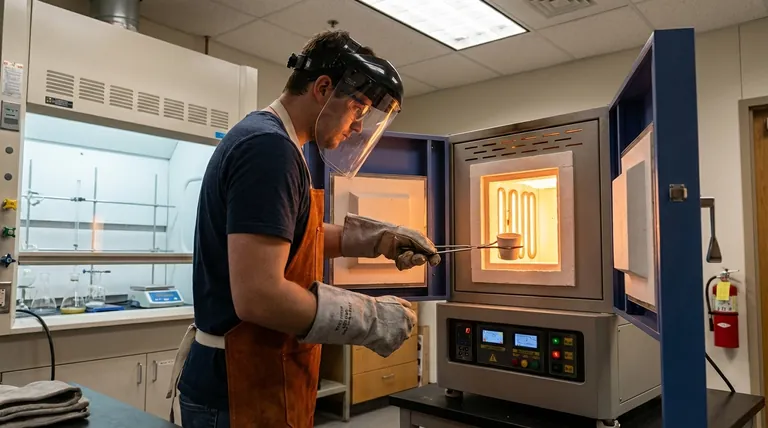
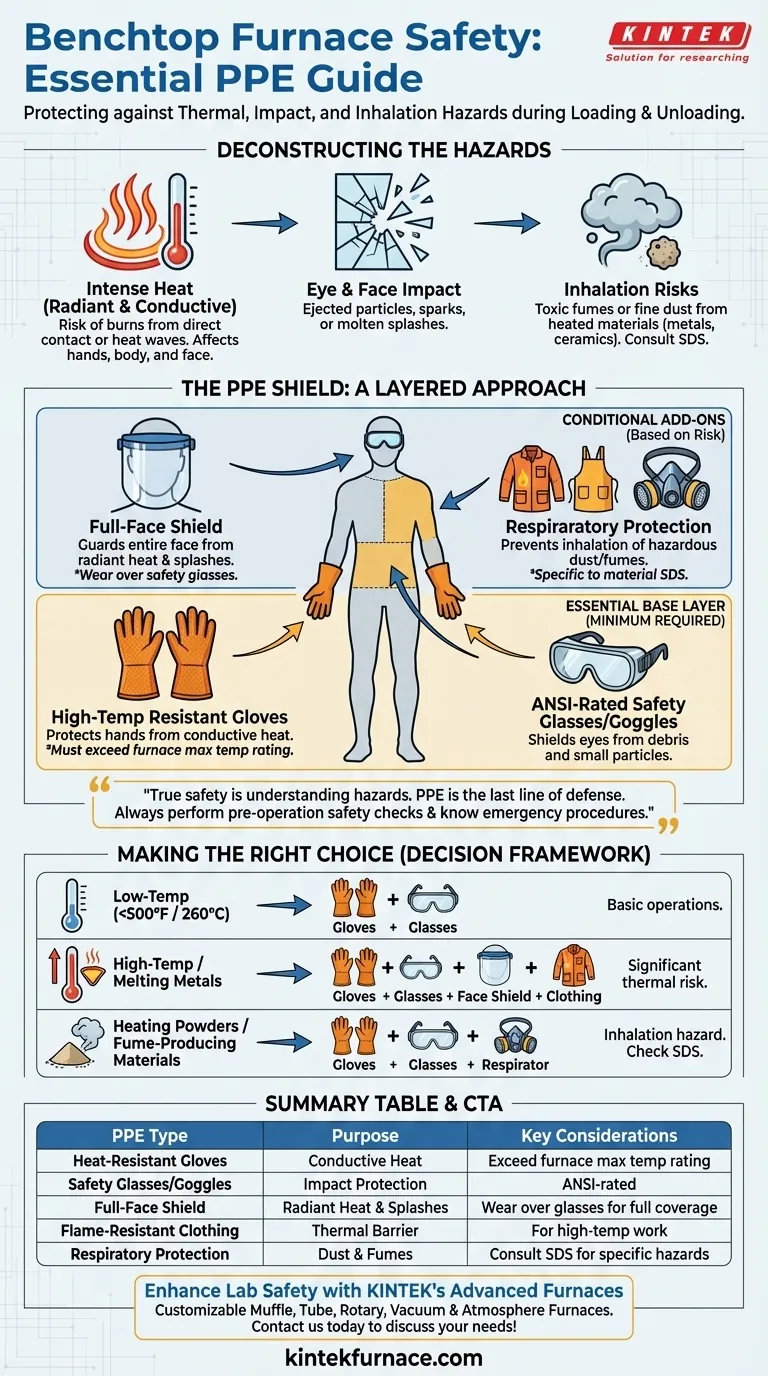
For loading and unloading a benchtop furnace, the minimum recommended Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) includes high-temperature resistant gloves and ANSI-rated safety glasses or goggles. Depending on the specific temperature and materials involved, this should be supplemented with a full-face shield and flame-resistant clothing to provide comprehensive protection from intense heat, sparks, and potential debris.
True operational safety isn't just about wearing gear; it's about understanding the specific thermal and material hazards of your process. Your choice of PPE must be a direct response to the risks you face each time you open the furnace door.

Deconstructing the Hazards: Why This PPE is Necessary
To select the right equipment, you must first understand the distinct risks a benchtop furnace presents. Each piece of PPE is designed to counter a specific danger.
Protecting Against Intense Heat
The most obvious danger is extreme heat, which exists in two forms: conductive heat (direct contact) and radiant heat (heat waves traveling through the air).
Your hands are most at risk for conductive heat when handling tools, crucibles, or the parts themselves. Heat-resistant gloves are non-negotiable for this reason.
Your body and face are vulnerable to radiant heat the moment you open the furnace door. Flame-resistant or heat-reflective clothing, such as an apron or jacket, provides a critical thermal barrier for your torso.
Shielding Your Eyes and Face
Your eyes are extremely sensitive to both impact and heat. At a minimum, safety glasses or goggles are required to protect against any small particles or debris that could be ejected.
However, glasses do little to protect your face from a blast of radiant heat. A polycarbonate face shield, worn over your safety glasses, is the proper tool for shielding your entire face from thermal radiation and potential splashes of molten material.
Addressing Inhalation Risks
The materials you heat can be a source of respiratory hazards. Certain metals, ceramics, or binders can release fine dust or toxic fumes when they reach high temperatures.
If you are working with powders or materials known to off-gas, respiratory protection is essential. This may range from a simple dust mask to a respirator with specific cartridges, depending on the hazard. Always consult the material's Safety Data Sheet (SDS) to understand the risks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Relying on PPE without understanding its limits creates a false sense of security. Effective safety requires a critical approach to your equipment and environment.
Not All Gloves Are Created Equal
The term "heat-resistant" is broad. Gloves have specific temperature ratings. A glove rated for 500°F is useless when handling a part from a 2000°F furnace. Always verify that your gloves' temperature rating exceeds your furnace's maximum operating temperature.
PPE is the Last Line of Defense
PPE protects you when other safety measures fail. A truly safe workspace is designed to prevent accidents from happening in the first place.
Before any operation, perform a quick safety check. Inspect electrical cords for frays or damage and ensure the unit is properly grounded. Know the location of the emergency shutdown procedure and keep a fire extinguisher suitable for electrical fires (Class C) within immediate reach.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Use this framework to select the appropriate level of protection for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is basic, low-temperature operations (below 500°F / 260°C): Your essential kit is properly-rated heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature work or melting metals: You must add a full-face shield and flame-resistant clothing to your essential kit for thermal protection.
- If your primary focus is heating powders or materials that may produce fumes: You must consult the SDS and add the specified respiratory protection to your setup.
Ultimately, proactive safety is a mindset, not just a checklist of gear.
Summary Table:
| PPE Type | Purpose | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Heat-Resistant Gloves | Protect hands from conductive heat | Must exceed furnace's max temperature rating |
| Safety Glasses/Goggles | Shield eyes from debris and particles | ANSI-rated for impact protection |
| Full-Face Shield | Guard face from radiant heat and splashes | Wear over safety glasses for full coverage |
| Flame-Resistant Clothing | Provide thermal barrier for body | Use for high-temp work to prevent burns |
| Respiratory Protection | Prevent inhalation of dust and fumes | Consult SDS for specific material hazards |
Ensure your lab's safety with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your operational safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development



















