distinguish between intentional sintering for aging studies and accidental sintering during activation. In activation stages (typically around 500 °C), temperature fluctuations are detrimental and result in permanent loss of activity. In aging studies (650 °C+), this loss of activity is the desired outcome to test material limits.
Furnace Type Limitations
Box (Muffle) Furnaces: Excellent for static air treatments and calcination to remove impurities like moisture or organic volatile components. However, they lack dynamic atmosphere control. Tube Furnaces: Essential for processes requiring gas flow, such as reduction or controlled oxidation. They allow for programmed temperature ramps that prevent "instantaneous" high-temperature shock, which can cause uncontrolled rather than simulated grain coarsening.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a thermal treatment protocol for Pt/Al2O3 catalysts, define your endpoint clearly.
- If your primary focus is Aging Simulation: Use the furnace to ramp temperatures to 650 °C to force Pt aggregation and mimic industrial failure.
- If your primary focus is Activation: Maintain a strict 500 °C limit with precise stability to establish metal-support interactions without inducing sintering.
- If your primary focus is Regeneration: Ensure your furnace can handle the specific gas flows (such as chlorine-based atmospheres) required to redisperse the sintered particles.
The value of the furnace lies not just in generating heat, but in the precise application of thermal stress to validate the catalyst's lifecycle resilience.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Box (Muffle) Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Static air treatments & calcination | Dynamic atmosphere control & gas flow |
| Sintering Application | Intentional thermal aging (650°C+) | Controlled reduction & oxychlorination |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited (Static) | High (H2, Cl2, etc.) |
| Temperature Goal | Uniform heat distribution | Programmed ramps & gas interaction |
Optimize Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let inconsistent thermal fields compromise your data. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory solutions specifically designed for the rigorous demands of catalyst aging and regeneration studies.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems are engineered for stability and precision.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailor your furnace to handle specific gas flows or unique thermal ramps required for your Pt/Al2O3 experiments.
- Proven Durability: Built to withstand the harsh environments of industrial simulation.
Ready to elevate your material testing? Contact our experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace for your lab's unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Lu Dong, Xinggui Zhou. Structure Robustness of Highly Dispersed Pt/Al2O3 Catalyst for Propane Dehydrogenation during Oxychlorination Regeneration Process. DOI: 10.3390/catal14010048
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of using a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Dynamic, Uniform Heating for Powders
- Why is it necessary to perform annealing in a tube furnace with a nitrogen atmosphere for VO2@AlF3 core-shell powder?
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in the heat treatment of NiTiCu alloys? Optimize Shape Memory Properties
- How does the injection probe in a Drop Tube Furnace ensure a high heating rate? Simulate Industrial Pyrolysis Expertly
- What role do multi zone tube furnaces play in new energy research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Innovation
- How does a laboratory tube furnace ensure the structural stability and quality of hard carbon? Expert Carbonization
- What environmental conditions does a high-temperature Tube furnace provide for AlN nanofibers? | KINTEK
- What kind of reaction environment does a laboratory tube furnace provide? Optimize Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) Synthesis



















