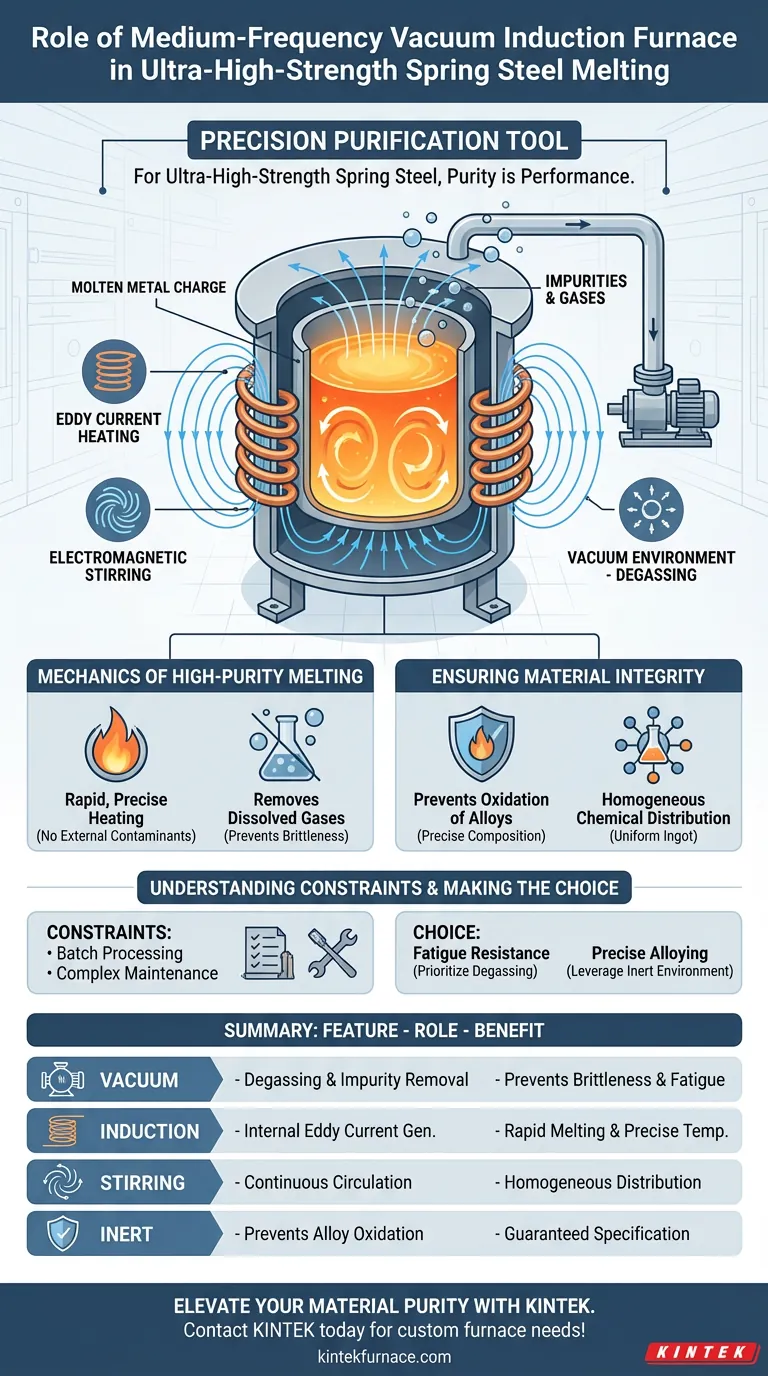
The medium-frequency vacuum induction furnace functions as a precision purification tool in the production of ultra-high-strength spring steel. It utilizes electromagnetic induction to generate eddy currents that heat and melt the metal charge within a strictly controlled vacuum environment. This process is essential for removing volatile impurities and gases while simultaneously preventing the oxidation of critical alloying elements.
Core Takeaway: For ultra-high-strength spring steel, purity is performance. The vacuum induction furnace provides the necessary controlled environment to eliminate defects and strictly maintain chemical composition, ensuring the material can withstand high-stress applications without failure.
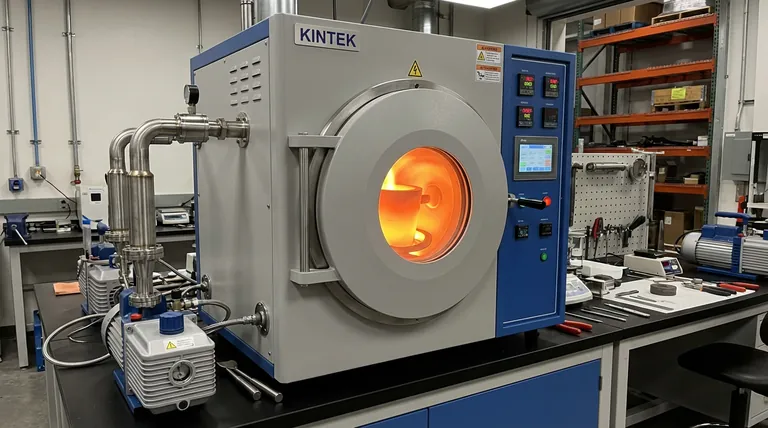

The Mechanics of High-Purity Melting
Heating via Electromagnetic Induction
The furnace does not rely on external heat sources. Instead, it employs electromagnetic induction to generate eddy currents directly within the metal charge.
This internal heating mechanism allows for rapid melting and precise temperature control. It ensures the steel reaches the necessary state for alloying without introducing external contaminants.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
Operating in a vacuum is the defining feature of this process for high-strength steel. The vacuum chamber effectively removes dissolved gases and volatile impurities from the molten steel.
By lowering the ambient pressure, the furnace forces unwanted gases out of the liquid metal. This reduction in impurities is vital for preventing brittleness and ensuring the longevity of the final spring product.
Ensuring Material Integrity
Preventing Oxidation of Alloys
Ultra-high-strength spring steel relies on a specific balance of micro-alloying elements to achieve its mechanical properties. In open-air melting, these active elements can easily oxidize and burn off.
The vacuum environment eliminates oxygen from the equation. This protection ensures that the precise amount of alloying elements remains in the steel, guaranteeing the final ingot matches the intended chemical specifications.
Homogeneity through Electromagnetic Stirring
A secondary but critical benefit of the induction process is the natural stirring effect it creates within the molten pool. The electromagnetic forces cause the liquid metal to circulate continuously.
This stirring action promotes thermal uniformity throughout the melt. It also ensures that alloying elements are distributed evenly, resulting in a chemically homogeneous ingot that serves as a consistent foundation for subsequent processing.
Understanding the Constraints
Batch Processing Limitations
While this furnace excels at quality, it typically operates as a batch process rather than a continuous one. This can limit throughput compared to other melting methods used for lower-grade steels.
Maintenance and Complexity
The requirement for a vacuum seal adds mechanical complexity. Maintaining high-purity levels requires diligent upkeep of the vacuum pumps and chamber seals to prevent atmospheric leaks that could compromise the melt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of a medium-frequency vacuum induction furnace, align its capabilities with your specific metallurgical objectives:
- If your primary focus is fatigue resistance: Prioritize the vacuum degassing phase to minimize gas content and non-metallic inclusions, as these are primary initiation sites for fatigue failure.
- If your primary focus is precise alloying: Leverage the inert environment to add reactive micro-alloys without fear of oxidation loss, ensuring the exact chemical composition required for ultra-high strength.
By controlling the atmosphere and the melt dynamics, this furnace technology transforms raw inputs into the flawless crystalline structure required for high-performance engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Spring Steel Production | Benefit to Material |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Degassing & impurity removal | Prevents brittleness and fatigue |
| Induction Heating | Internal eddy current generation | Rapid melting and precise temperature |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Continuous liquid circulation | Homogeneous chemical distribution |
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents alloy oxidation | Guaranteed chemical specification |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK
Precision engineering starts with high-purity melting. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers professional Vacuum Induction Melters, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical needs.
Whether you are producing ultra-high-strength spring steel or developing advanced alloys, our high-temperature furnace solutions ensure the thermal uniformity and contamination-free environment your lab requires.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Fang Shi, Liqing Chen. Heat Treatment Process, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of Spring Steel with Ultra-High Strength and Toughness. DOI: 10.3390/met14020180
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- In which industries is the IGBT induction melting machine commonly used? Key Applications & Benefits
- How do induction furnaces enhance productivity in foundries? Boost Melting Speed and Automation for Higher Output
- How does electrical conductivity affect induction coil life? Maximize Furnace Durability with Superior Conductivity
- What role does a vacuum non-consumable arc furnace play in high-entropy alloys? Master Complex Alloy Synthesis
- Why is high-precision gas atomization equipment necessary for alloy powders? Precision for Nanoporous Copper (NPCu)
- What is induction welding and how is it performed? Discover High-Speed, Non-Contact Welding for Metals and Plastics
- How do induction furnaces improve working conditions? A Safer, Cleaner Foundry Environment
- How are vacuum casting furnaces utilized in the medical industry? Ensure Purity and Precision for Medical Devices



















