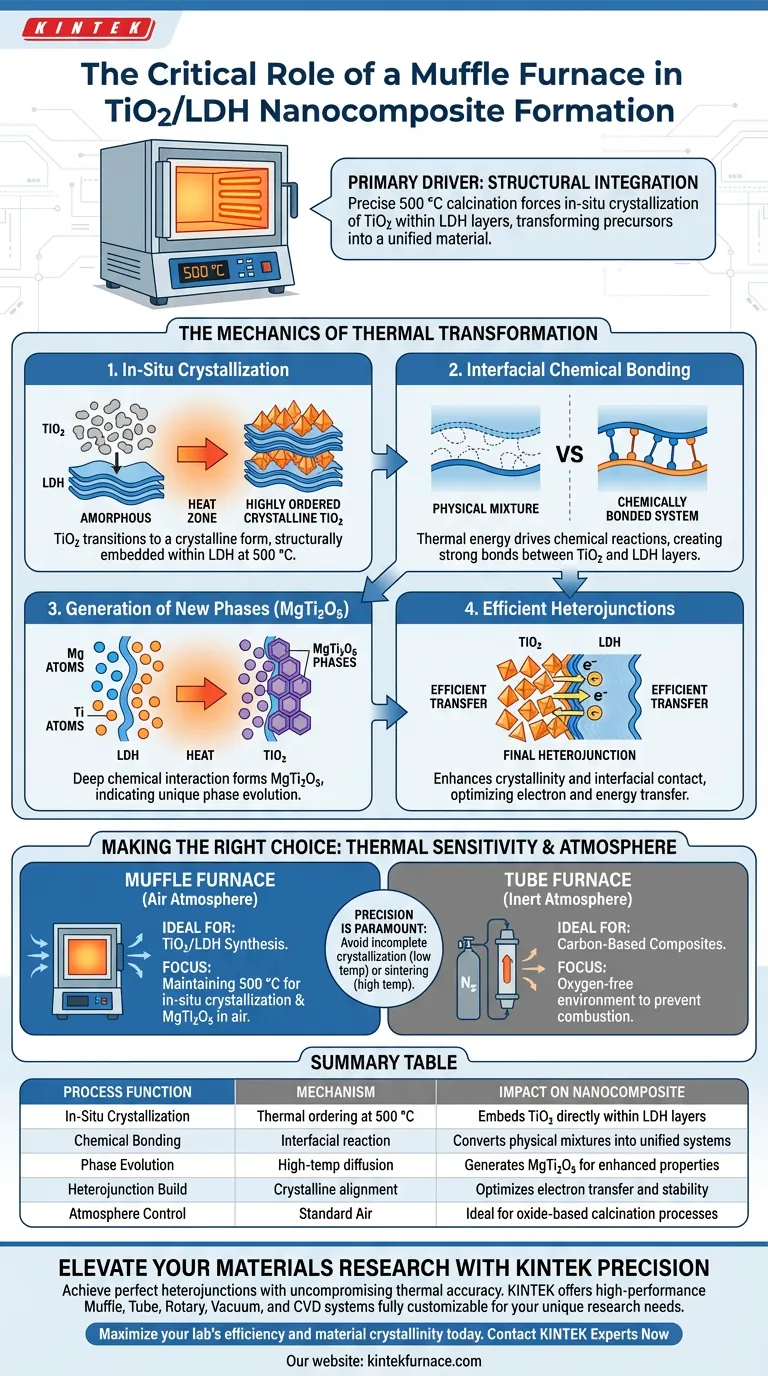
The high-temperature muffle furnace acts as the primary driver for structural integration in TiO2/LDH nanocomposites. Its critical role is to provide a precise 500 °C calcination environment that forces TiO2 particles to undergo in-situ crystallization directly within the layers of Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs). This thermal treatment transforms a physical mixture of precursors into a chemically bonded, unified material system.
The muffle furnace is essential for converting raw precursors into a high-performance heterojunction. By sustaining a 500 °C environment, it drives the formation of new phases like MgTi2O5 and solidifies the chemical interface between TiO2 and LDH, ensuring the material achieves the necessary crystallinity and structural stability.
The Mechanics of Thermal Transformation
In-Situ Crystallization
The furnace does not simply heat the material; it creates the thermodynamic conditions required for crystallization within the LDH layers.
At 500 °C, the TiO2 particles transition from an amorphous or precursor state into a highly ordered crystalline form. Because this happens "in-situ" (in place), the TiO2 is structurally embedded within the LDH matrix rather than existing as a separate aggregate.
Interfacial Chemical Bonding
A critical function of the calcination process is facilitating chemical bonding at the interface of the two phases.
Without this high-temperature treatment, the TiO2 and LDH might only be physically interacting. The thermal energy provided by the furnace drives the chemical reactions necessary to bond these layers together, creating a robust composite structure.
Generation of New Phases
The thermal environment promotes the generation of distinct new phases, specifically MgTi2O5.
The emergence of MgTi2O5 indicates a deep chemical interaction between the magnesium in the LDH and the titanium in the TiO2. This phase evolution is a direct result of the specific 500 °C calcination protocol and contributes to the material's unique properties.
Construction of Efficient Heterojunctions
The ultimate goal of using the muffle furnace is to construct an efficient heterojunction structure.
By enhancing the material's crystallinity and ensuring strong interfacial contact, the furnace enables the efficient transfer of electrons or energy between the TiO2 and LDH components. This heterojunction is the "engine" of the nanocomposite, defining its effectiveness in applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Atmosphere Limitations
Standard muffle furnaces typically operate in an air atmosphere.
While this is ideal for oxides like TiO2/LDH where oxidation or calcination is the goal, it is unsuitable for materials requiring oxygen-free environments. For processes requiring protective atmospheres (such as nitrogen for carbonization), a tube furnace is generally the required alternative.
Thermal Sensitivity
Precision is paramount; deviating from the 500 °C target can have detrimental effects.
Temperatures that are too low may result in incomplete crystallization or weak bonding. conversely, excessive heat could induce sintering that destroys the delicate layered structure of the LDH or causes unwanted phase degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you are selecting the correct thermal treatment for your nanocomposite synthesis, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is TiO2/LDH Synthesis: Ensure your muffle furnace is calibrated to maintain exactly 500 °C to promote in-situ crystallization and MgTi2O5 formation in an air atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is Heterojunction Quality: Prioritize the duration of the calcination step to allow sufficient time for atomic diffusion and interfacial bonding between phases.
- If your primary focus is Carbon-Based Composites: Do not use a standard muffle furnace; switch to a tube furnace to maintain the inert atmosphere required to prevent combustion.
The muffle furnace is not just a heating element; it is the architect of the nanocomposite's final crystal structure and chemical identity.
Summary Table:
| Process Function | Mechanism | Impact on Nanocomposite |
|---|---|---|
| In-Situ Crystallization | Thermal ordering at 500 °C | Embeds TiO2 directly within LDH layers |
| Chemical Bonding | Interfacial reaction | Converts physical mixtures into unified systems |
| Phase Evolution | High-temp diffusion | Generates MgTi2O5 for enhanced properties |
| Heterojunction Build | Crystalline alignment | Optimizes electron transfer and stability |
| Atmosphere Control | Standard Air | Ideal for oxide-based calcination processes |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect heterojunction requires uncompromising thermal accuracy. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are synthesizing TiO2/LDH nanocomposites at 500 °C or require inert atmospheres for advanced carbonization, our lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Maximize your lab's efficiency and material crystallinity today.
Visual Guide
References
- Synthesis and Characterization of Visible-Light-Responsive TiO2/LDHs Heterostructures for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation Performance. DOI: 10.3390/w17172582
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What specific PPE is recommended for loading and unloading a benchtop furnace? Essential Gear for Safe High-Temperature Handling
- Why is precise temperature control important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Reliable Results in Heat Treatment
- What role does a Muffle Furnace play in 1100°C oxidation experiments? Precision Thermal Control for Coatings
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What is the function of a high-temperature Muffle Furnace in the two-step heat treatment of PTFE-coated Nickel Foam?
- What are some specific processes modern Muffle Furnaces can perform? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Applications
- How are muffle furnaces used in electronics manufacturing? Essential for Precision Thermal Processing
- What critical testing environment does a high-temperature muffle furnace provide for resin burn-off analysis?



















