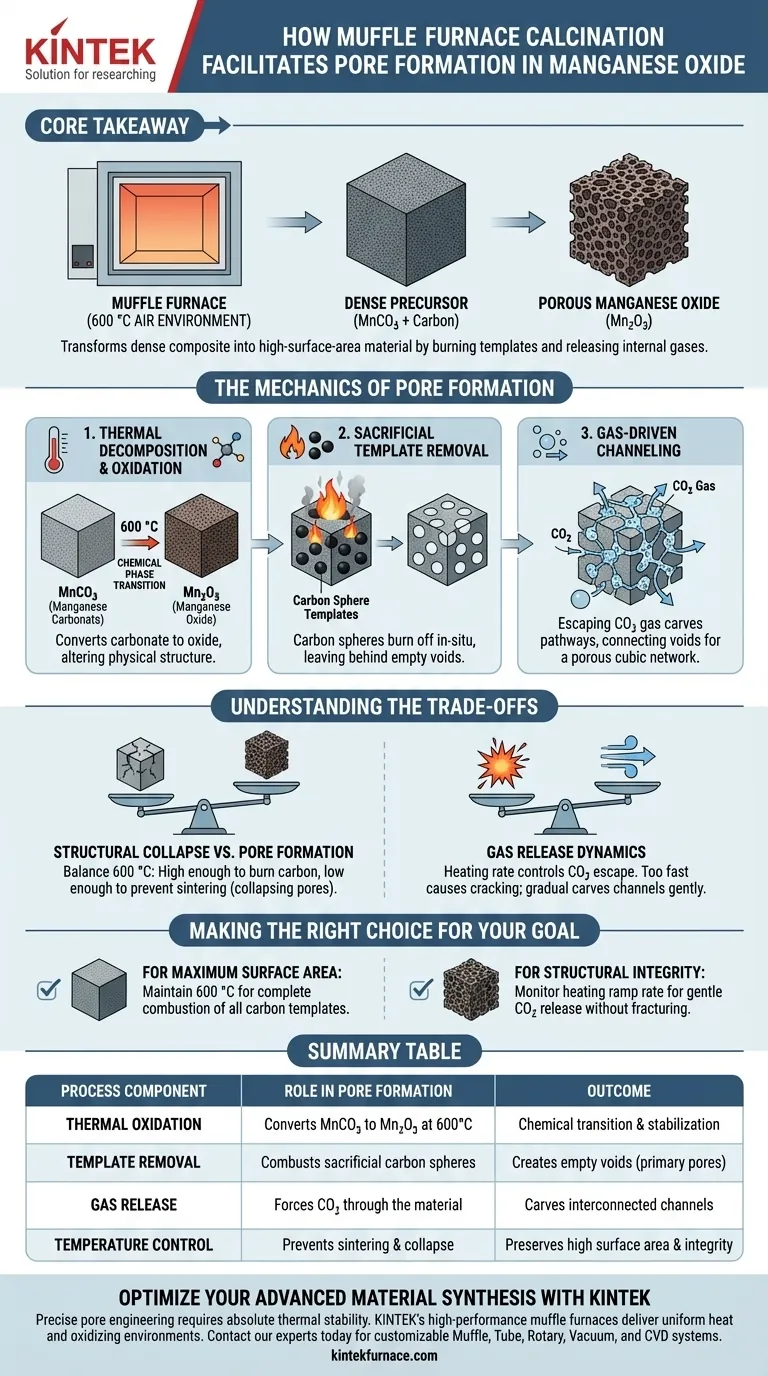
Calcination in a muffle furnace facilitates pore formation through a simultaneous process of thermal decomposition and sacrificial template removal. By subjecting the material to a 600 °C air environment, the furnace triggers the oxidation of manganese carbonate (MnCO3) into manganese oxide (Mn2O3). This high heat burns away embedded carbon sphere templates and forces the release of CO2 gas, which collectively hollows out the material to create a porous structure.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace acts as a reactive chamber that transforms a dense composite into a high-surface-area material. By burning off carbon templates and releasing internal gases, the process vacates physical volume to engineer a porous cubic network in-situ.

The Mechanics of Pore Formation
The transformation from a dense solid to a porous framework relies on strictly controlled thermal reactions. The muffle furnace provides the stable, oxidizing environment required to execute three critical physical-chemical changes simultaneously.
Thermal Decomposition and Oxidation
At 600 °C, the furnace initiates the breakdown of the precursor material, manganese carbonate (MnCO3).
This reaction converts the carbonate into manganese oxide (Mn2O3) through oxidation. This chemical phase transition is the foundational step that allows the physical structure to be altered.
Sacrificial Template Removal
The precursor material contains carbon sphere templates designed to define the size and shape of the pores.
The high-temperature environment causes these carbon spheres to burn off in-situ. As the carbon combusts and vanishes, it leaves behind empty voids, effectively vacating the space it previously occupied to form the primary pores.
Gas-Driven Channeling
The decomposition of MnCO3 and the combustion of carbon generates significant amounts of CO2 gas.
As this gas escapes from the interior of the material to the surface, it "carves out" channels. These pathways connect the voids left by the carbon spheres, completing the transformation into a highly porous, high-surface-area cubic structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While calcination is effective, relying on thermal decomposition for pore formation introduces specific process variables that must be managed to ensure structural integrity.
Structural Collapse vs. Pore Formation
The temperature must be high enough to burn the carbon but not so high that it causes the manganese oxide to sinter.
If sintering occurs, the newly formed pores may collapse or fuse together, drastically reducing the surface area. The 600 °C setpoint is a critical balance between removing the template and preserving the rigid oxide framework.
Gas Release Dynamics
The rate at which CO2 escapes is determined by the heating profile.
If the gas is generated too rapidly due to sudden heating, it can cause structural cracking rather than forming controlled micropores. The "carving" action of the gas must be gradual enough to create channels without destroying the material's overall stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of the calcination process, align your heating strategy with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Surface Area: Ensure the temperature is maintained at 600 °C for sufficient duration to guarantee the complete combustion of all carbon templates.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Monitor the heating ramp rate to ensure the escaping CO2 carves channels gently without fracturing the bulk material.
Precise thermal control turns the destructive power of combustion into a constructive tool for nano-engineering.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in Pore Formation | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Oxidation | Converts MnCO3 to Mn2O3 at 600°C | Chemical phase transition and stabilization |
| Template Removal | Combusts sacrificial carbon spheres | Creates empty voids (primary pores) |
| Gas Release | Forces CO2 through the material | Carves interconnected channels and pathways |
| Temperature Control | Prevents sintering and structural collapse | Preserves high surface area and integrity |
Optimize Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise pore engineering requires absolute thermal stability. KINTEK’s high-performance muffle furnaces deliver the uniform heat and oxidizing environments essential for successful calcination and template removal.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding laboratory and industrial high-temperature applications. Whether you are developing catalysts or energy storage materials, our systems ensure your structural integrity remains uncompromised.
Ready to elevate your material research? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Jing Zhu, Run-Min Yao. Synthesis of Porous Lithium Ion Sieve with High Purity for Li+ Adsorption. DOI: 10.3390/ma18102373
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the key applications of box type resistance furnaces? Versatile Heating for Metals, Ceramics, and More
- What are the advantages of using a Microwave Muffle Furnace? Faster, Higher-Quality Activated Carbon Preparation
- What is the core function of a laboratory muffle furnace in diatomaceous earth conversion? | KINTEK
- What is the role of a high-temperature calcination furnace in preparing ultra-fine oxide nanopowders? Master Purity
- What are the different control types for muffle furnaces? Choose the Right System for Precision and Efficiency
- How does the insulation in a muffle furnace contribute to its efficiency? Unlock Energy Savings and Precision
- What design features enhance the versatility of box furnaces? Boost Your Lab's Thermal Processing Flexibility
- What types of heating media are compatible with muffle furnaces? Unlock Optimal Process Atmospheres



















