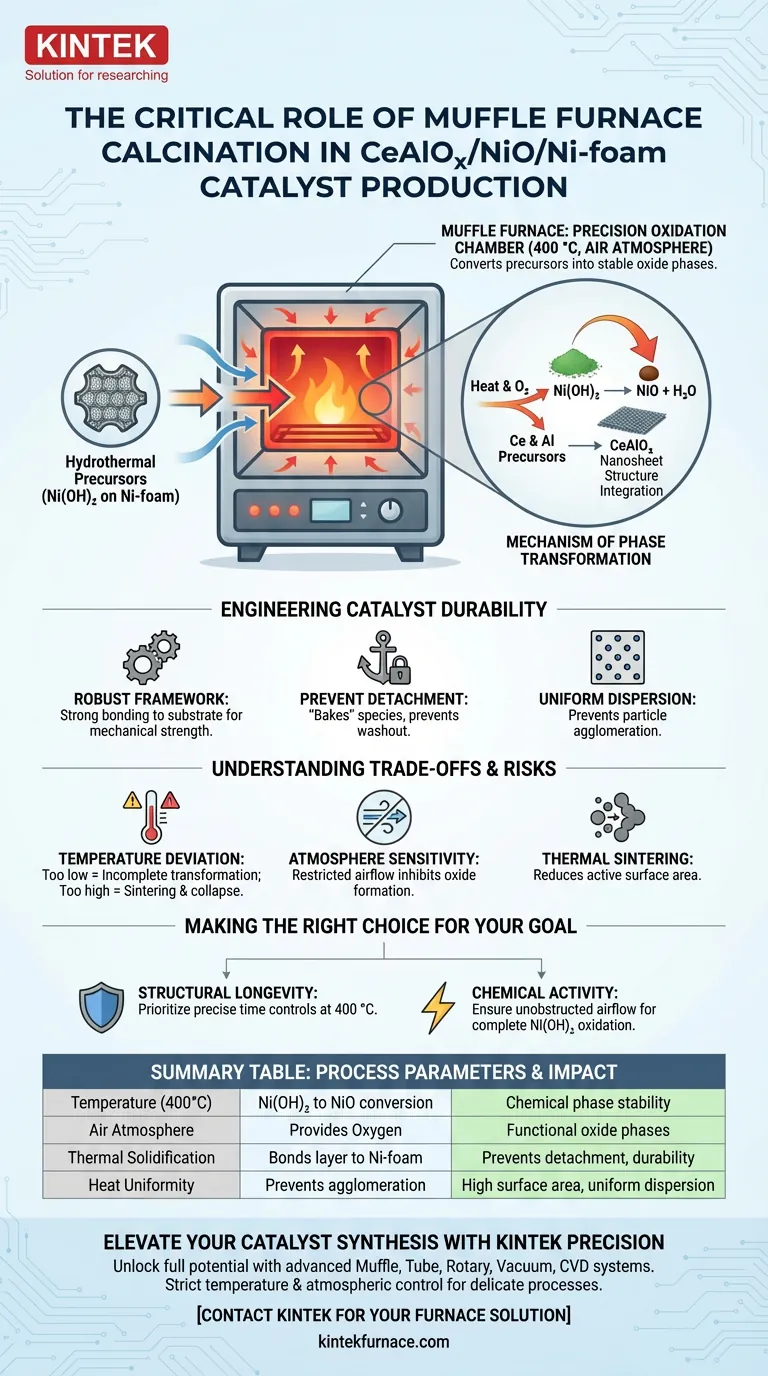
The muffle furnace functions as a precision oxidation chamber. Its primary role is to convert hydrothermal precursors into stable oxide phases by maintaining a controlled air atmosphere, specifically at 400 °C. This thermal treatment drives the chemical transformation of nickel hydroxide—Ni(OH)₂—into nickel oxide (NiO) while simultaneously solidifying cerium and aluminum components into a uniform dispersion on the nickel foam substrate.
The calcination stage is the defining moment where the material transitions from a raw precursor to a functional catalyst. It locks active species into a robust framework, preventing mechanical detachment and ensuring long-term stability during reaction cycles.
The Mechanism of Phase Transformation
Controlled Oxidation at 400 °C
The muffle furnace provides a stable, high-temperature air environment essential for chemical conversion. For this specific catalyst, the target temperature is strictly regulated at 400 °C.
Converting Nickel Precursors
The primary chemical reaction driven by the furnace is the transformation of the nickel component. The heat causes Ni(OH)₂ (nickel hydroxide) to decompose and oxidize, converting it into NiO (nickel oxide).
Stabilizing the Nanosheet Structure
Beyond simple conversion, the furnace ensures the physical solidification of the catalyst's architecture. It integrates the Cerium and Aluminum components into the nanosheet structure, ensuring they are not just surface coatings but integral parts of the material.
Engineering Catalyst Durability
Creating a Robust Framework
The thermal energy supplied by the furnace facilitates strong bonding between the catalytic layer and the nickel foam support. This heating process solidifies the framework, which is critical for mechanical strength.
Preventing Active Species Detachment
Without this specific thermal treatment, the active catalytic materials would remain loosely attached. The furnace effectively "bakes" the species onto the substrate, preventing them from detaching or washing away during subsequent chemical reactions.
Ensuring Uniform Dispersion
The muffle furnace environment promotes the even distribution of elements across the substrate. By maintaining a constant temperature, it prevents the agglomeration of particles, ensuring the active sites remain accessible.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Temperature Deviation
Precision is paramount; deviation from the 400 °C target can compromise the catalyst. Temperatures that are too low may result in incomplete phase transformation, leaving unstable precursors in the mix.
Thermal Sintering Risks
Conversely, excessive heat or uncontrolled ramp rates can lead to sintering. This causes the nanosheets to collapse or particles to merge, drastically reducing the active surface area and overall efficiency.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The process relies on an air atmosphere to provide necessary oxygen. Restricting airflow or introducing inert gases during this specific stage would inhibit the formation of the required oxide phases (NiO, CeAlOx).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the production of CeAlOx/NiO/Ni-foam catalysts, align your furnace parameters with your specific objective:
- If your primary focus is structural longevity: Prioritize precise time controls at 400 °C to fully solidify the framework and prevent material detachment.
- If your primary focus is chemical activity: Ensure the airflow within the muffle furnace is unobstructed to facilitate the complete oxidation of Ni(OH)₂ into active NiO.
The muffle furnace is not merely a heating element; it is the tool that dictates the final structural integrity and chemical potency of your catalytic layer.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Role in Catalyst Production | Impact on Final Material |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (400°C) | Facilitates Ni(OH)₂ to NiO conversion | Ensures chemical phase stability and active sites |
| Air Atmosphere | Provides oxygen for thermal oxidation | Converts precursors into functional oxide phases |
| Thermal Solidification | Bonds catalytic layer to Ni-foam substrate | Prevents mechanical detachment and increases durability |
| Heat Uniformity | Prevents particle agglomeration | Maintains high surface area and uniform dispersion |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your material science research with KINTEK's advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to provide the strict temperature uniformity and atmospheric control required for delicate processes like the calcination of CeAlOx/NiO/Ni-foam catalysts.
Whether you need a standard laboratory furnace or a fully customizable system tailored to your unique research needs, our engineering team is ready to support your innovation. Ensure structural longevity and chemical potency in every batch.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? Contact us today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Xin Tang, Lili Lin. Thermally stable Ni foam-supported inverse CeAlOx/Ni ensemble as an active structured catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation to methane. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47403-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are some additional options available for Box Furnaces? Enhance Your Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How are muffle furnaces used in glassmaking? Achieve Clean, Controlled Heat for Superior Glass Quality
- What is a benchtop furnace and its common types? Choose the Right One for Your Lab
- What temperature range can muffle furnaces reach? Find Your Ideal Lab Furnace Temperature
- What is the purpose of using a muffle furnace in incineration? Achieve Pure Ash for Accurate Inorganic Analysis
- How do box resistance furnaces facilitate the optimization of mechanical properties in AlSi10Mg alloys? Expert Thermal Analysis
- What are some important 'Do's' when operating a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Efficiency in Your Lab
- How does the calcination process in a muffle furnace facilitate the formation of pores in manganese oxide?



















