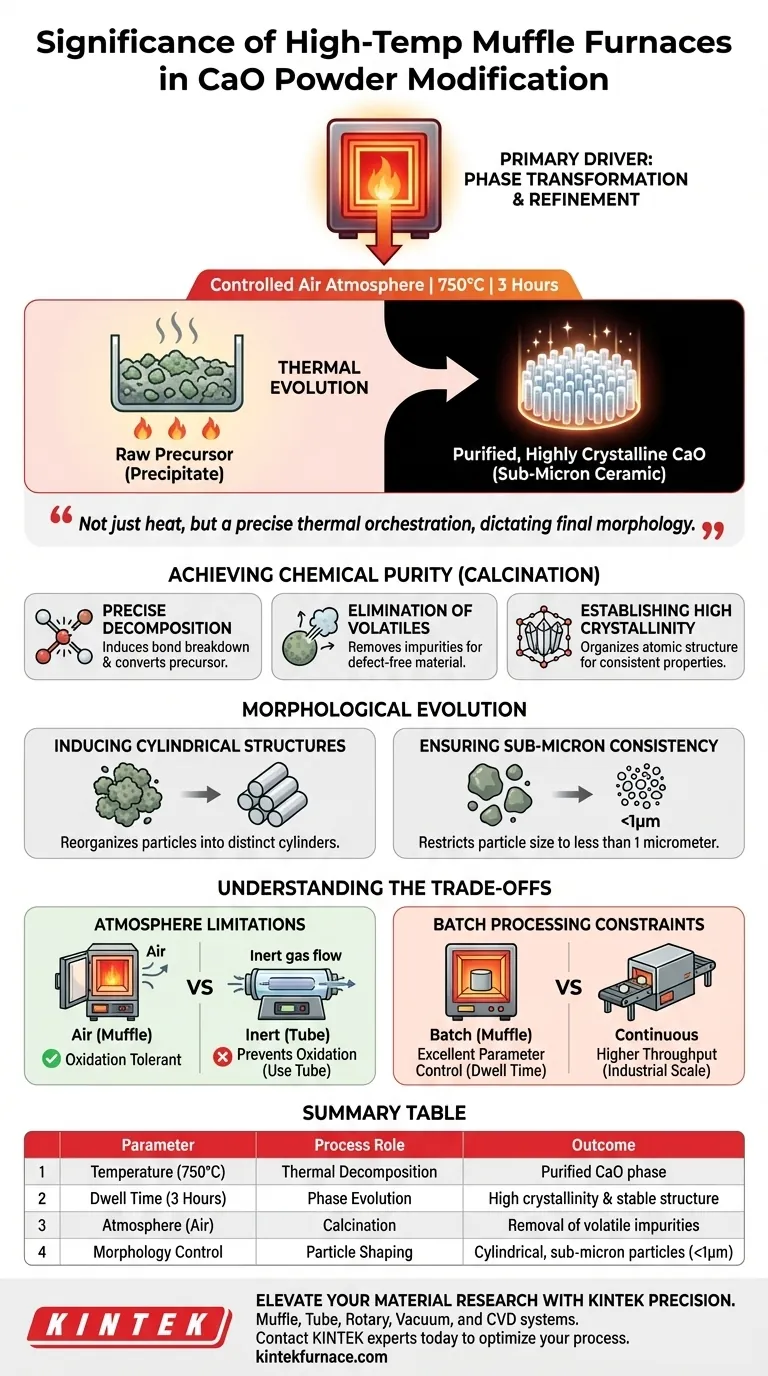
A high-temperature muffle furnace acts as the primary driver for phase transformation during the modification of calcium oxide (CaO) ceramic powders. By sustaining a controlled air atmosphere at exactly 750 degrees Celsius for 3 hours, the furnace triggers thermal decomposition, converting raw precursors into a purified, highly crystalline calcium oxide phase while refining the physical particle structure.
The muffle furnace does not merely heat the material; it orchestrates a precise thermal evolution. It facilitates the removal of volatile impurities and dictates the final morphology of the powder, ensuring the transition from a raw precipitate to a functional, sub-micron ceramic material.

Achieving Chemical Purity through Calcination
Precise Thermal Decomposition
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this context is to facilitate calcination.
By heating the precursor precipitate to 750 degrees Celsius, the furnace induces the breakdown of chemical bonds in the raw material.
This thermal treatment effectively converts the precursor into the desired calcium oxide phase through decomposition.
Elimination of Volatiles
To achieve high-performance ceramics, the powder must be free of contaminants.
The sustained heat of the muffle furnace ensures the complete removal of volatile impurities.
This purification step is critical for preventing defects during later processing stages.
Establishing High Crystallinity
The muffle furnace provides the thermal energy required to organize the atomic structure of the material.
Holding the temperature at 750 degrees Celsius for 3 hours allows the calcium oxide to develop a highly crystalline phase.
High crystallinity is essential for ensuring the material exhibits consistent physical and chemical properties.
Morphological Evolution of the Powder
Inducing Cylindrical Structures
Beyond chemical changes, the furnace environment drives the physical evolution of the particles.
The thermal treatment causes the powder particles to reorganize into a distinct cylindrical structure.
This morphological control is often vital for specific applications where packing density or surface area is a key performance metric.
Ensuring Sub-Micron Consistency
The muffle furnace prevents the uncontrolled growth of particles commonly seen in uneven heating environments.
The process restricts the final particle size to less than 1 micrometer.
This fine particle size is crucial for subsequent sintering steps, allowing for better densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Atmosphere Limitations
While excellent for oxidative processes, a standard muffle furnace typically uses a controlled air atmosphere.
This is ideal for calcium oxide modification where oxidation or air tolerance is acceptable.
However, if your material requires a strictly inert environment (such as Argon to prevent oxidation), a tube furnace with sealed atmosphere control would be the superior choice over a muffle furnace.
Batch Processing Constraints
Muffle furnaces are generally designed for batch processing rather than continuous flow.
This provides excellent control over specific parameters like the 3-hour dwell time for calcium oxide.
However, it may limit throughput compared to continuous processing equipment used in large-scale industrial manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is synthesizing active ceramic powder: Ensure your furnace is programmed for 750°C for 3 hours to achieve the necessary decomposition and cylindrical morphology.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity of formed parts: Utilize the furnace for pre-sintering green compacts (typically around 800°C) to improve bonding before high-pressure densification.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation: Do not use a standard muffle furnace; opt for a tube furnace that allows for a continuous inert gas flow (such as Argon).
Precision in thermal processing is the difference between a raw precipitate and a high-performance ceramic material.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Process Role | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (750°C) | Thermal Decomposition | Converts precursors into purified CaO phase |
| Dwell Time (3 Hours) | Phase Evolution | Establishes high crystallinity and stable structure |
| Atmosphere (Air) | Calcination | Ensures removal of volatile impurities |
| Morphology Control | Particle Shaping | Produces cylindrical, sub-micron particles (<1µm) |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect sub-micron morphology and chemical purity in calcium oxide ceramics requires uncompromising thermal control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your specific dwell time, atmosphere, and temperature requirements.
Ready to optimize your ceramic modification process?
Contact KINTEK experts today to find the ideal thermal solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Roberto Ananias Ribeiro. Síntese e caracterização de ésteres metílicos obtidos com o uso do catalisador de CaO preparado por precipitação alcalina. DOI: 10.55905/cuadv17n5-073
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory box resistance furnace play in lunar ISRU? Advancing Space Construction with KINTEK
- What types of controllers are used in muffle furnaces? Choose the Right One for Precise Thermal Control
- How are muffle furnaces applied in heat treatment processes? Achieve Precise Control for Superior Material Properties
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in preparing expanded graphite? Achieve High-Efficiency PCM Carriers
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Achieving Pure, Contaminant-Free Heating
- Why are muffle furnaces particularly useful in material science? Unlock Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- What are the environmental requirements for muffle furnace operation? Ensure Safety and Precision in Your Lab
- What are the design features of Box Furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment with Advanced Engineering



















