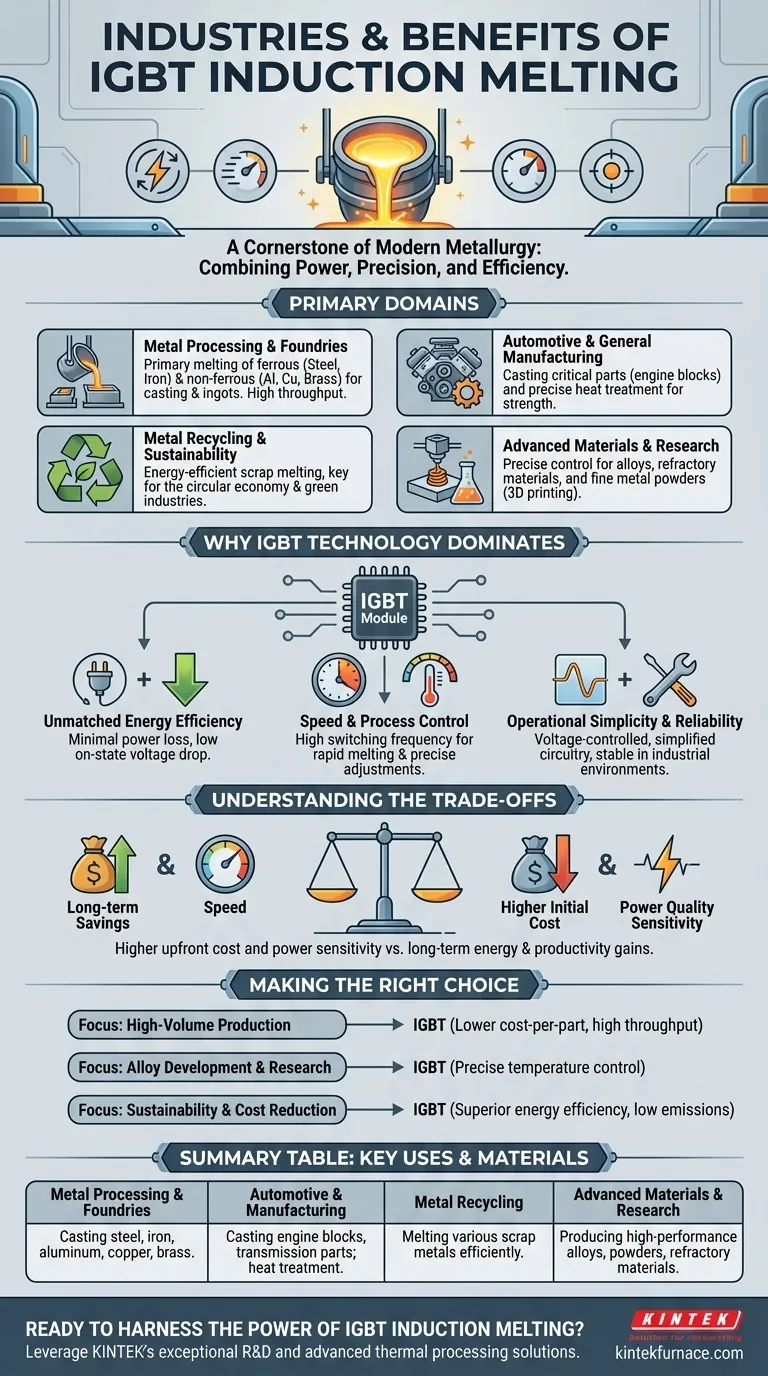
At its core, the IGBT induction melting machine is a cornerstone of modern metallurgy and manufacturing. It is most prominently used in the metal processing, foundry, automotive, and recycling industries. Its adoption is driven by its exceptional efficiency, speed, and the precise control it offers over the melting process for a wide range of metals like steel, iron, copper, and aluminum.
While often associated with large-scale foundries, the true significance of IGBT induction melting lies in its combination of power and precision. This technology is the go-to solution for any industrial process that demands rapid, clean, and highly controllable heating of conductive materials.
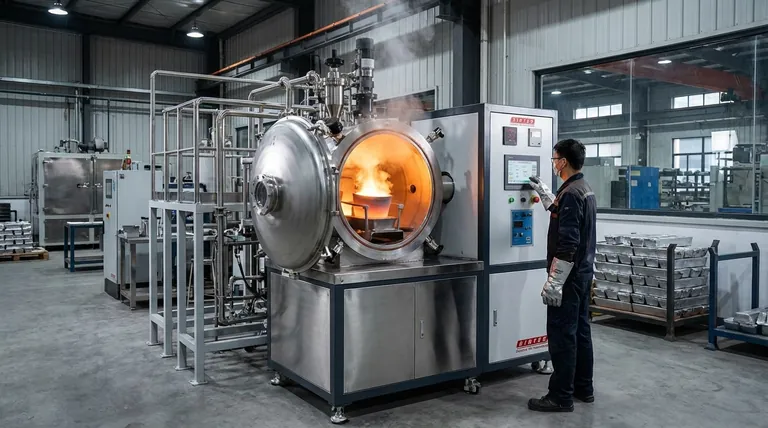

The Primary Domains of IGBT Induction Melting
The versatility of IGBT induction technology allows it to serve several critical industrial sectors, from raw material processing to the creation of highly specialized products.
Metal Processing and Foundries
This is the most common application. Foundries use these machines for the primary melting of ferrous metals (like iron and steel) and non-ferrous metals (like aluminum, copper, and brass).
The goal here is to produce high-quality molten metal for casting into parts, ingots, or other semi-finished forms. The speed of IGBT systems allows for higher throughput and productivity.
Automotive and General Manufacturing
The automotive industry relies on induction melting for casting engine blocks, transmission components, and other critical parts.
Beyond melting, the underlying technology is also used for heat treatment, a process that improves the strength, hardness, and durability of metal components after they have been formed.
Metal Recycling and Sustainability
IGBT induction furnaces are highly effective at melting down scrap metal. This process is far more energy-efficient and cleaner than traditional blast furnaces, making it a key technology in the circular economy.
This efficiency also makes it valuable in "green" industries, such as the production of high-purity silicon for solar panels, where minimizing energy consumption is crucial.
Advanced Materials and Research
The precise temperature control of IGBT systems is essential for specialized applications. This includes producing high-performance alloys, processing refractory materials that have extremely high melting points, and creating fine metal powders for use in additive manufacturing (3D printing).
Why IGBT Technology Dominates Induction Heating
The "IGBT" (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) is the electronic heart of the machine, and its characteristics are the primary reason for this technology's widespread adoption over older methods.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
IGBT modules have a very low on-state voltage drop and minimal power dissipation. In practical terms, this means less electrical energy is wasted as heat in the control system, and more of it is directed into the metal you are trying to melt.
Speed and Process Control
IGBTs operate at a high switching frequency. This allows the system to transfer energy into the metal very quickly, resulting in faster melting times compared to resistance or flame heating. This high frequency also enables extremely precise temperature adjustments.
Operational Simplicity and Reliability
These systems are voltage-controlled, which simplifies the required driver circuitry. They are also known for stable performance across a wide range of operating temperatures and do not require complex supporting components like snubber circuits, making them more robust for industrial environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly advantageous, IGBT induction technology is not without its considerations. A clear-eyed assessment is necessary before any investment.
Initial Capital Investment
The upfront cost of an IGBT induction furnace is typically higher than that of simpler, older technologies like gas-fired or resistance furnaces. The long-term savings in energy and productivity must be weighed against this initial expense.
Power Quality Sensitivity
As with most advanced power electronics, the performance and longevity of an IGBT system can be affected by the quality of the incoming electrical supply. Facilities may need to invest in power conditioning equipment to protect the furnace from voltage spikes or harmonics.
Specialized Maintenance
Repairing an IGBT-based system requires technicians with expertise in power electronics, which is a different skillset than traditional mechanical or refractory maintenance. This can impact maintenance costs and downtime if qualified personnel are not readily available.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this technology fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: The rapid melting times and energy efficiency of an IGBT system will deliver a lower cost-per-part and higher throughput.
- If your primary focus is alloy development or material research: The precise temperature control offered by IGBT technology is non-negotiable for achieving repeatable and specific metallurgical properties.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability and cost reduction: The superior energy efficiency and low emissions make IGBT induction melting a clear winner over fossil fuel-based methods.
Ultimately, adopting IGBT induction technology empowers an organization to produce higher-quality materials with greater speed, control, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use | Key Metals/Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Processing & Foundries | Primary melting for casting | Steel, Iron, Aluminum, Copper, Brass |
| Automotive & Manufacturing | Casting components & heat treatment | Engine blocks, transmission parts |
| Metal Recycling | Melting scrap metal efficiently | Various scrap metals |
| Advanced Materials & Research | Producing high-performance alloys & powders | Refractory materials, metal powders |
Ready to harness the power, precision, and efficiency of IGBT induction melting for your operation?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal processing solutions. Our expertise in high-temperature furnace technology, including advanced induction systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique production or research requirements.
Whether you are in metal processing, automotive, recycling, or advanced materials development, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your productivity and quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















