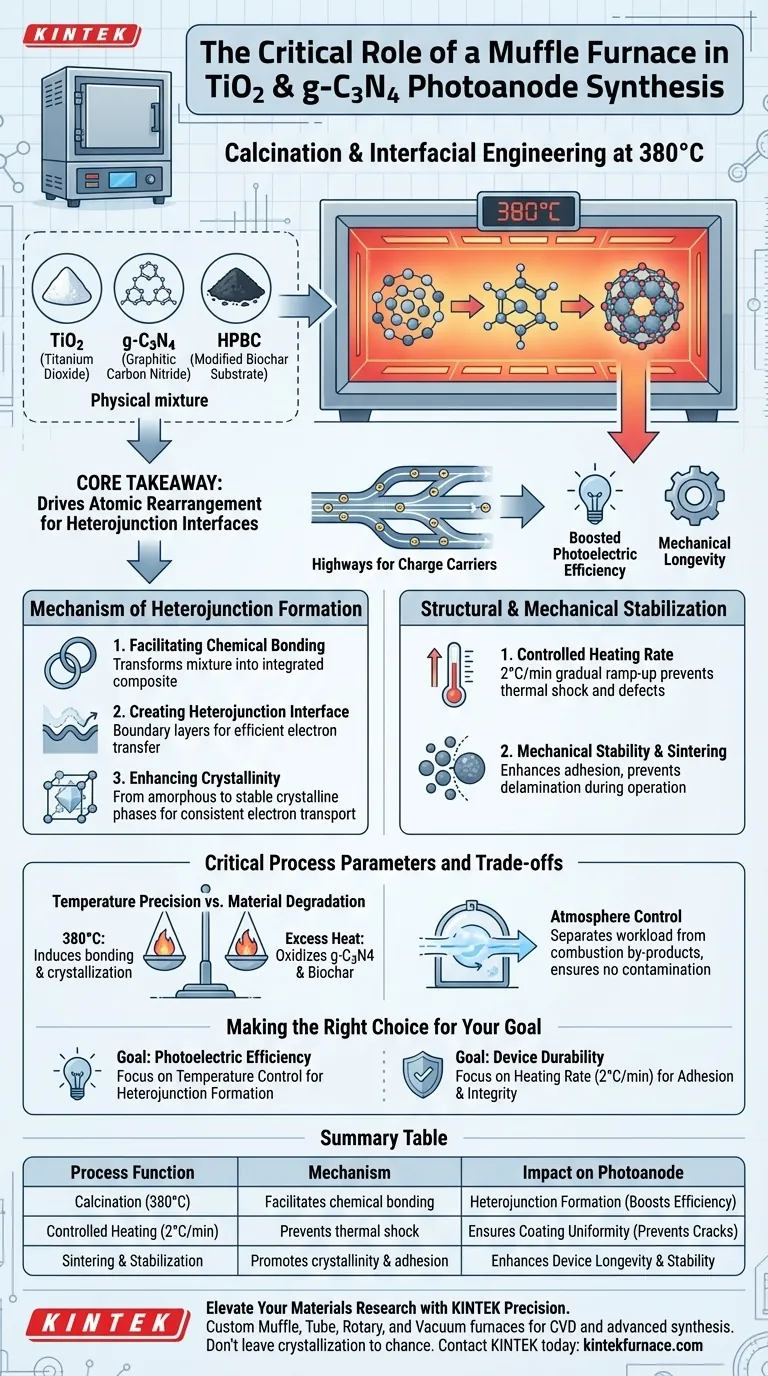
The muffle furnace serves as the critical instrument for precise calcination and interfacial engineering in the synthesis of the composite photoanode.
By subjecting the precursor materials to a controlled temperature of 380°C, the furnace facilitates the chemical bonding required to integrate titanium dioxide (TiO2), graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4), and the modified biochar (HPBC) substrate into a unified functional unit.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace does more than simply dry or harden the material; it drives the atomic rearrangement necessary to form heterojunction interfaces. These interfaces are the "highways" for photogenerated charge carriers, directly determining the photoelectric conversion efficiency and mechanical longevity of the final device.

The Mechanism of Heterojunction Formation
Facilitating Chemical Bonding
The primary role of the muffle furnace is to provide the thermal energy required to forge strong chemical bonds.
At 380°C, the furnace drives a reaction between the TiO2, g-C3N4, and the HPBC substrate. This transforms a physical mixture of components into a chemically integrated composite.
Creating the Heterojunction Interface
The most critical outcome of this thermal treatment is the creation of heterojunction interfaces.
These interfaces are the boundary layers where the different materials meet. A high-quality heterojunction reduces the energy barrier for electron movement, allowing for efficient transfer of photogenerated charge carriers. Without this thermal step, the materials would remain isolated, leading to poor conductivity and low efficiency.
Enhancing Crystallinity
The heat treatment promotes the transition of materials from amorphous or low-crystalline states into stable crystalline phases.
Better crystallinity generally correlates with improved electronic properties. The furnace ensures that the atomic structure is ordered sufficiently to support consistent electron transport.
Structural and Mechanical Stabilization
Controlled Heating Rate
The muffle furnace is programmed to raise the temperature at a specific, slow rate—typically 2°C per minute.
This gradual ramp-up is essential to prevent thermal shock. A slow heating rate ensures that volatile components bond or evaporate uniformly without causing cracks or structural defects in the coating.
Mechanical Stability and Sintering
The process acts similarly to sintering, where particles are heated to form a solid, cohesive mass without melting.
This significantly enhances the mechanical stability of the photoanode coating. It ensures the composite adheres firmly to the substrate, preventing delamination during operation in liquid electrolytes or under light irradiation.
Critical Process Parameters and Trade-offs
Temperature Precision vs. Material Degradation
The specific temperature of 380°C is a calculated trade-off.
It must be high enough to induce crystallization and bonding, but low enough to preserve the structure of the carbon-based components (g-C3N4 and biochar). Excessive heat could oxidize or degrade the carbon nitride, destroying the very heterojunctions you aim to create.
Atmosphere Control
A defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is its ability to separate the workload from combustion by-products.
This ensures that the sensitive TiO2 and g-C3N4 surfaces are not contaminated by impurities from the heat source. However, one must ensure the chamber is clean to avoid unintended doping or surface fouling during the anneal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When optimizing your synthesis protocol, consider how the furnace parameters align with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Photoelectric Efficiency: Prioritize precise temperature control to maximize heterojunction formation, ensuring the interface allows for rapid charge transfer.
- If your primary focus is Device Durability: Focus on the heating rate (2°C/min) and dwell time to ensure maximum mechanical adhesion and structural integrity of the coating.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace transforms a loose assembly of precursors into a robust, high-performance photoanode capable of efficient energy conversion.
Summary Table:
| Process Function | Mechanism | Impact on Photoanode |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination (380°C) | Facilitates chemical bonding between TiO2, g-C3N4, and HPBC | Transforms physical mixtures into a chemically integrated composite |
| Heterojunction Formation | Creates boundary layers for efficient charge transfer | Reduces energy barriers and boosts photoelectric conversion efficiency |
| Controlled Heating (2°C/min) | Prevents thermal shock and structural defects | Ensures coating uniformity and prevents cracking/delamination |
| Sintering & Stabilization | Promotes crystallinity and mechanical adhesion | Enhances device longevity and stability in liquid electrolytes |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect heterojunction interface requires more than just heat—it requires absolute thermal control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces, all customizable to meet the rigorous demands of CVD and advanced material synthesis.
Whether you are optimizing TiO2/g-C3N4 photoanodes or developing next-generation catalysts, our expert R&D and manufacturing ensure your lab is equipped for excellence. Don't leave your crystallization to chance.
Contact KINTEK today to find your custom heating solution
Visual Guide
References
- Chun Zhao, Shaojun Zhang. TiO₂/g-C₃N₄@HPBC Photoanode in PMFC for Shipboard Oily Wastewater Degradation. DOI: 10.54691/kk8pft70
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does an industrial muffle furnace contribute to the thermal treatment of γ-Al2O3 carriers? Optimize Phase Transition
- How are box type electric furnaces applied in electronic component manufacturing? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing
- How does the temperature control system of a muffle furnace work? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Your Lab
- What are the typical specifications for lab box furnaces? Find Your Perfect Fit for Materials Processing
- What is the objective of utilizing a benchtop high-temperature furnace with a two-stage heating process for alloying?
- What is the purpose of the insulated ceramic chamber in a muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- Why is it necessary to control the heating rate of a muffle furnace during calcination? Optimize Bioactive Glass Quality
- What types of materials are commonly processed in muffle furnaces? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Metals, Ceramics, and More



















