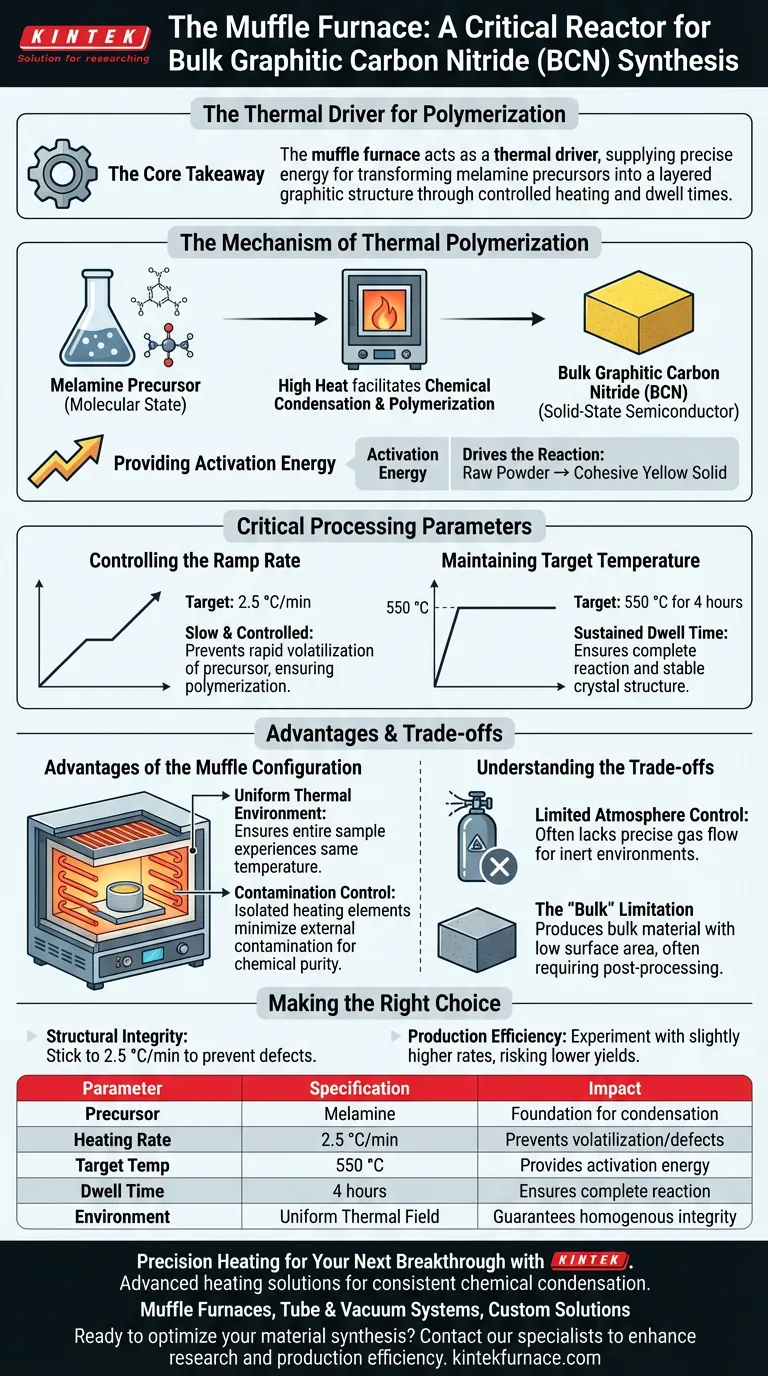
In the preparation of bulk graphitic carbon nitride (BCN), the muffle furnace serves as the critical reactor for thermal polymerization. It provides a stable, isolated environment that allows organic precursors, specifically melamine, to undergo the chemical condensation required to form a solid-state semiconductor.
The Core Takeaway The muffle furnace acts as a thermal driver, supplying the precise energy needed to transform molecular precursors into a layered graphitic structure. By strictly controlling the heating rate and dwell temperature, the furnace ensures the successful polymerization of the material into its bulk form.

The Mechanism of Thermal Polymerization
Transforming Precursors into Solids
The primary role of the furnace is to facilitate thermal polymerization. Precursors like melamine start in a molecular state.
Under high heat, these molecules lose ammonia and condense. This process links the molecules together, forming the characteristic graphitic, layered structure of BCN.
Providing Activation Energy
The chemical bonds required to form graphitic carbon nitride do not form spontaneously at room temperature. The furnace provides the necessary activation energy.
This energy input drives the reaction, converting the raw powder into a cohesive, yellow solid mass.
Critical Processing Parameters
Controlling the Ramp Rate
The muffle furnace must regulate how quickly the temperature rises. The primary reference specifies a heating rate of 2.5 °C per minute.
A slow, controlled ramp rate is vital. It prevents the rapid volatilization of the precursor, ensuring the material polymerizes rather than simply evaporating or decomposing too quickly.
Maintaining Target Temperature
Once the target temperature is reached, the furnace maintains a steady thermal field. For BCN synthesis, the material is typically held at 550 °C.
This temperature must be sustained for a specific duration, commonly 4 hours. This "dwell time" ensures the reaction is complete and the resulting crystal structure is stable.
Advantages of the Muffle Configuration
Uniform Thermal Environment
Muffle furnaces are designed to provide a uniform thermal field. This ensures that the entire sample experiences the same temperature simultaneously.
Uniform heating prevents temperature gradients within the crucible. This consistency is essential for producing a homogenous bulk material with uniform structural integrity.
Contamination Control
In a muffle furnace, the heating elements are often isolated from the chamber, or the chamber allows for a "muffled" environment. This minimizes external contamination.
For laboratory synthesis, this contamination-free heating is critical to ensure the chemical purity of the final graphitic carbon nitride.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Limited Atmosphere Control
While muffle furnaces are excellent for static heating in air, they often lack the precise gas flow controls found in tube furnaces.
If your synthesis requires a specific flow of inert gas (like argon) to strictly prevent oxidation or modify the defect structure, a standard muffle furnace may be less effective than a tube furnace.
The "Bulk" Limitation
The muffle furnace produces bulk BCN. This material typically has a low surface area compared to nanosheets.
While the furnace successfully creates the material, the resulting bulk solid usually requires post-processing (such as exfoliation) if high surface area is required for catalytic applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your BCN synthesis, consider how the furnace parameters align with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Stick to a slower ramp rate (2.5 °C/min) to prevent defects caused by rapid off-gassing during polymerization.
- If your primary focus is Production Efficiency: You may experiment with slightly higher ramp rates (up to 5 °C/min), but you risk lower yields due to sublimation.
Success in BCN synthesis relies not just on reaching 550 °C, but on the precision of the journey there.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification for BCN Synthesis | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor | Melamine (typically) | Foundation for chemical condensation |
| Heating Rate | 2.5 °C per minute | Prevents rapid volatilization and defects |
| Target Temp | 550 °C | Provides activation energy for polymerization |
| Dwell Time | 4 hours | Ensures complete reaction and stable structure |
| Environment | Uniform Thermal Field | Guarantees homogenous bulk integrity |
Precision Heating for Your Next Breakthrough
Successful synthesis of bulk graphitic carbon nitride (BCN) demands absolute control over thermal ramps and temperature stability. KINTEK provides the advanced heating solutions you need to ensure consistent chemical condensation and high-purity results.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces, including:
- Muffle Furnaces: For uniform thermal fields and stable bulk polymerization.
- Tube & Vacuum Systems: For precise atmosphere control and inert gas processing.
- Custom Solutions: Tailored rotary and CVD systems for unique material needs.
Ready to optimize your material synthesis? Contact our lab equipment specialists today to discover how our customizable furnaces can enhance your research and production efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Z. Kalantari Bolaghi, Dongling Ma. Exploring the Remarkably High Photocatalytic Efficiency of Ultra-Thin Porous Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets. DOI: 10.3390/nano14010103
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the muffle chamber in the furnace? Ensure Purity and Control in High-Temp Processes
- How are box type electric furnaces applied in electronic component manufacturing? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing
- How are muffle furnaces utilized in dental laboratories? Essential for Sintering, Firing, and Casting
- What temperature ranges are used for different muffle furnace applications? Optimize Your Heat Processes with KINTEK
- What is the function of a box-type resistance furnace in GFRP studies? Mastering High-Temperature Material Simulation
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the pretreatment of calcium carbonate? Ensure Accurate Thermal Studies
- What are the key performance benefits of using a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Uniform, and Contamination-Free Heating
- What atmosphere control options are available in advanced muffle furnaces? Master Materials Processing with Precision



















