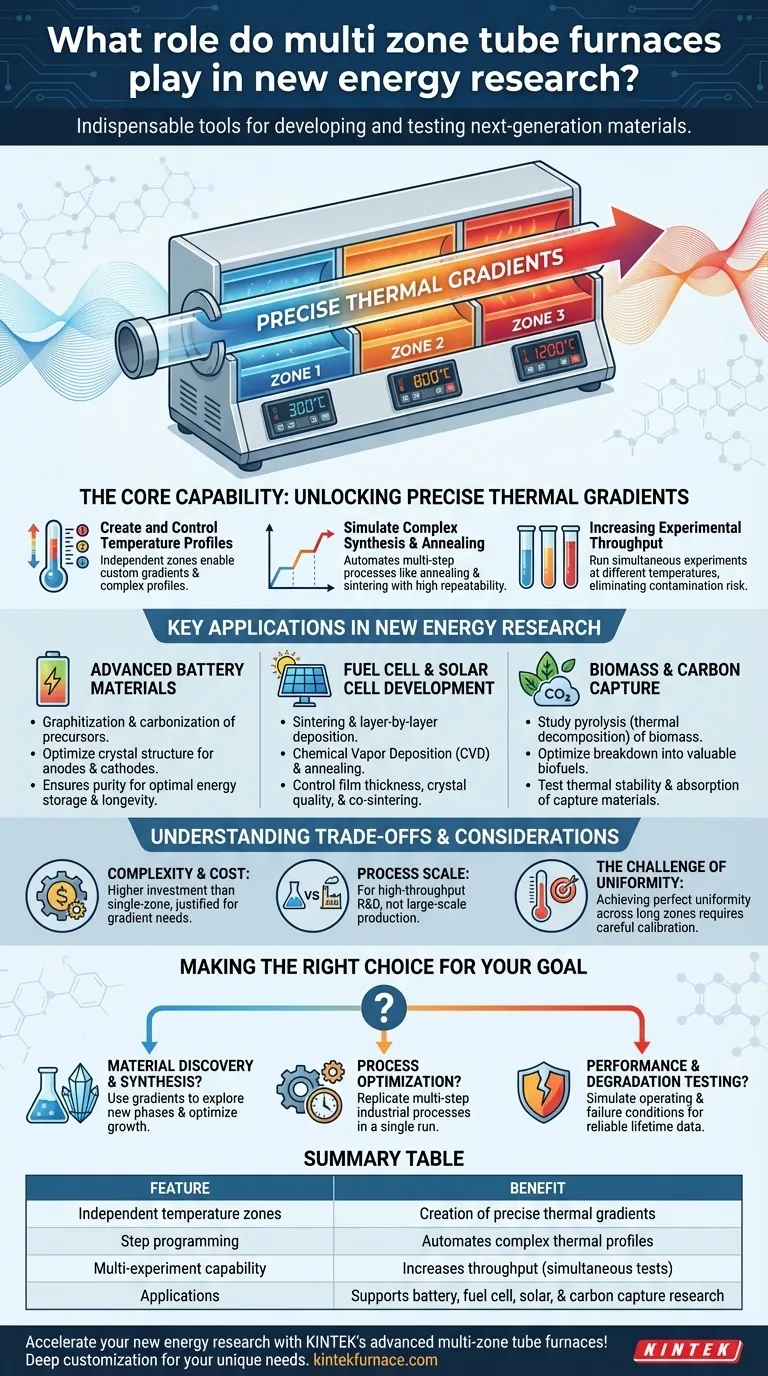
In the field of new energy research, multi-zone tube furnaces are indispensable tools for both developing and testing the materials that power next-generation technologies. They are mission-critical for fabricating and analyzing advanced battery components, preparing fuel cell materials, optimizing thin films for solar cells, and investigating methods for carbon capture. Their unique ability to control distinct temperature zones along a single axis allows researchers to precisely replicate and accelerate complex thermal processes.
The core value of a multi-zone furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its power to create precise, independent temperature gradients within a single experiment. This allows researchers to simulate and optimize complex material synthesis and degradation processes that are impossible to study in a standard single-zone furnace.
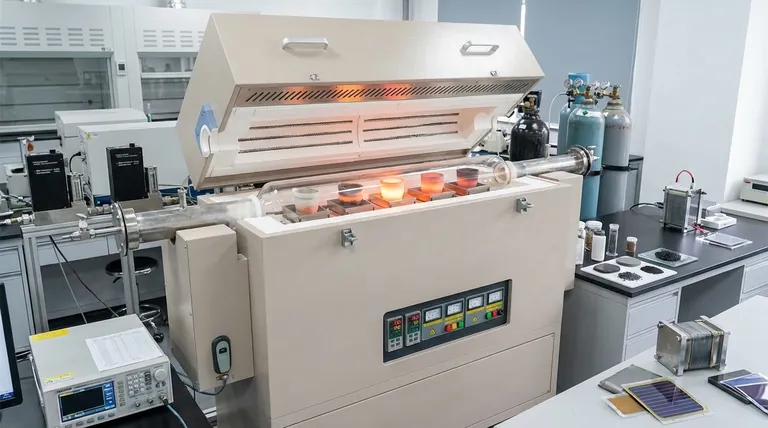

The Core Capability: Unlocking Precise Thermal Gradients
The fundamental advantage of a multi-zone furnace over a standard model is its ability to move beyond simple, uniform heating. This unlocks more sophisticated experimental designs.
Creating and Controlling Temperature Profiles
A multi-zone furnace divides the heated tube length into two or more independent sections. Each section has its own thermocouple and controller, allowing you to set a unique temperature for each zone.
This enables the creation of a temperature gradient—a smooth or stepped change in temperature along the length of the processing tube.
Simulating Complex Synthesis and Annealing
Many advanced materials do not form under uniform heat. They require a sequence of heating, holding, and cooling steps, a process known as annealing or sintering.
With step programming capabilities, a multi-zone furnace can execute these complex thermal profiles automatically, ensuring perfect repeatability between experiments.
Increasing Experimental Throughput
The multiple zones can be used to run several experiments simultaneously at different temperatures. This dramatically increases research throughput compared to running sequential tests in a single-zone furnace.
It also eliminates process variables and potential contamination that can occur when moving a sample between different furnaces for multi-step processing.
Key Applications in New Energy Research
This precise thermal control directly enables progress in the most critical areas of new energy development.
Advanced Battery Materials
The performance of lithium-ion batteries is dictated by the microscopic structure of their anode and cathode materials.
Multi-zone furnaces are used for critical processes like graphitization and carbonization of precursor materials. The precise temperature control ensures the final material has the desired crystal structure and purity for optimal energy storage and longevity.
Fuel Cell and Solar Cell Development
Fuel cells and thin-film solar cells rely on materials sintered at high temperatures or deposited layer by layer.
These furnaces are used for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and annealing processes, where a temperature gradient can be used to control film thickness and crystal quality. They are also used to co-sinter different components of a fuel cell that require different processing temperatures.
Biomass and Carbon Capture
Multi-zone furnaces are vital for studying pyrolysis, the thermal decomposition of biomass in the absence of oxygen to produce biofuels. The gradient allows researchers to optimize the breakdown of complex organic matter into valuable gases and liquids.
Similarly, they are used to test the thermal stability and absorption capacity of materials designed for carbon capture and storage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, these instruments are not universally necessary. Understanding their limitations is key to making a sound investment.
Complexity and Cost
The added controllers, power supplies, and insulation make multi-zone furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than their single-zone counterparts. Their use is only justified when a temperature gradient or multi-step process is a core experimental requirement.
Process Scale vs. Experimental Throughput
These furnaces are research instruments designed for high experimental throughput, not large-scale production. While they accelerate the discovery and optimization of materials, the processes developed within them must later be adapted for industrial-scale manufacturing equipment.
The Challenge of True Uniformity
While excellent at creating gradients, achieving perfect temperature uniformity within a single, long zone can still be a challenge. For applications demanding absolute uniformity over a large area, careful calibration and material placement are critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a multi-zone furnace should be driven entirely by your research objectives.
- If your primary focus is material discovery and synthesis: The ability to create controlled temperature gradients is your most powerful tool for exploring new material phases and optimizing crystal growth.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Use the multiple zones to replicate a multi-step industrial process in a single, condensed run, rapidly identifying ideal parameters.
- If your primary focus is performance and degradation testing: The furnace's precise control allows you to simulate specific operating temperatures and failure conditions with high repeatability, providing reliable data on material lifetime.
Ultimately, a multi-zone tube furnace transforms a simple heating element into a sophisticated platform for materials innovation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Independent temperature zones | Enables creation of precise thermal gradients for complex processes |
| Step programming | Automates annealing and sintering with high repeatability |
| Multi-experiment capability | Increases throughput by running tests at different temperatures simultaneously |
| Applications | Supports battery material synthesis, fuel cell development, solar cell optimization, and carbon capture research |
Accelerate your new energy research with KINTEK's advanced multi-zone tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve faster material discovery and process optimization. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your innovation and drive breakthroughs in battery, fuel cell, and solar technologies!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What advantages do multi zone tube furnaces offer for chemical reaction studies? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients



















