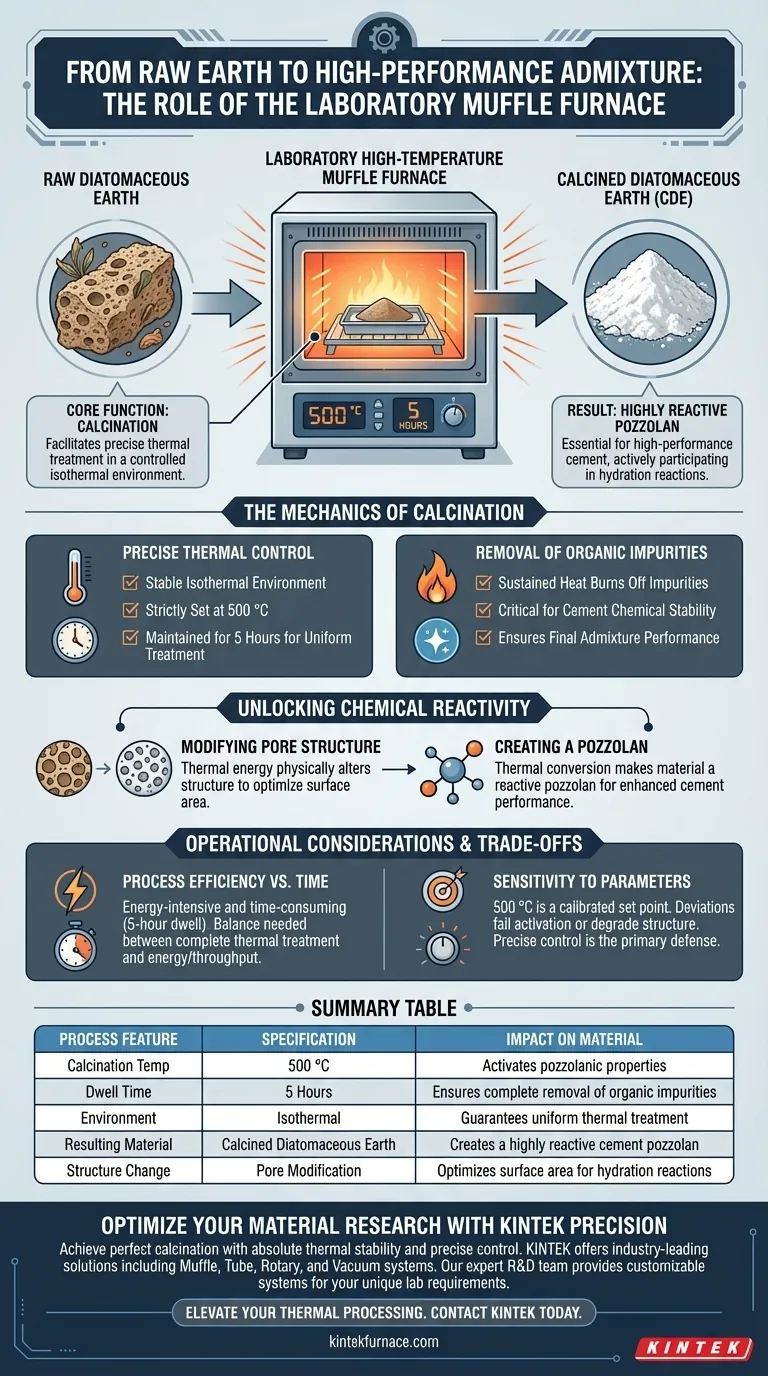
The core function of a laboratory high-temperature muffle furnace in this context is to facilitate a precise thermal treatment known as calcination. By maintaining a controlled isothermal environment at 500 °C for a duration of five hours, the furnace thermally activates the raw material to convert it into a usable construction admixture.
The muffle furnace transforms raw diatomaceous earth into Calcined Diatomaceous Earth (CDE) by eliminating organic impurities and modifying internal pore structure, creating a highly reactive pozzolan essential for high-performance cement.

The Mechanics of Calcination
Precise Thermal Control
The fundamental role of the muffle furnace is to provide a stable isothermal environment.
For diatomaceous earth, the target temperature is strictly set at 500 °C.
This temperature must be maintained consistently for 5 hours to ensure the entire mass of the material is treated uniformly.
Removal of Organic Impurities
Raw diatomaceous earth often contains organic matter that can be detrimental to concrete performance.
The sustained heat of the muffle furnace burns off these impurities effectively.
This purification step is critical for ensuring the final admixture does not interfere with the chemical stability of the cement.
Unlocking Chemical Reactivity
Modifying Pore Structure
Beyond simple cleaning, the thermal energy physically alters the material.
The heat treatment modifies the internal pore structure of the diatomaceous earth.
This structural change is necessary to optimize the surface area available for chemical reactions.
Creating a Pozzolan
The ultimate goal of this process is the creation of Calcined Diatomaceous Earth (CDE).
Through this thermal conversion, the material becomes a reactive pozzolan.
This reactivity allows the CDE to actively participate in cement hydration reactions, significantly enhancing the performance of the final mineral admixture.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
Process Efficiency vs. Time
The calcination process is energy-intensive and time-consuming.
Requiring a 5-hour dwell time at 500 °C limits the throughput of the laboratory furnace.
Operators must balance the need for complete thermal treatment against the energy costs and time required for each batch.
Sensitivity to Parameters
The specific temperature of 500 °C is not arbitrary; it is a calibrated set point.
Significant deviations in temperature could fail to fully activate the pozzolanic properties or, conversely, degrade the porous structure.
Precise control—a hallmark of muffle furnaces—is the primary defense against inconsistent material quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When utilizing a muffle furnace for diatomaceous earth conversion, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is material purity: Ensure the furnace maintains the full 5-hour dwell time to guarantee the complete removal of all organic contaminants.
- If your primary focus is reactivity optimization: Strictly monitor the 500 °C isothermal set point to maximize the development of pozzolanic traits without overheating the structure.
Success relies on using the furnace not just as a heater, but as a precision instrument for chemical activation.
Summary Table:
| Process Feature | Specification | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination Temp | 500 °C | Activates pozzolanic properties |
| Dwell Time | 5 Hours | Ensures complete removal of organic impurities |
| Environment | Isothermal | Guarantees uniform thermal treatment |
| Resulting Material | Calcined Diatomaceous Earth | Creates a highly reactive cement pozzolan |
| Structure Change | Pore Modification | Optimizes surface area for hydration reactions |
Optimize Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect calcination for diatomaceous earth requires the absolute thermal stability and precise control that only a high-end laboratory furnace can provide. KINTEK empowers researchers and manufacturers with industry-leading high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum systems.
Our furnaces are engineered to maintain the strict isothermal environments necessary for chemical activation and material purification. Whether you are developing high-performance pozzolans or advanced ceramics, our expert R&D team offers customizable systems tailored to your unique lab requirements.
Ready to elevate your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and find the perfect furnace for your high-performance mineral development.
Visual Guide
References
- Muttaqin Hasan, Taufiq Saidi. Properties of High-Strength Concrete Incorporating Calcined Diatomaceous Earth, Polypropylene, and Glass Fibers. DOI: 10.3390/buildings15020225
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are some advancements in modern muffle furnace technology? Boost Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the curing process of GaN and TiO2? Optimize Your Photoanode Sintering
- What role does heating equipment play in the synthesis of PdPc? Mastering Precision Thermal Fusion
- What fire safety equipment should be available when using a benchtop furnace? Essential Gear for Lab Safety
- How is a laboratory high-temperature muffle furnace utilized in g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Thermal Polycondensation
- What are the standard features included with Box Furnaces? A Guide to Core Capabilities & Performance
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace necessary for LLZO calcination? Master Phase Purity in Solid-State Electrolytes
- Why is precise temperature control important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Reliable Results in Heat Treatment



















