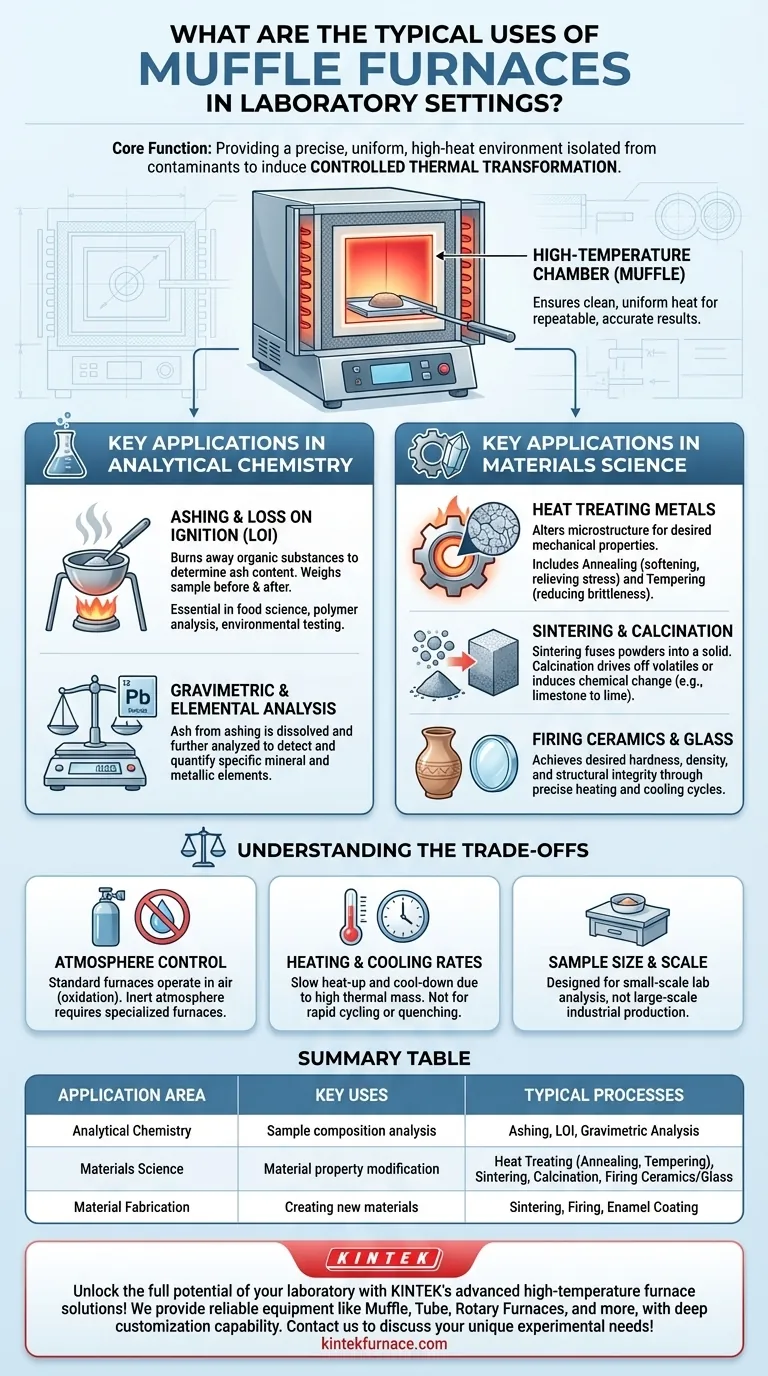
In a modern laboratory, a muffle furnace serves as a high-temperature oven used for three primary purposes: analyzing a sample's composition, altering a material's physical properties through heat treatment, and fabricating new materials like ceramics or glass. Its core function is to provide a precise, uniform, and high-heat environment, isolated from flames or heating elements, to induce controlled changes in a sample.
The true value of a muffle furnace is not simply reaching high temperatures, but its ability to controllably transform materials. It allows you to either reveal a material's fundamental composition or to create entirely new material properties for testing and production.

The Core Principle: Controlled Thermal Transformation
A muffle furnace is essentially an insulated box containing a high-temperature chamber. The "muffle" is the retort or chamber that insulates the material being heated from the direct radiation and combustion byproducts of the heating elements.
This design ensures clean, uniform heat, which is critical for repeatable and accurate results. The process inside is not just heating; it is a controlled thermal transformation.
Key Applications in Analytical Chemistry
One of the most common uses for a muffle furnace is to determine what a sample is made of by separating its organic and inorganic components.
Ashing and Loss on Ignition (LOI)
Ashing is a process where a sample is heated to a high temperature in the presence of air to burn away all organic substances.
The non-combustible inorganic residue that remains is called ash. By weighing the sample before and after ashing, you can precisely calculate the ash content. This is fundamental in food science, polymer analysis, and environmental testing.
Loss on Ignition (LOI) is a related technique that measures the total weight lost from a sample upon heating. This can include water, volatile organic compounds, and other combustible materials.
Gravimetric and Elemental Analysis
Ashing is often the first step in a more complex analytical workflow. The resulting ash, which contains the sample's mineral and metallic content, can be dissolved and further analyzed using other techniques.
This allows for the precise detection and quantification of specific elements within the original sample, a process vital in mining, material quality control, and environmental compliance.
Key Applications in Materials Science
Muffle furnaces are indispensable tools for engineers and scientists looking to create or modify materials with specific physical characteristics.
Heat Treating Metals
Heat treatment involves heating and cooling a metal to alter its microstructure and, therefore, its mechanical properties like hardness, ductility, and strength.
Annealing is a common heat treatment process where a metal is heated and then slowly cooled to relieve internal stresses, increase softness, and improve machinability.
Other processes like tempering (to reduce brittleness in hardened steel) or stress relief are also performed using the precise temperature control of a muffle furnace.
Sintering and Calcination
Sintering is the process of taking a powdered material and heating it to just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together into a solid piece. This is a cornerstone of modern ceramics manufacturing and powder metallurgy.
Calcination involves heating a material to drive off volatile substances or induce a chemical change. For example, heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) is a calcination process.
Firing Ceramics and Glass
The creation of technical ceramics, glass components, and enamel coatings relies on the uniform high temperatures provided by a muffle furnace.
The furnace allows for precise control over the heating and cooling cycles, which is critical for achieving the desired hardness, density, and structural integrity in the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in ambient air. The oxygen present will cause oxidation on the surface of many materials, which may be undesirable.
For processes requiring an inert or controlled atmosphere (e.g., using nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation), a specialized and more expensive furnace is required.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Muffle furnaces are designed for uniform, stable heat. Due to their significant thermal mass and insulation, they typically heat up and cool down slowly.
They are not suitable for applications requiring rapid thermal cycling or quenching, although they are used for the heating step prior to a separate quenching process.
Sample Size and Scale
Laboratory muffle furnaces are benchtop devices designed for small-scale analysis and testing, not large-scale industrial production. Their chamber size limits the volume of material that can be processed at one time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific use of a muffle furnace is determined entirely by your scientific or technical objective.
- If your primary focus is compositional analysis: Use the furnace for ashing, loss on ignition (LOI), and preparing samples for gravimetric or elemental analysis.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties: Use the furnace for heat treating metals through processes like annealing, tempering, and stress relieving.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials: Use the furnace for sintering powders, firing ceramics, fusing glass, and creating enamel coatings.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is a foundational tool that empowers you to either deconstruct a material to understand its parts or construct new materials with desired properties.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Typical Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry | Sample composition analysis | Ashing, Loss on Ignition (LOI), Gravimetric Analysis |
| Materials Science | Material property modification | Heat Treating (Annealing, Tempering), Sintering, Calcination, Firing Ceramics/Glass |
| Material Fabrication | Creating new materials | Sintering, Firing, Enamel Coating |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, whether for ashing, heat treatment, or material fabrication. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















