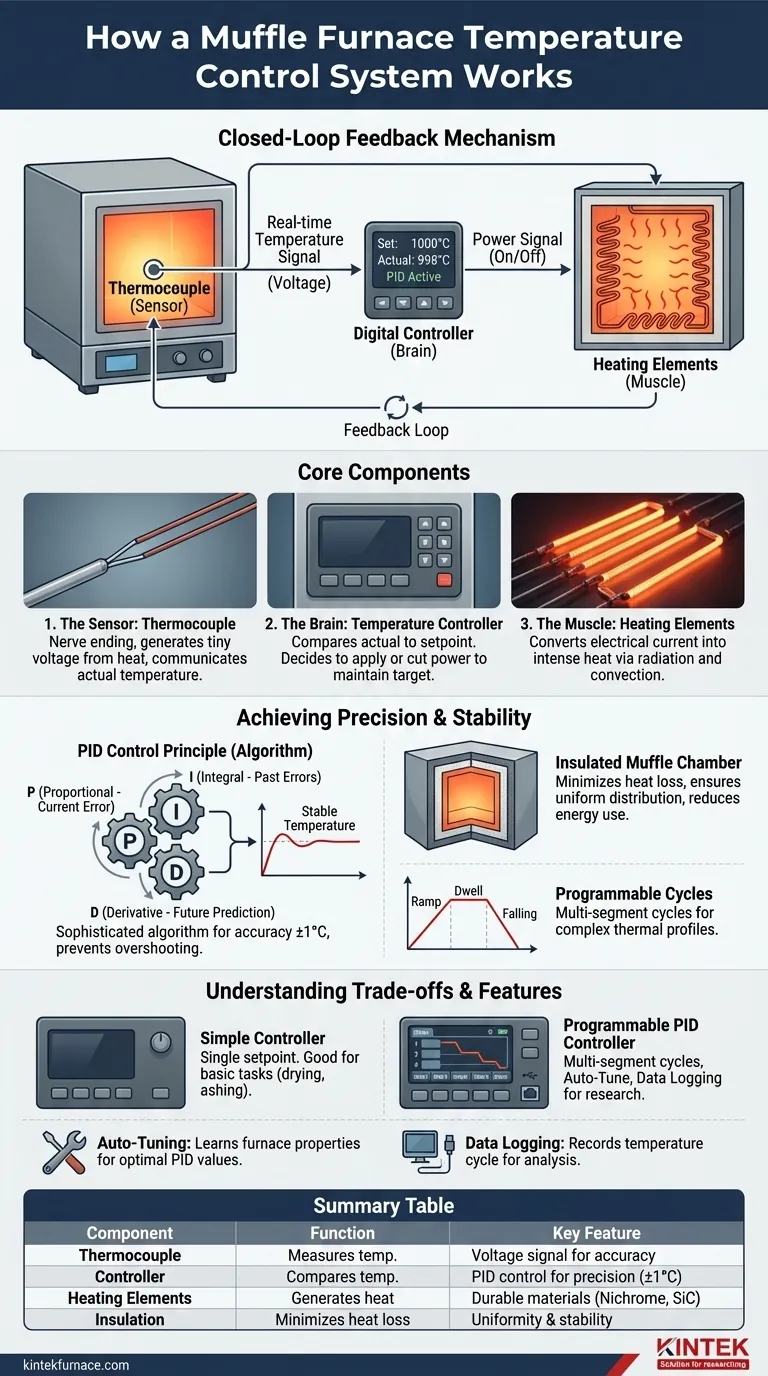
At its core, a muffle furnace's temperature control system operates as a closed-loop feedback mechanism. A temperature sensor (a thermocouple) inside the furnace chamber constantly measures the actual temperature and sends this information to a digital controller. The controller compares this reading to the desired temperature you have set and intelligently switches the electric heating elements on or off to precisely maintain that setpoint.
The true effectiveness of a muffle furnace lies not in its ability to simply get hot, but in the sophisticated interplay between its physical design and its electronic brain. It combines a highly insulated, uniform heating chamber with a responsive control system to deliver precise, stable, and repeatable high-temperature environments.
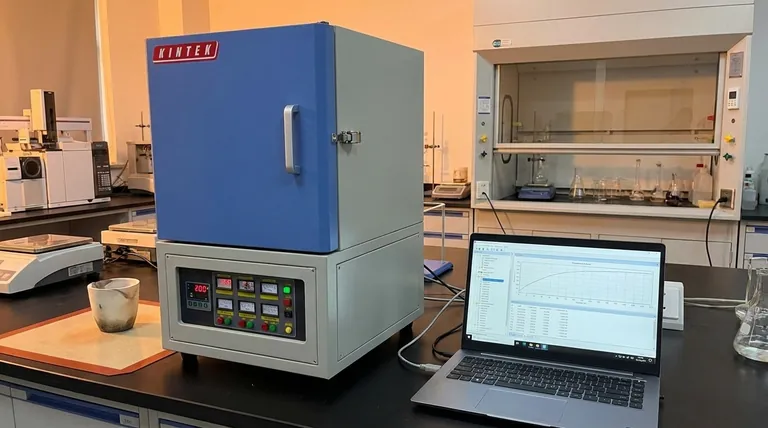

The Core Components of the Control System
To understand how the furnace achieves such precise control, it's essential to look at the three key components that work in constant communication.
The Sensor: The Thermocouple
A thermocouple is the system's nerve ending, placed directly inside the heating chamber. It is made of two different metal wires joined at one end.
This junction produces a tiny voltage that changes predictably with temperature. This voltage signal provides the real-time, accurate temperature measurement that the entire control system relies upon.
The Brain: The Temperature Controller
The temperature controller is the central processing unit of the operation. It receives the voltage signal from the thermocouple and converts it into a temperature reading (e.g., in Celsius or Fahrenheit).
Its primary job is to continuously compare this actual temperature to the setpoint temperature programmed by the user. Based on the difference, it makes the decision to either apply power to the heating elements or cut it off.
The Muscle: The Heating Elements
Lining the walls of the internal chamber are heating elements, typically made of high-resistance materials like nichrome or silicon carbide wires.
When the controller sends a signal to apply power, an electrical current flows through these elements, causing them to glow hot and generate intense heat through radiation and convection. When the controller cuts power, the elements stop generating new heat.
How the System Achieves Precision and Stability
The simple on/off switching described above is functional, but modern furnaces employ more advanced methods to prevent temperature overshooting and ensure exceptional stability.
The Principle of PID Control
Most high-quality furnace controllers use a sophisticated algorithm known as PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control. This is what allows for accuracy often within a single degree (+/- 1°C).
- Proportional (P): Reacts to the current difference between the setpoint and the actual temperature. A bigger difference results in a stronger response.
- Integral (I): Corrects for past errors, eliminating the small, steady-state temperature droop that can occur over time.
- Derivative (D): Predicts the future temperature by looking at the rate of change, slowing down the heating as it approaches the setpoint to prevent overshooting.
The Role of the Insulated Muffle Chamber
The control system does not work in a vacuum. The physical design of the furnace is critical. The internal ceramic chamber, or muffle, is encased in thick layers of high-grade insulation.
This design minimizes heat loss to the outside environment. A well-insulated chamber holds temperature effectively, meaning the controller doesn't have to work as hard, and the heating elements can be switched less frequently, leading to greater stability and a uniform temperature distribution.
Programmable Control Cycles
Modern digital controllers elevate the furnace from a simple oven to a precise process tool. They allow users to program multi-segment heating cycles.
Instead of just setting one temperature, you can define a complete process with specific ramp rates (how fast to heat up), dwell times (how long to hold at a temperature), and cooling periods. This is essential for advanced materials processing and scientific research where reproducibility is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, not all control systems are created equal. Understanding the differences is key to choosing and using a furnace effectively.
Controller Type: Simple vs. Programmable
A basic furnace may come with a simple digital controller that only allows for a single temperature setpoint. This is perfectly adequate for simple applications like drying or ashing.
However, for complex processes like annealing, sintering, or crystal growth, a programmable PID controller with dozens or even hundreds of programmable steps is non-negotiable.
The Importance of Auto-Tuning
PID controllers work best when their parameters (the P, I, and D values) are matched to the furnace's specific thermal properties. The auto-tune function, found on many modern controllers, automates this process.
Activating auto-tune causes the furnace to cycle around a setpoint, allowing the controller to "learn" how fast it heats and cools. It then calculates the optimal PID values for that specific machine, ensuring maximum stability and minimal temperature overshoot.
Data Logging and Connectivity
For research or quality control environments, proving a process was run correctly is vital. Many advanced controllers include a communication port (like a DB9 or USB port) to connect the furnace to a computer.
This allows for real-time monitoring and, more importantly, data logging of the entire temperature cycle for analysis and record-keeping.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal dictates the level of control you need.
- If your primary focus is simple ashing, drying, or basic heat treating: A furnace with a standard, single-setpoint digital controller is efficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is complex materials synthesis or reproducible annealing: A programmable PID controller with multi-segment capabilities is essential for defining precise thermal profiles.
- If your primary focus is process validation and data analysis: You must select a controller that includes an auto-tuning function and a communication port for data logging.
By understanding how the sensor, controller, and heating elements work together, you can confidently operate your furnace to achieve precise and repeatable thermal processing results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple | Measures temperature inside chamber | Produces voltage signal for real-time accuracy |
| Temperature Controller | Compares actual vs. setpoint temperature | Uses PID control for precision (±1°C) |
| Heating Elements | Generates heat when powered | Made of nichrome or silicon carbide for durability |
| Insulated Muffle Chamber | Minimizes heat loss | Ensures uniform temperature distribution and stability |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with precision? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can deliver superior temperature control and repeatability for your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















