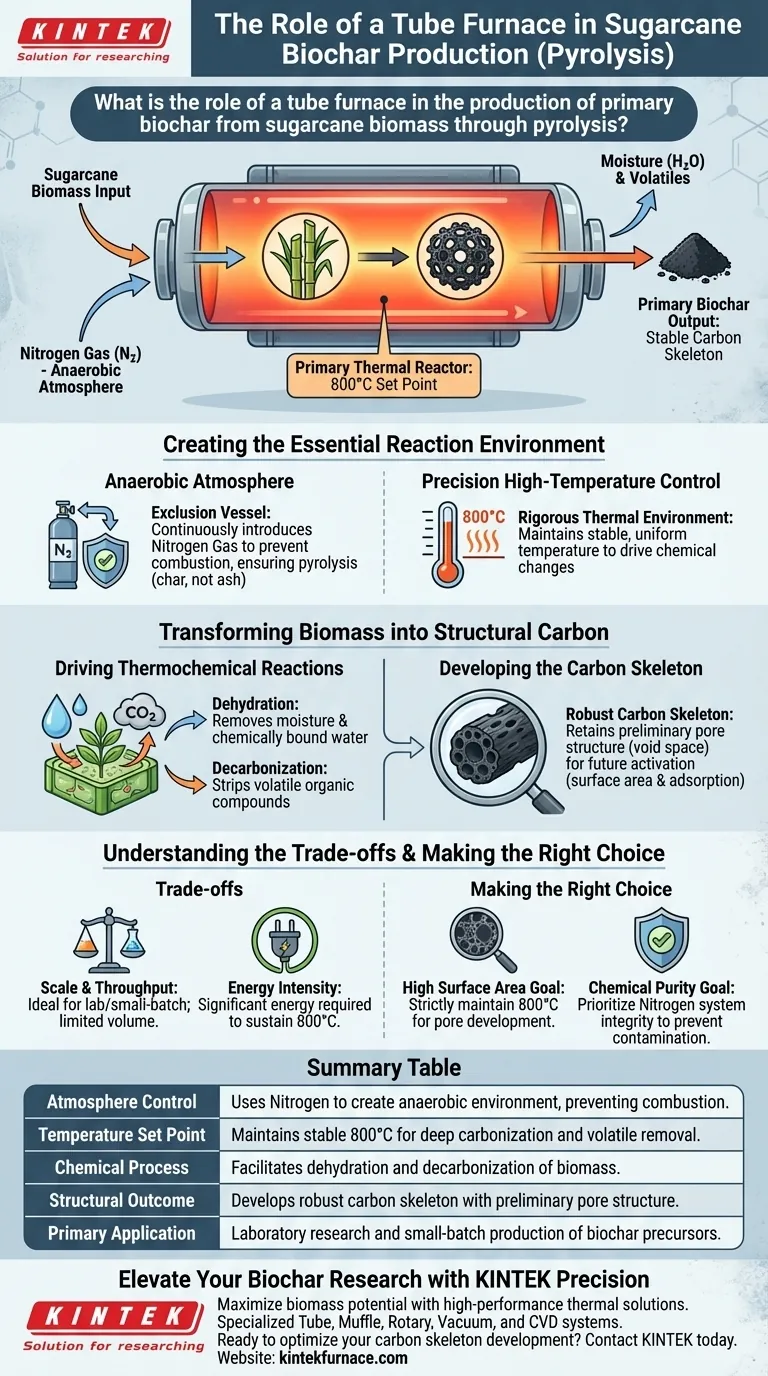
The tube furnace acts as the primary thermal reactor in the conversion of sugarcane biomass into biochar, creating a strictly controlled anaerobic environment essential for pyrolysis. By introducing nitrogen gas and maintaining a specific high-temperature set point—typically 800°C for this feedstock—the furnace drives thermochemical reactions that convert raw sugarcane into a stable carbon skeleton.
Core Takeaway: The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is an exclusion vessel that prevents combustion. Its primary function is to facilitate deep carbonization through dehydration and decarbonization, establishing the preliminary pore structure that serves as the physical foundation for any subsequent activation.

Creating the Essential Reaction Environment
Establishing an Anaerobic Atmosphere
The most critical role of the tube furnace is to isolate the sugarcane biomass from oxygen.
By continuously introducing nitrogen gas, the furnace creates an inert atmosphere.
This prevents the biomass from burning (combustion) and ensures it undergoes pyrolysis, turning the organic material into char rather than ash.
Precision High-Temperature Control
For sugarcane biomass, the tube furnace is tasked with maintaining a rigorous thermal environment, specifically around 800°C.
This high heat is necessary to drive the chemical changes required for primary biochar production.
Unlike open-fire methods, the tube furnace ensures the temperature remains stable and uniform throughout the reaction zone.
Transforming Biomass into Structural Carbon
Driving Thermochemical Reactions
Under the heat of the tube furnace, the sugarcane undergoes two specific processes: dehydration and decarbonization.
Dehydration removes moisture and chemically bound water from the plant structure.
Decarbonization strips away volatile organic compounds, leaving behind a concentrated carbon matrix.
Developing the Carbon Skeleton
The result of this thermal processing is a robust carbon skeleton.
This skeleton retains a preliminary pore structure, which is the void space left behind after volatile components are expelled.
This physical foundation is critical if the biochar is intended for later activation steps, as it defines the material's potential surface area and adsorption capabilities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Scale and Throughput Limitations
While tube furnaces offer exceptional control over atmospheric conditions and temperature, they are generally limited by volume.
They are ideal for laboratory research or small-batch production but may not be suitable for high-throughput industrial manufacturing without significant modification or parallelization.
Energy Intensity
maintaining a consistent temperature of 800°C requires significant energy input.
Operators must balance the need for high-quality, high-porosity char against the operational costs of sustaining such high temperatures for the duration of the pyrolysis cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a tube furnace for sugarcane pyrolysis, consider your specific end-goals:
- If your primary focus is high surface area: Ensure your furnace is calibrated to strictly maintain 800°C, as this maximizes the development of the preliminary pore structure.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity: Prioritize the integrity of the nitrogen flow system to prevent any trace oxygen from contaminating the carbon skeleton.
The tube furnace is the defining tool that transforms sugarcane from agricultural waste into a high-value carbon precursor ready for advanced application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Sugarcane Pyrolysis |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Uses nitrogen to create an anaerobic environment, preventing combustion. |
| Temperature Set Point | Maintains a stable 800°C for deep carbonization and volatile removal. |
| Chemical Process | Facilitates dehydration and decarbonization of the biomass. |
| Structural Outcome | Develops a robust carbon skeleton with a preliminary pore structure. |
| Primary Application | Laboratory research and small-batch production of biochar precursors. |
Elevate Your Biochar Research with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the potential of your biomass research with high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of pyrolysis and carbonization. Whether you need precise atmospheric control for sugarcane biomass or customizable high-temp furnaces for unique lab requirements, our equipment ensures consistent, high-purity results.
Ready to optimize your carbon skeleton development? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Yanan Zhao, Jian Wang. Magnetically recoverable bagasse-activated carbon composite anodes for sediment microbial fuel cells: enhanced performance in chromium-contaminated soil remediation. DOI: 10.1039/d5ra02890f
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in Nb2O5 nanogrids? Achieve 550°C Precision for Synthesis
- What types of heating methods are used in split tube furnaces? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- What types of atmospheres can be controlled in a drop tube furnace? Master Precise Gas Control for Superior Materials
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the calcination of superconducting ceramics? Expert Insights
- What critical process conditions does a tube furnace provide for orange peel activated carbon synthesis?
- What is the purpose of using a tube furnace with an external heating module? Isolating Catalytic Mechanisms
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in geological and mineralogical research? Unlock Earth's Secrets with Precision
- What conditions does a tubular reactor provide for catalyst reduction? Master Platinum, Copper, and Nickel Activation



















