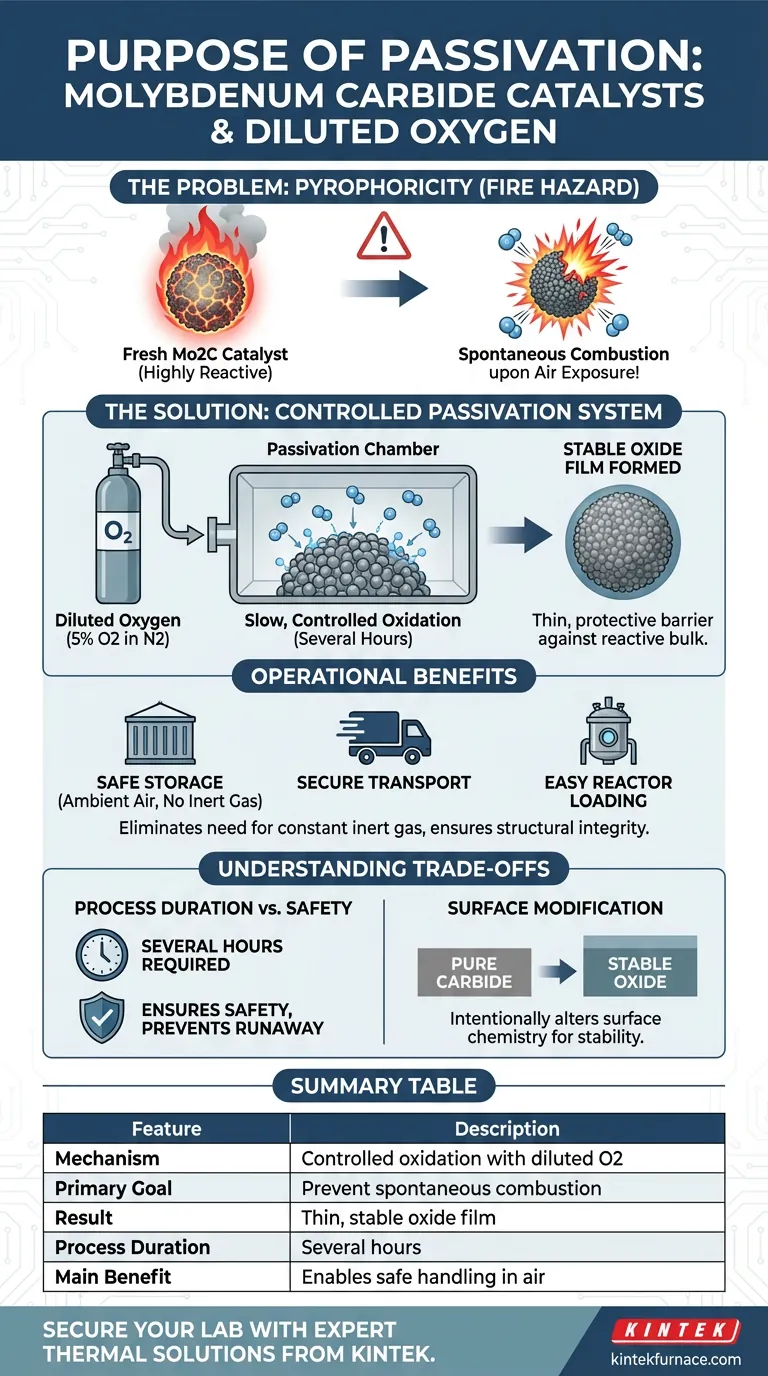
The primary purpose of a passivation system is to prevent spontaneous combustion upon exposure to air. Freshly prepared molybdenum carbide catalysts are pyrophoric, meaning they are highly reactive and unstable in an oxygen-rich atmosphere. By treating them with diluted oxygen, you create a controlled surface modification that renders the material safe for handling.
Fresh molybdenum carbide catalysts are chemically unstable in ambient air and pose a significant fire hazard. Passivation utilizes a low-concentration oxygen stream to engineer a protective, stable oxide film on the catalyst surface, ensuring safety during storage and transport.

The Critical Need for Passivation
The Danger of Pyrophoricity
Freshly synthesized molybdenum carbide is highly reactive.
If these catalysts are exposed to standard atmospheric air immediately after preparation, they can spontaneously combust. This poses an immediate safety hazard to laboratory personnel and equipment.
The Role of Diluted Oxygen
To manage this reactivity, the catalyst is subjected to a passivation process using diluted oxygen.
This typically involves a mixture such as 5% oxygen ($\text{O}_2$) in nitrogen ($\text{N}_2$). This low concentration prevents the violent exothermic reaction that would occur with pure air.
Mechanism of Action
Controlled Oxidation
The passivation system introduces the diluted gas stream slowly over a period of several hours.
This gradual exposure allows the surface chemistry to change in a controlled, predictable manner rather than a chaotic thermal runaway.
Formation of a Stable Film
The specific goal of this process is to create a very thin and stable oxide film on the catalyst surface.
This film acts as a barrier, "sealing" the reactive bulk of the catalyst beneath it. Once this film is established, the catalyst is no longer pyrophoric and becomes stable enough for exposure to ambient air.
Operational Benefits
Logistics and Storage
Without passivation, molybdenum carbide would require constant storage under inert gas (like argon or nitrogen).
The oxide film allows the catalyst to be stored in standard containers without the risk of fire or degradation.
Safe Transport and Loading
The passivation layer ensures the structural integrity of the catalyst during transport.
It also allows technicians to safely load the catalyst into reactors for future use without requiring specialized, air-free handling equipment at every step.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Duration vs. Safety
The passivation process is not instantaneous; it requires several hours to complete effectively.
Rushing this process by increasing oxygen concentration too quickly defeats the purpose and reintroduces the risk of combustion or thermal damage to the catalyst structure.
Surface Modification
While necessary for safety, this process intentionally alters the surface chemistry of the catalyst.
You are effectively trading a highly active, dangerous surface for a stable, oxidized one. Users must be aware that the surface is now an oxide, not a pure carbide, which ensures stability but changes the immediate surface properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To effectively manage molybdenum carbide catalysts, you must prioritize safety protocols during the post-synthesis phase.
- If your primary focus is Personnel Safety: Strictly adhere to the usage of low-concentration oxygen (e.g., 5%) to prevent spontaneous combustion events.
- If your primary focus is Material Integrity: Allow the passivation gas to flow for the full recommended duration (several hours) to ensure the oxide film is uniform and stable before exposing the catalyst to air.
Controlled passivation is the bridge that transforms a volatile chemical hazard into a usable, manageable industrial tool.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Controlled oxidation using diluted oxygen (e.g., 5% O2 in N2) |
| Primary Goal | Prevent pyrophoricity and spontaneous combustion in ambient air |
| Result | Formation of a thin, stable oxide film on the catalyst surface |
| Process Duration | Several hours for uniform surface modification |
| Main Benefit | Enables safe storage, transport, and loading into reactors |
Secure Your Lab’s Safety with Expert Thermal Solutions
Molybdenum carbide synthesis requires precision and safety. KINTEK provides high-performance, customizable thermal systems—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Whether you need precise atmosphere control for passivation or robust high-temperature furnaces, our equipment is designed to meet your unique research and industrial needs.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your catalyst synthesis and safety protocols!
Visual Guide
References
- Linyuan Zhou, Changwei Hu. Regulating the Hydrodeoxygenation Activity of Molybdenum Carbide with Different Diamines as Carbon Sources. DOI: 10.3390/catal14020138
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What challenges are associated with batch furnaces? Overcome Inefficiency and Quality Issues
- How does the perpendicular orientation of substrate holders benefit VTD? Maximize Efficiency and Thermal Control
- What is the purpose of the annealing process in OLED preparation? Optimize Film Stability and Device Efficiency
- Why is thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) necessary for modified hard carbon? Optimize Stability & Composition
- What is the primary role of a carbonization curing chamber? Unlock High Strength in Magnesium Slag Mortar
- What is a batch furnace and how does it operate? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Diverse Applications
- Why is immediate water quenching required for CuAlMn alloys? Master Phase Retention in Shape Memory Alloys
- What is the purpose of using a thermal evaporation coating system? Enhancing I-V Testing Accuracy for Nanocomposites













