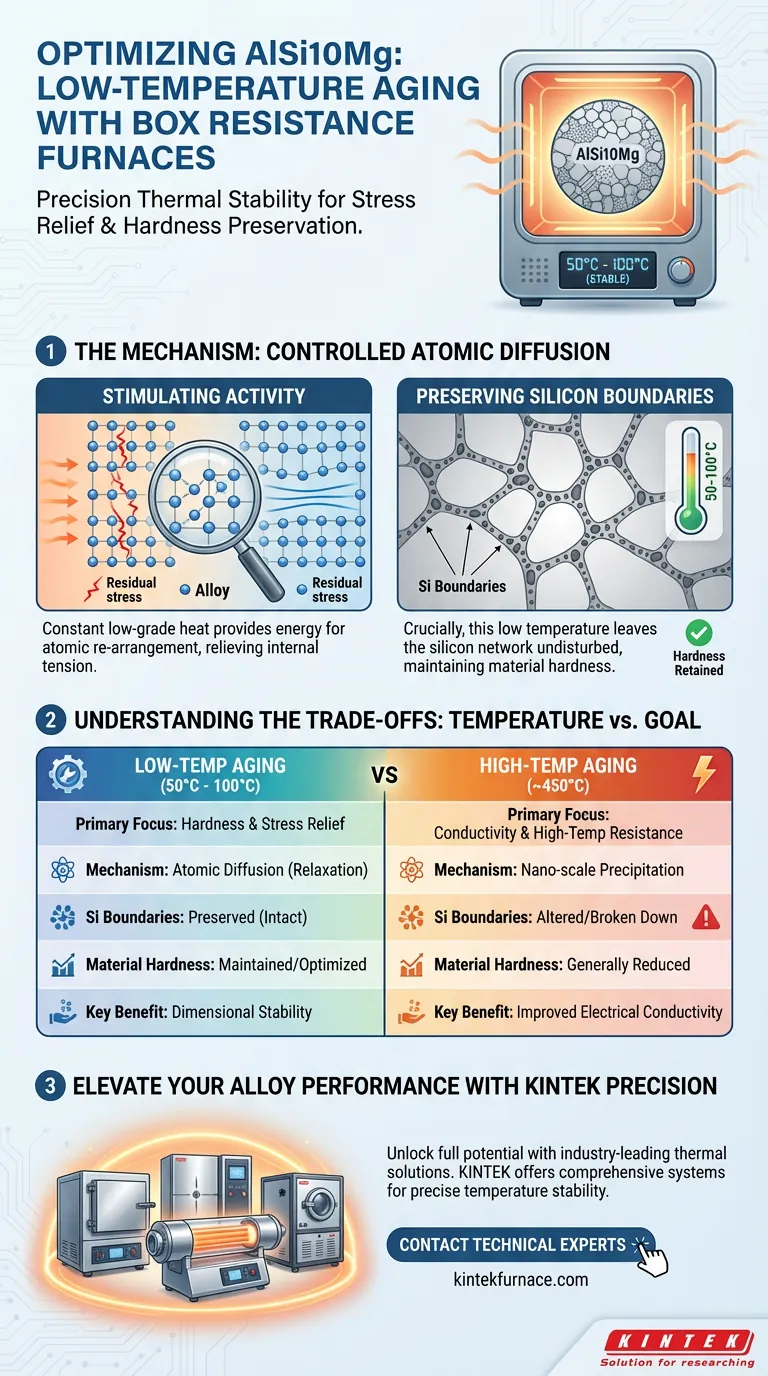
Box resistance furnaces provide the critical thermal stability required to optimize AlSi10Mg alloys without compromising their microstructure. By maintaining a precise, constant-temperature environment—typically between 50°C and 100°C—these furnaces generate steady thermal energy that stimulates atomic activity. This controlled diffusion relieves residual stresses within the aluminum matrix while preserving the integrity of the eutectic silicon boundaries.
Core Takeaway The value of a box resistance furnace lies in its ability to decouple stress relief from microstructural degradation. It allows for the precise application of low-grade heat, facilitating atomic re-arrangement to improve mechanical performance while preventing the disruption of silicon boundaries that maintains material hardness.
The Role of Thermal Stability in Low-Temperature Aging
Precise Environmental Control
Box resistance furnaces, also known as muffle furnaces, are engineered to deliver a highly stable thermal environment. This consistency is non-negotiable for AlSi10Mg alloys undergoing low-temperature aging.
Because the process often involves long-duration treatments at specific set points like 50°C or 100°C, any fluctuation in temperature can lead to inconsistent results. The furnace ensures that the thermal activation energy remains constant throughout the entire cycle.
Stimulating Atomic Diffusion
The primary function of the heat provided by the furnace is to stimulate atomic activity within the alloy. Even at these lower temperatures, the constant heat input provides enough energy for atoms to diffuse within the aluminum matrix.
This diffusion is the mechanism that allows the material to "relax." It adjusts the internal lattice structure to a lower energy state without requiring the high temperatures necessary for phase changes.
Optimizing Mechanical Properties
Relieving Residual Stress
The diffusion process facilitated by the furnace is specifically designed to target residual stresses. These stresses are often locked into the material during casting or additive manufacturing processes.
By allowing the matrix to adjust at a molecular level, the furnace treatment mitigates these internal tensions. This leads to improved mechanical performance and dimensional stability in the final part.
Preserving Silicon Boundaries
The most critical aspect of low-temperature aging is what it avoids doing. High heat can break down eutectic silicon networks, leading to softening.
The box furnace’s precise low-temperature control ensures that while the matrix relaxes, the eutectic silicon boundaries remain undisturbed. This allows the alloy to retain its hardness while simultaneously benefiting from stress relief.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Selection vs. Material Goals
It is vital to distinguish between low-temperature stress relief and high-temperature aging. While a box furnace is capable of higher temperatures (e.g., 450°C) to promote nano-scale precipitation and electrical conductivity, that is a fundamentally different mechanism.
The Risk of Overheating
Applying too much thermal energy is a common pitfall. If the furnace temperature drifts higher than the 50°C–100°C range intended for this specific optimization, you risk altering the silicon morphology.
This "over-aging" can lead to a desirable increase in conductivity but will unintentionally sacrifice the hardness and strength preserved by the low-temperature boundary protection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your box resistance furnace for AlSi10Mg, you must align your temperature settings with your specific mechanical requirements.
- If your primary focus is Hardness and Stress Relief: Maintain a strict low-temperature regime (50°C–100°C) to relieve matrix stress without disrupting silicon boundaries.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity and High-Temperature Resistance: Utilize the furnace's capability for higher temperatures (approx. 450°C) to trigger precipitation strengthening, accepting that the mechanism differs from low-temp optimization.
Precision in thermal control is the only path to predictable mechanical performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Low-Temperature Aging (50°C - 100°C) | High-Temperature Aging (~450°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Atomic diffusion & stress relief | Nano-scale precipitation |
| Silicon Boundaries | Preserved (remains intact) | Altered/Broken down |
| Material Hardness | Maintained/Optimized | Generally reduced |
| Key Benefit | Dimensional stability | Improved electrical conductivity |
| Thermal Goal | Relief of residual matrix stress | Phase change and strengthening |
Elevate Your Alloy Performance with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your AlSi10Mg components with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all designed to deliver the precise temperature stability required for critical aging processes. Whether you need a standard box resistance furnace or a custom solution tailored to your unique metallurgy needs, our equipment ensures predictable, high-quality results every time.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment workflow? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace for your laboratory or production line.
Visual Guide
References
- Busisiwe J. Mfusi, Ntombi Mathe. Optimisation of the Heat Treatment Profile for Powder-Bed Fusion Built AlSi10Mg by Age Hardening and Ice-Water Quenching. DOI: 10.3390/met14030292
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the preparation of bulk graphitic carbon nitride (BCN)? Master BCN Synthesis
- What personal protective equipment (PPE) is recommended for benchtop furnace use? Ensure Lab Safety with Proper Gear
- What are the environmental conditions for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe, Accurate High-Temperature Operations
- Why is a high-temperature box resistance furnace with argon gas protection necessary for CoCrFeMnNi homogenization?
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace utilized for g-C3N4 nanosheet synthesis? Master Two-Step Thermal Exfoliation
- What is the primary function of a Muffle Furnace in the heat treatment of beryl? Master Gemstone Color Modification
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the solid-state reaction synthesis of Dy4T1-xGa12? Achieve Pure Alloy Phases
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace during SCBA pretreatment? Mastering Sugarcane Bagasse Carbonization



















