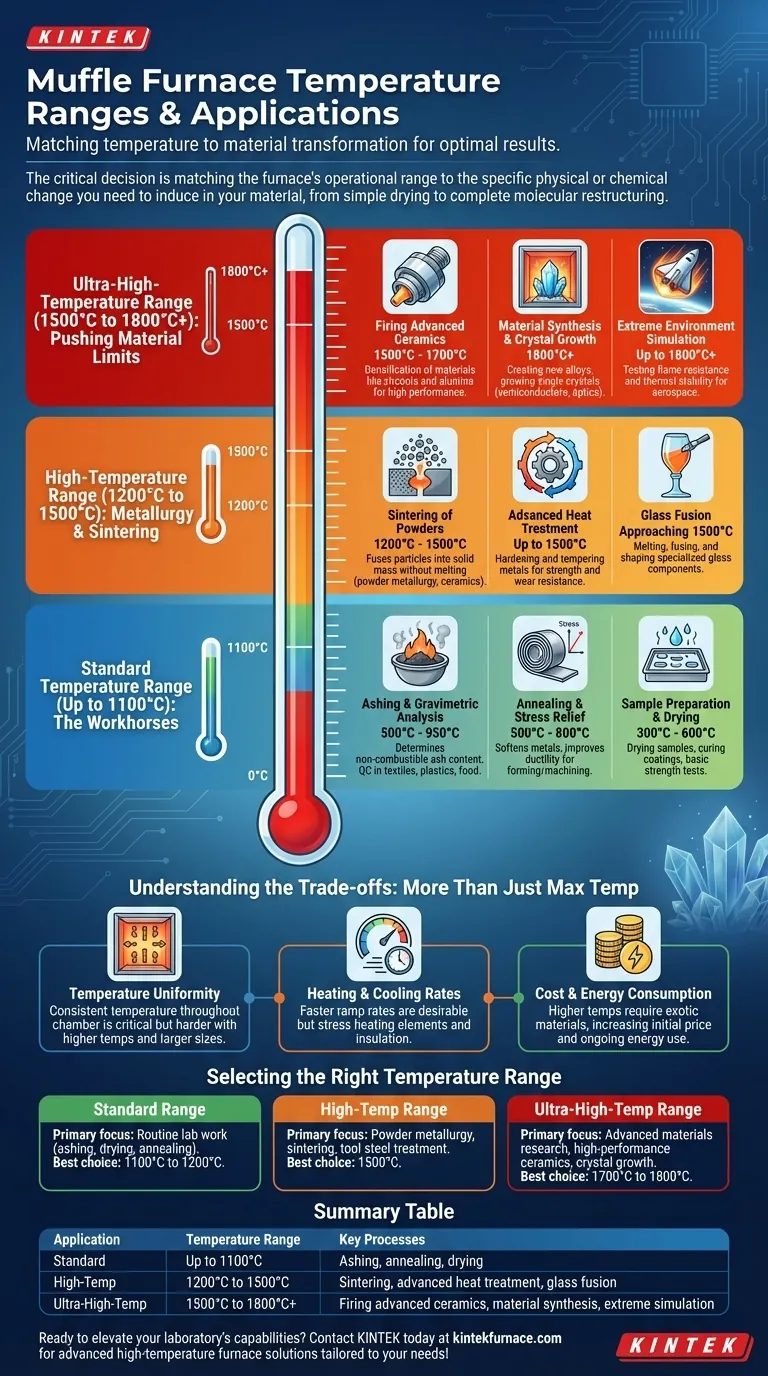
In practice, muffle furnace temperatures are matched directly to the desired material transformation. Standard models operating up to 1100°C handle processes like ashing and basic heat treatment, while high-temperature furnaces reach 1500°C to 1800°C for demanding applications like metallurgy, advanced ceramics firing, and sintering.
Choosing a muffle furnace goes beyond its maximum temperature rating. The critical decision is matching the furnace's operational range to the specific physical or chemical change you need to induce in your material, from simple drying to complete molecular restructuring.

Standard Temperature Range (Up to 1100°C): The Workhorses
Furnaces in this category are the most common in general laboratory and light industrial settings. They are designed for reliability and precision in routine thermal processing tasks.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Temperatures typically between 500°C and 950°C are used for ashing. This process involves burning off all organic material to determine the non-combustible ash content.
This is a critical quality control step in industries like textiles, plastics, and food science for analyzing material composition.
Annealing and Stress Relief
For metals, annealing is performed at lower temperatures, often between 500°C and 800°C. This heat treatment softens the material, relieves internal stresses, and improves ductility.
This makes the metal easier to work with in subsequent forming or machining processes.
Sample Preparation and Drying
The lower end of this range, from 300°C to 600°C, is ideal for drying samples, curing coatings, or conducting basic material strength tests in industries from paint to plastics.
High-Temperature Range (1200°C to 1500°C): Metallurgy and Sintering
This range moves from basic preparation into the realm of material transformation, where the fundamental properties of materials are intentionally altered.
Sintering of Powders
Sintering uses heat to fuse particles together without melting them, forming a solid, coherent mass. This is a core process in powder metallurgy and ceramics manufacturing.
Temperatures between 1200°C and 1500°C are required to sinter many common metal powders and technical ceramics.
Advanced Heat Treatment
This range enables more aggressive heat treatments for metals, such as hardening and tempering, which significantly increase strength and wear resistance. These processes are foundational in tool and die manufacturing.
Glass Fusion
In the glass industry, temperatures approaching 1500°C are used for melting, fusing, and shaping specialized glass components.
Ultra-High-Temperature Range (1500°C to 1800°C+): Pushing Material Limits
Reserved for advanced research and specialized production, these furnaces operate at the frontier of material science.
Firing Advanced Ceramics
Materials like zirconia and alumina require temperatures of 1500°C to 1700°C to achieve full densification and develop their unique high-performance properties.
Material Synthesis and Crystal Growth
Creating entirely new alloys or growing single crystals for semiconductors and optics demands the extreme, precisely controlled heat provided by furnaces capable of reaching 1800°C or more.
Extreme Environment Simulation
In aerospace, these furnaces are used to test the flame resistance and thermal stability of components, simulating the brutal conditions of atmospheric re-entry or engine exhaust.
Understanding the Trade-offs: More Than Just Max Temp
Selecting the right furnace involves balancing performance characteristics, as a higher maximum temperature introduces significant engineering complexities.
Temperature Uniformity
Achieving a consistent temperature throughout the entire heating chamber is critical for reliable results. Larger chambers and higher temperatures make temperature uniformity more difficult and expensive to achieve.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The speed at which a furnace can reach and cool down from its setpoint (ramp rate) is a key factor. Faster rates are desirable but place immense stress on heating elements and insulation, increasing cost and maintenance.
Cost and Energy Consumption
Higher temperature capabilities require more exotic materials for heating elements (e.g., molybdenum disilicide) and thicker, multi-layer insulation. This leads to a dramatic increase in both initial purchase price and ongoing energy consumption.
Selecting the Right Temperature Range for Your Application
Use your primary application as the deciding factor to ensure you invest in the right capability without overspending on unnecessary temperature overhead.
- If your primary focus is routine lab work like ashing, drying, or basic metal annealing: A standard furnace with a maximum temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is powder metallurgy, sintering common ceramics, or advanced tool steel treatment: A high-temperature model capable of reaching 1500°C is necessary to achieve the required material transformations.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research, developing high-performance ceramics, or crystal growth: An ultra-high-temperature furnace rated for 1700°C to 1800°C is required to work with these demanding materials.
Ultimately, the right muffle furnace is the one whose temperature range reliably enables the specific material science you aim to perform.
Summary Table:
| Application | Temperature Range | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Up to 1100°C | Ashing, annealing, drying |
| High-Temp | 1200°C to 1500°C | Sintering, advanced heat treatment, glass fusion |
| Ultra-High-Temp | 1500°C to 1800°C+ | Firing advanced ceramics, material synthesis, extreme simulation |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with a muffle furnace tailored to your exact needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering enhanced efficiency, precision, and reliability. Don't settle for one-size-fits-all—contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















