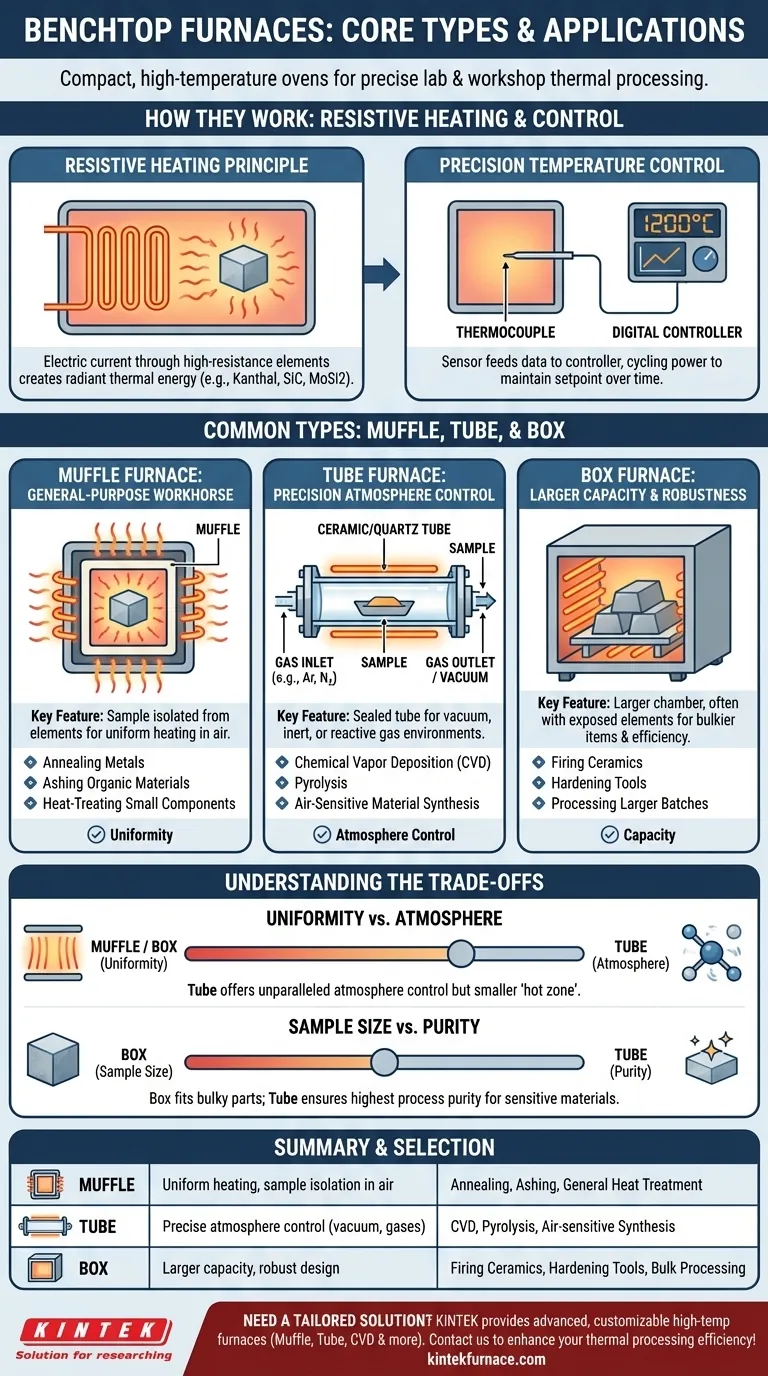
At its core, a benchtop furnace is a compact, high-temperature oven designed to sit on a laboratory or workshop table. It provides precise thermal processing for small-scale applications, with the most common types being muffle, tube, and box furnaces, each engineered for a distinct purpose.
The critical distinction between furnace types is not their maximum temperature, but how they control the heating environment. Your choice depends entirely on whether your priority is sample purity, atmosphere control, or sheer processing volume.

The Core Function: How Benchtop Furnaces Work
The Principle of Resistive Heating
Nearly all benchtop furnaces operate on the principle of resistive heating. An electric current is passed through high-resistance heating elements, causing them to glow hot and radiate thermal energy into the furnace chamber.
These elements are typically made from materials like Kanthal (an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy) for temperatures up to 1300°C or silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) for higher-temperature applications.
Precision Temperature Control
A thermocouple acts as a sensor, constantly measuring the internal temperature of the chamber. This information is fed to a digital controller, which cycles the power to the heating elements to precisely maintain the desired temperature setpoint over time.
Decoding the Common Furnace Types
The design of the heating chamber is what truly differentiates one furnace from another and dictates its ideal use case.
Muffle Furnaces: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A muffle furnace features an inner chamber, or "muffle," that isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements. This creates a highly uniform heating environment and protects the sample from any potential contamination from the elements themselves.
Its design makes it ideal for general-purpose thermal processing like annealing metals, ashing organic materials, or heat-treating small components where a standard air atmosphere is acceptable.
Tube Furnaces: Precision Atmosphere Control
A tube furnace uses a narrow cylindrical chamber, typically made of ceramic or quartz, around which the heating elements are placed. The ends of the tube can be sealed, allowing for precise control over the internal atmosphere.
This is the furnace's key advantage. It enables processes that must be performed under a vacuum, in the presence of an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen), or with a specific reactive gas. Common applications include chemical vapor deposition (CVD), pyrolysis, and synthesizing air-sensitive materials.
Box Furnaces: Larger Capacity and Robustness
The term box furnace is often used interchangeably with muffle furnace, but it typically implies a larger chamber and a more robust, industrial design. The primary distinction is often scale and directness of heating.
While many have muffles, some larger box furnaces may have exposed elements to maximize heating speed and efficiency for bulkier items. They are suited for tasks like firing ceramics, hardening tools, and processing larger batches that would not fit in a standard muffle or tube furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing three competing factors: uniformity, atmosphere, and capacity.
Uniformity vs. Atmosphere Control
Muffle and box furnaces provide excellent temperature uniformity over a relatively large, three-dimensional space. However, they offer minimal control over the gaseous atmosphere inside.
Tube furnaces, conversely, provide unparalleled atmosphere control but have a much smaller, one-dimensional "hot zone." Achieving perfect temperature uniformity along the entire length of the tube can be a challenge.
Sample Size vs. Process Purity
The open, rectangular chamber of a box furnace is perfect for processing bulky, awkwardly shaped parts or large batches of samples simultaneously.
A tube furnace is restrictive in sample size and shape but ensures the highest process purity, protecting sensitive materials from oxygen and other contaminants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, first define your most critical process requirement.
- If your primary focus is general heat-treating, drying, or ashing in air: A muffle furnace offers the best combination of versatility, uniform heating, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is working with air-sensitive materials or requiring a specific gas environment: A tube furnace is the essential tool for achieving the necessary process control and purity.
- If your primary focus is processing larger batches, bulky items, or robust materials: A box furnace provides the capacity and rugged construction needed for higher-throughput applications.
Ultimately, understanding how each furnace manages its heating environment empowers you to select the right tool for your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Uniform heating, sample isolation in air | Annealing, ashing, general heat treatment |
| Tube Furnace | Precise atmosphere control (vacuum, inert gases) | CVD, pyrolysis, air-sensitive material synthesis |
| Box Furnace | Larger capacity, robust design | Firing ceramics, hardening tools, bulk processing |
Need a benchtop furnace tailored to your lab's unique requirements? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processing efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation



















