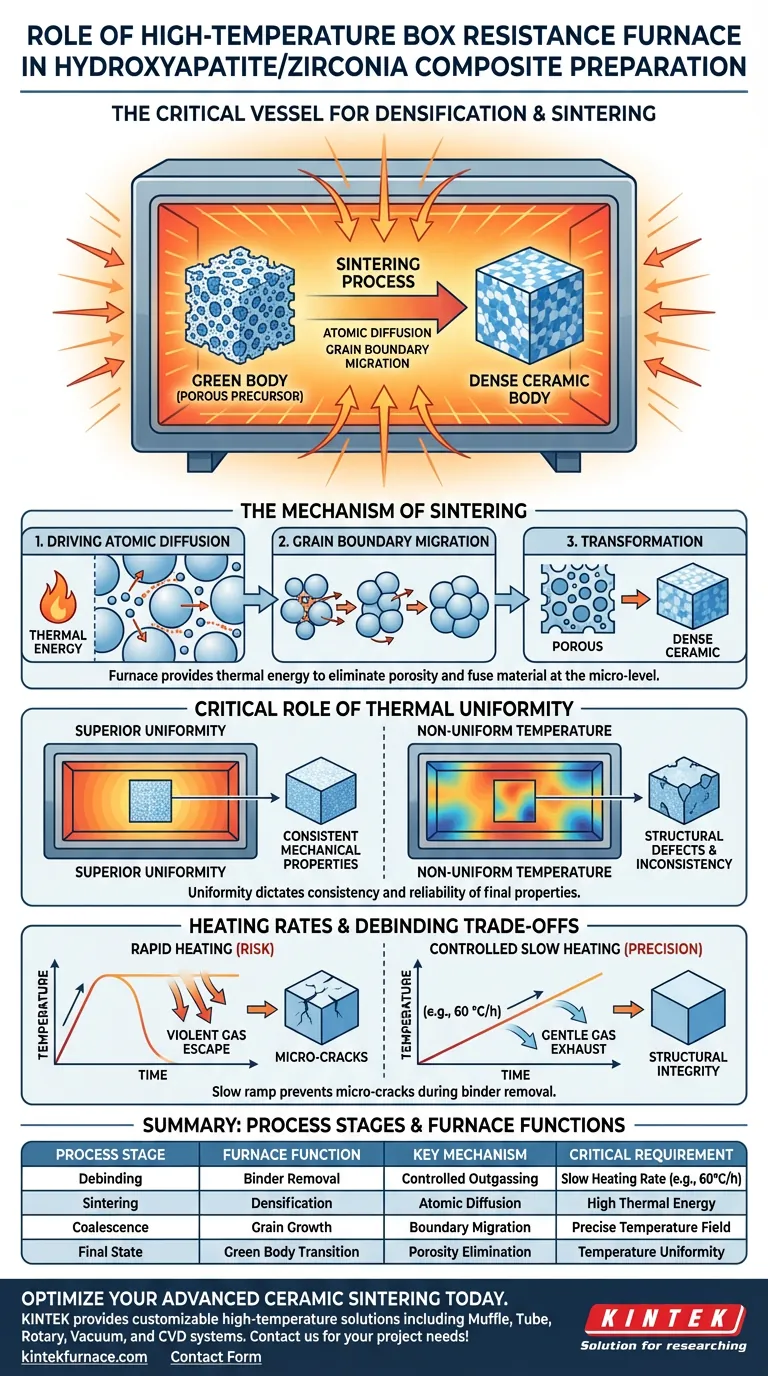
The high-temperature box resistance furnace acts as the critical vessel for densification. It provides the strictly controlled thermal environment necessary to transform a porous "green body" of Hydroxyapatite and Zirconia into a solid, dense ceramic composite. This process, known as sintering, relies on the furnace's ability to maintain specific high temperatures to fuse the material at the micro-level.
The furnace supplies the thermal energy required to drive atomic diffusion and grain boundary migration, effectively eliminating porosity between powder particles. Consequently, the uniformity of the furnace’s temperature field directly dictates the consistency and reliability of the composite's final mechanical properties.
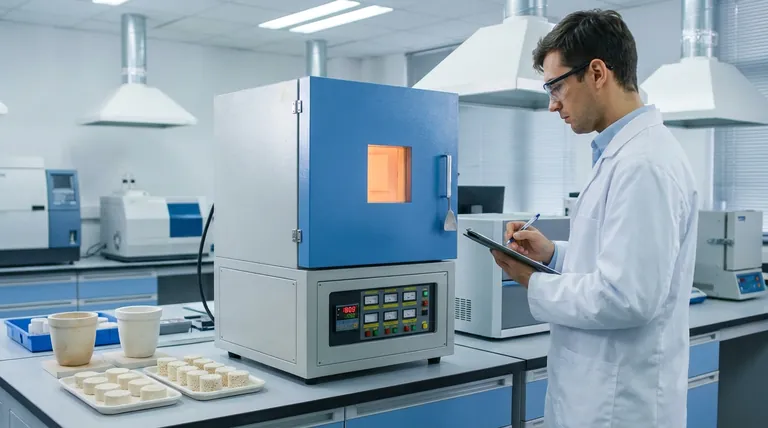

The Mechanism of Sintering
The primary function of the muffle furnace is to facilitate the physical transformation of the material from a loose powder compact into a unified solid.
Driving Atomic Diffusion
Inside the furnace chamber, thermal energy acts as the catalyst for movement at the atomic level.
At specific high temperatures, this energy drives atomic diffusion, causing atoms to move across the boundaries of the Hydroxyapatite and Zirconia powder particles.
Grain Boundary Migration
As diffusion accelerates, the furnace environment facilitates grain boundary migration.
This process allows individual grains within the powder to coalesce and grow. This migration is essential for closing the gaps (pores) between particles.
Transformation from Green Body to Ceramic
The ultimate goal of this thermal treatment is the conversion of the "green body" (the pressed, porous precursor).
Through the furnace's sustained heat, the material sheds its porous nature and becomes a dense ceramic body, achieving the structural characteristics required for performance.
The Critical Role of Thermal Uniformity
While generating heat is the furnace's basic function, its value lies in how evenly that heat is distributed.
Ensuring Mechanical Consistency
The primary reference highlights that the superior temperature field uniformity of the chamber is non-negotiable.
If the temperature varies across the furnace chamber, the rate of atomic diffusion will vary across the composite sample.
Preventing Structural Defects
A uniform thermal field ensures that densification happens evenly throughout the material.
Without this uniformity, the Hydroxyapatite/Zirconia composite will suffer from inconsistent mechanical properties, creating weak points where sintering was incomplete.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Heating Rates and Debinding
While the primary focus is sintering, the furnace also plays a vital role in the earlier "debinding" stage, where improper operation can destroy the material.
The Risk of Rapid Heating
Before full sintering, residual organic binders must be removed from the composite.
If the furnace temperature increases too rapidly, gases generated by decomposing binders will escape violently from between the zirconia particles.
Preventing Micro-Cracks
To mitigate this, the furnace must be capable of extremely slow, controlled heating rates (e.g., 60 °C/h).
This slow ramp prevents the formation of micro-cracks, ensuring the structural integrity of the component before it even reaches sintering temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The effective preparation of Hydroxyapatite/Zirconia composites requires balancing high heat for sintering with precise control for structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is mechanical consistency: Prioritize a furnace with a certified, high-uniformity temperature field to ensure even densification across the entire ceramic body.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Ensure your furnace allows for programmable, low-velocity heating rates to facilitate the gentle exhaust of binder gases without causing micro-cracking.
Success depends not just on reaching the target temperature, but on the uniformity of the heat and the precision of the ramp rate used to get there.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Furnace Function | Key Mechanism | Critical Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debinding | Binder Removal | Controlled Outgassing | Slow Heating Rate (e.g., 60°C/h) |
| Sintering | Densification | Atomic Diffusion | High Thermal Energy |
| Coalescence | Grain Growth | Boundary Migration | Precise Temperature Field |
| Final State | Green Body Transition | Porosity Elimination | Temperature Uniformity |
Optimize Your Advanced Ceramic Sintering Today
Precision is the difference between a durable composite and a structural failure. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature thermal solutions designed specifically for rigorous material science applications. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific ramp rates and uniformity standards.
Whether you are preparing Hydroxyapatite/Zirconia composites or advanced bioceramics, KINTEK ensures your laboratory is equipped for success. Contact us today to discuss your unique project needs!
Visual Guide
References
- S.V. Maksymova, V.V. Voronov. Morphology of Barrier Coatings and Formation of an Interphase Boundary by Brazing of Dissimilar Alloys. DOI: 10.15407/mfint.45.08.0963
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature laboratory muffle furnace play in Indium-doped LLZO? Optimize Solid Electrolyte Synthesis
- How are muffle furnaces used in high-temperature sintering within the pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Precision and Purity in Drug Development
- What design features enhance the versatility of box furnaces? Boost Your Lab's Thermal Processing Flexibility
- What are the typical uses of muffle furnaces in laboratory settings? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab
- What is the function of a vertical muffle furnace in dolomite preparation? Optimize High-Iron Aluminum Sintering
- Why are muffle furnaces particularly useful in material science? Unlock Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- What role do muffle furnaces play in the ceramics industry? Essential for Precision Firing and Purity
- What key components are used in vacuum muffle furnaces to ensure precise gas dispersion? Discover the MFC and BPR System



















