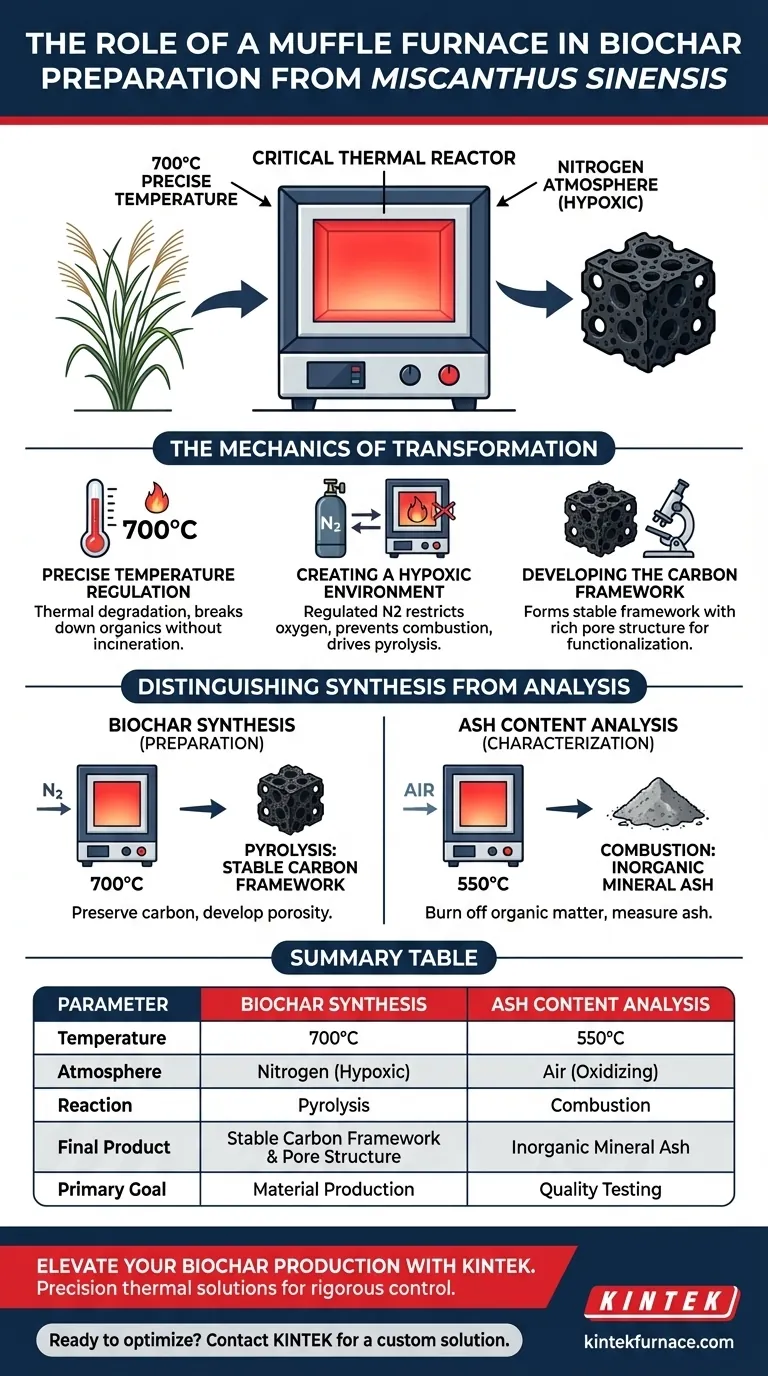
A Muffle Furnace serves as the critical thermal reactor in the preparation of biochar from Miscanthus sinensis, providing a precisely controlled environment to drive pyrolysis. Specifically, it maintains the biomass at a steady temperature of 700°C while utilizing a regulated nitrogen atmosphere to strictly limit oxygen exposure.
The Muffle Furnace acts as a hypoxic chamber that forces thermal decomposition rather than combustion. By excluding oxygen at high temperatures, it transforms raw plant matter into a stable carbon framework with a rich pore structure, rather than allowing it to burn down to ash.

The Mechanics of Transformation
Precise Temperature Regulation
For Miscanthus sinensis, the Muffle Furnace must maintain a specific high-temperature setpoint of 700°C.
At this temperature, the furnace drives the thermal degradation of the biomass. This heat energy is sufficient to break down the organic components of the plant without incinerating the carbon skeleton.
Creating a Hypoxic Environment
The furnace plays a dual role by not only heating the sample but also housing a regulated nitrogen atmosphere.
This restricts the entry of oxygen, creating a hypoxic (low oxygen) condition. This is the defining factor of pyrolysis; without this atmospheric control, the high heat would simply cause the biomass to catch fire and burn away.
Developing the Carbon Framework
The primary output of this controlled environment is the formation of a stable carbon framework.
By driving off volatile components under nitrogen protection, the furnace ensures the remaining material develops a rich pore structure. This porosity is essential if the biochar is intended for subsequent functionalization or adsorption applications.
Distinguishing Synthesis from Analysis
The Risk of Combustion
It is critical to understand that a Muffle Furnace is a versatile tool that behaves differently based on atmospheric control.
If the nitrogen atmosphere is removed and air is allowed to enter, the furnace functions as a combustion chamber. In this mode, it is used to determine ash content by burning samples completely (often at 550°C), leaving only inorganic minerals behind.
Operational Intent
For biochar preparation, you are utilizing the furnace's ability to isolate the sample from oxygen.
For biochar characterization (ash testing), you are utilizing the furnace's ability to facilitate oxidation. Confusing these two operational modes will result in the total loss of your carbon yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your Muffle Furnace for Miscanthus sinensis, apply the following guidelines:
- If your primary focus is Biochar Synthesis: Ensure a steady flow of nitrogen to maintain a hypoxic environment at 700°C to preserve the carbon skeleton and develop porosity.
- If your primary focus is Material Characterization: Allow oxygen entry and lower the temperature to approx. 550°C to burn off organic matter and measure inorganic ash content.
Success depends not just on the heat applied, but on the strict control of the atmosphere surrounding your sample.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Biochar Synthesis (Preparation) | Ash Content Analysis (Characterization) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 700°C | 550°C |
| Atmosphere | Nitrogen (Hypoxic) | Air (Oxidizing) |
| Reaction | Pyrolysis (Thermal Decomposition) | Combustion (Burning) |
| Final Product | Stable Carbon Framework & Pore Structure | Inorganic Mineral Ash |
| Primary Goal | Material Production | Quality Testing |
Elevate Your Biochar Production with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between high-surface-area biochar and simple ash. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum furnaces designed to deliver the rigorous atmospheric control and temperature stability your research demands. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet the unique requirements of Miscanthus sinensis pyrolysis and other lab high-temperature applications.
Ready to optimize your carbon yields? Contact KINTEK today for a custom thermal solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Meenakshi Sundaram Sharmila, Gurusamy, Annadurai. Biogenic fabrication of biochar-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles using Miscanthus sinensis for oxytetracycline removal and toxicological assessment. DOI: 10.12692/jbes/27.2.10-20
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the design characteristics of muffle furnaces that contribute to their efficiency? Discover Key Features for Superior Performance
- How are box type electric furnaces utilized in laboratory research? Enhance Precision in Material Synthesis and Testing
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the carbonization synthesis of orange peel biochar? Precision Thermal Pyrolysis
- How long does it take for a muffle furnace to reach its maximum temperature? Optimize Your Lab's Heating Process
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in plant leaf ash analysis? Master Precision Dry Ashing
- Why is a programmable temperature control box furnace required for Bi-2223? Ensure High-Purity Superconductor Synthesis
- What role does a high-temperature box resistance furnace play in Hydroxyapatite/Zirconia composite preparation?
- Why are muffle furnaces used to determine moisture, ash, and volatile content in pharmaceutical materials? Essential for Precise Quality Control



















