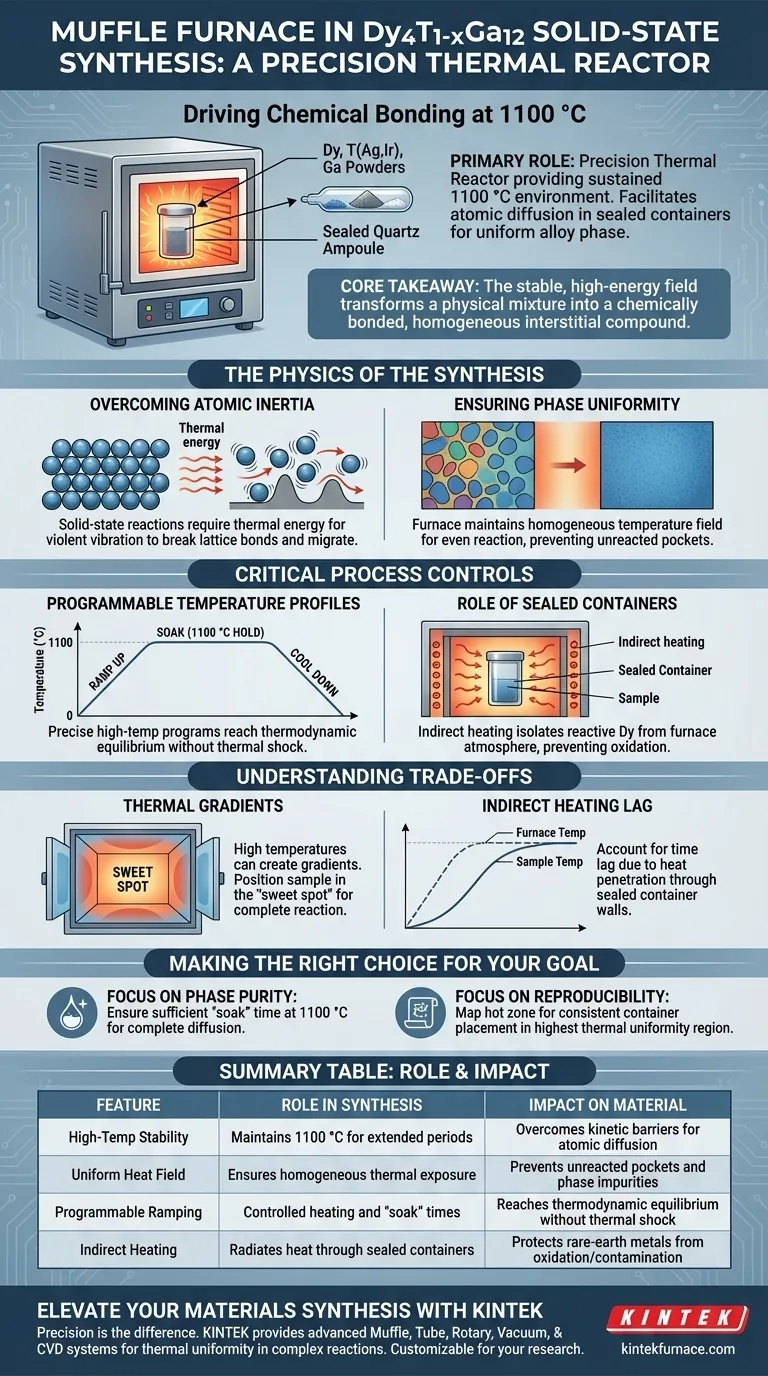
The primary role of a muffle furnace in this synthesis is to act as a precision thermal reactor, providing the sustained 1100 °C environment necessary to drive the chemical bonding between dysprosium (Dy), transition metals (Ag or Ir), and gallium (Ga). It allows researchers to subject the starting mixture, enclosed in sealed containers, to rigorous temperature programs that facilitate atomic diffusion and result in a uniform alloy phase.
Core Takeaway Solid-state synthesis relies on heat to overcome the kinetic barriers of combining solid materials. The muffle furnace provides the stable, high-energy field required to transform a physical mixture of elemental powders into a chemically bonded, homogeneous interstitial compound.

The Physics of the Synthesis
Overcoming Atomic Inertia
Solid-state reactions differ significantly from liquid or gas phase reactions because the atoms are locked in place.
To create Dy4T1-xGa12, the atoms of Dysprosium, Silver (or Iridium), and Gallium must physically move and diffuse into one another.
The muffle furnace provides the thermal energy required to vibrate these atoms violently enough to break their lattice bonds and migrate, enabling the formation of new chemical structures.
Ensuring Phase Uniformity
The goal of this synthesis is not just to melt the components, but to achieve a specific crystal structure.
The furnace maintains a homogeneous temperature field, ensuring that the reaction proceeds evenly throughout the entire sample.
Without this consistent heat application, you would risk creating a heterogeneous sample with unreacted pockets of raw metal rather than a uniform alloy phase.
Critical Process Controls
Programmable Temperature Profiles
The reaction does not happen instantly; it requires a specific "thermal history."
The muffle furnace implements precise high-temperature programs, which typically involve ramping up to 1100 °C at a controlled rate and holding that temperature for a set duration.
This programmability allows the material to reach thermodynamic equilibrium without subjecting the container to thermal shock.
The Role of Sealed Containers
Unlike oxide sintering which often occurs in open air, this synthesis takes place within sealed containers placed inside the furnace.
The muffle furnace heats the container, which then radiantly heats the sample inside.
This indirect heating is vital because it isolates the reactive rare-earth metal (Dysprosium) from the furnace's heating elements and the ambient atmosphere, preventing unwanted oxidation or contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Gradients
While muffle furnaces are designed for stability, high-temperature operations (above 1000 °C) can sometimes generate thermal gradients near the door or walls.
If the sample is not positioned in the "sweet spot" of the furnace, the resulting compound may suffer from incomplete reaction due to insufficient heat.
Indirect Heating Lag
Because the sample is inside a sealed container, there is a thermal lag between the furnace controller's reading and the actual sample temperature.
Operators must account for the time it takes for heat to penetrate the container walls to ensure the sample actually spends the required time at 1100 °C.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Dy4T1-xGa12 synthesis, consider how you utilize the furnace's capabilities.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure your temperature program includes a sufficient "soak" time at 1100 °C to allow complete diffusion within the sealed environment.
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: Map your furnace's hot zone to ensure the sealed container is always placed in the region with the highest thermal uniformity.
Mastering the thermal profile is the difference between a mixture of powders and a high-quality intermetallic compound.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Dy4T1-xGa12 Synthesis | Impact on Final Material |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Stability | Maintains 1100 °C for extended periods | Overcomes kinetic barriers for atomic diffusion |
| Uniform Heat Field | Ensures homogeneous thermal exposure | Prevents unreacted pockets and phase impurities |
| Programmable Ramping | Controlled heating and 'soak' times | Reaches thermodynamic equilibrium without thermal shock |
| Indirect Heating | Radiates heat through sealed containers | Protects rare-earth metals from oxidation/contamination |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a mixture of powders and a high-quality intermetallic compound. KINTEK provides advanced lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—engineered to deliver the thermal uniformity required for complex solid-state reactions like Dy4T1-xGa12 synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs. Contact us today to optimize your thermal processing and ensure phase purity in every sample.
Visual Guide
References
- S. Lee, Daniel C. Fredrickson. Interstitial Atoms and the Frustrated and Allowed Structural Transitions Principle: Tunability in the Electronic Structure of AuCu<sub>3</sub>‐type Frameworks in Dy<sub>4</sub>T<sub>1−<i>x</i></sub>Ga<sub>12</sub> (T = Ag, Ir). DOI: 10.1002/zaac.202500079
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a box type resistance furnace? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it differ from conventional furnaces? Discover the Key to Contamination-Free Heating
- What should be avoided when handling samples in a muffle furnace? Prevent Explosions and Damage
- What are some critical 'Don'ts' when operating a muffle furnace? Avoid Explosions and Damage
- What is a muffle furnace and what is its primary use? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Processes
- How do industrial electric heating chamber furnaces provide critical process assurance for ASTM A36 carburizing?
- How does a muffle furnace work? A Guide to Clean, Uniform Heat Treatment
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it function? Discover Clean, Precise Heating Solutions



















