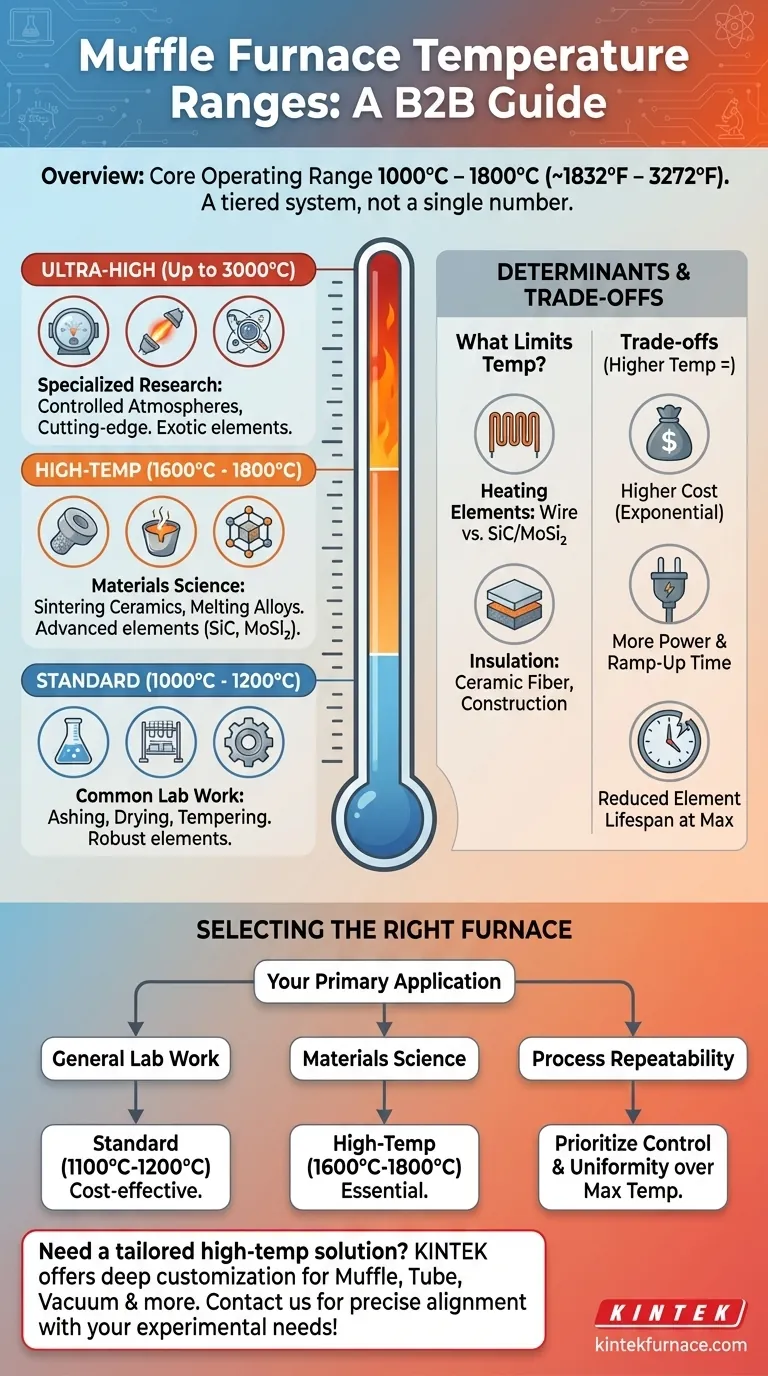
In practice, most muffle furnaces operate within a range of 1000°C to 1800°C (approximately 1832°F to 3272°F). Standard laboratory models typically reach up to 1200°C, which is sufficient for the majority of common applications. High-temperature models are required for more advanced processes and can achieve 1800°C, while some highly specialized units can exceed this.
The maximum temperature of a muffle furnace is not a single number, but a tiered system based on its design and intended application. Choosing the right furnace means looking beyond the maximum temperature and considering factors like control, uniformity, and the specific requirements of your process.

Deconstructing Muffle Furnace Temperature Ranges
The term "muffle furnace" covers a broad category of equipment. Understanding the typical temperature capabilities of each class is key to selecting the correct tool for your work.
Standard Laboratory & Industrial Furnaces
Most general-purpose muffle furnaces, found in both academic labs and industrial quality control, operate in the 1000°C to 1200°C range.
These are the workhorses for common applications like chemical analysis, ashing organic materials, tempering metals, and drying samples. Their heating elements are robust and offer a long service life when operated within this range.
High-Temperature Models
For more demanding applications in materials science and engineering, high-temperature furnaces are required. These models reliably achieve temperatures between 1600°C and 1800°C.
This capability is essential for processes like sintering advanced ceramics, melting certain metals and alloys, and conducting high-temperature materials testing. These furnaces use more advanced heating elements and insulation to safely sustain these temperatures.
Specialized Ultra-High Temperature Systems
In rare cases, highly specialized furnaces can reach up to 3000°C. These are not typical muffle furnaces and are reserved for cutting-edge research.
They often require controlled atmospheres (e.g., vacuum or inert gas) to prevent the graphite or tungsten heating elements from oxidizing and failing instantly.
What Determines a Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
A furnace's temperature limit is not an arbitrary number; it is a direct result of its physical components and engineering design.
The Role of Heating Elements
The material used for the heating elements is the single greatest factor limiting a furnace's temperature. Common wire elements often max out around 1200°C.
To achieve higher temperatures, manufacturers must use more exotic and expensive materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂), which can operate effectively up to 1800°C.
Insulation and Construction
Reaching and holding extreme temperatures requires exceptional thermal insulation. High-temperature furnaces use thicker, multi-layered insulation made from high-purity ceramic fiber.
The overall construction must also be more robust to handle the immense thermal stress of repeated heating and cooling cycles, which is why these models are significantly heavier and more expensive.
Beyond Maximum Temperature: Control and Uniformity
A furnace's value is not just in how hot it can get, but how well it can hold a specific temperature. Programmable controls and temperature uniformity are critical features.
The ability to precisely control heating and cooling rates, and to ensure the temperature is consistent throughout the entire chamber, is often more important for achieving repeatable results than a high maximum temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace with a higher temperature rating than you need can lead to unnecessary costs and complications.
Cost vs. Temperature
The relationship between cost and maximum temperature is exponential. A furnace rated for 1800°C can be many times more expensive than a 1200°C model due to its specialized materials.
Ramp-Up Time and Energy Consumption
Higher temperatures require more power. These furnaces have higher energy consumption and can take a significant amount of time—often an hour or more—to reach their setpoint, which can impact laboratory workflow.
Maintenance and Element Lifespan
Consistently operating a furnace at its absolute maximum rated temperature drastically reduces the lifespan of its heating elements. This leads to more frequent and costly replacements, increasing the total cost of ownership.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Focus on your primary application to make an informed and cost-effective decision.
- If your primary focus is general lab work (ashing, drying, basic heat treating): A standard furnace reaching 1100°C or 1200°C is the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is materials science (sintering, melting, advanced ceramics): You must invest in a high-temperature model capable of reaching at least 1600°C to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and accuracy: Prioritize a model with advanced programmable controls and verified temperature uniformity over a higher, but unnecessary, maximum temperature.
By matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific procedural needs, you ensure both accurate results and a wise investment.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1000°C - 1200°C | Ashing, drying, tempering metals | Cost-effective, long element life |
| 1600°C - 1800°C | Sintering ceramics, melting alloys | Higher cost, advanced insulation |
| Up to 3000°C | Specialized research | Requires controlled atmospheres |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















