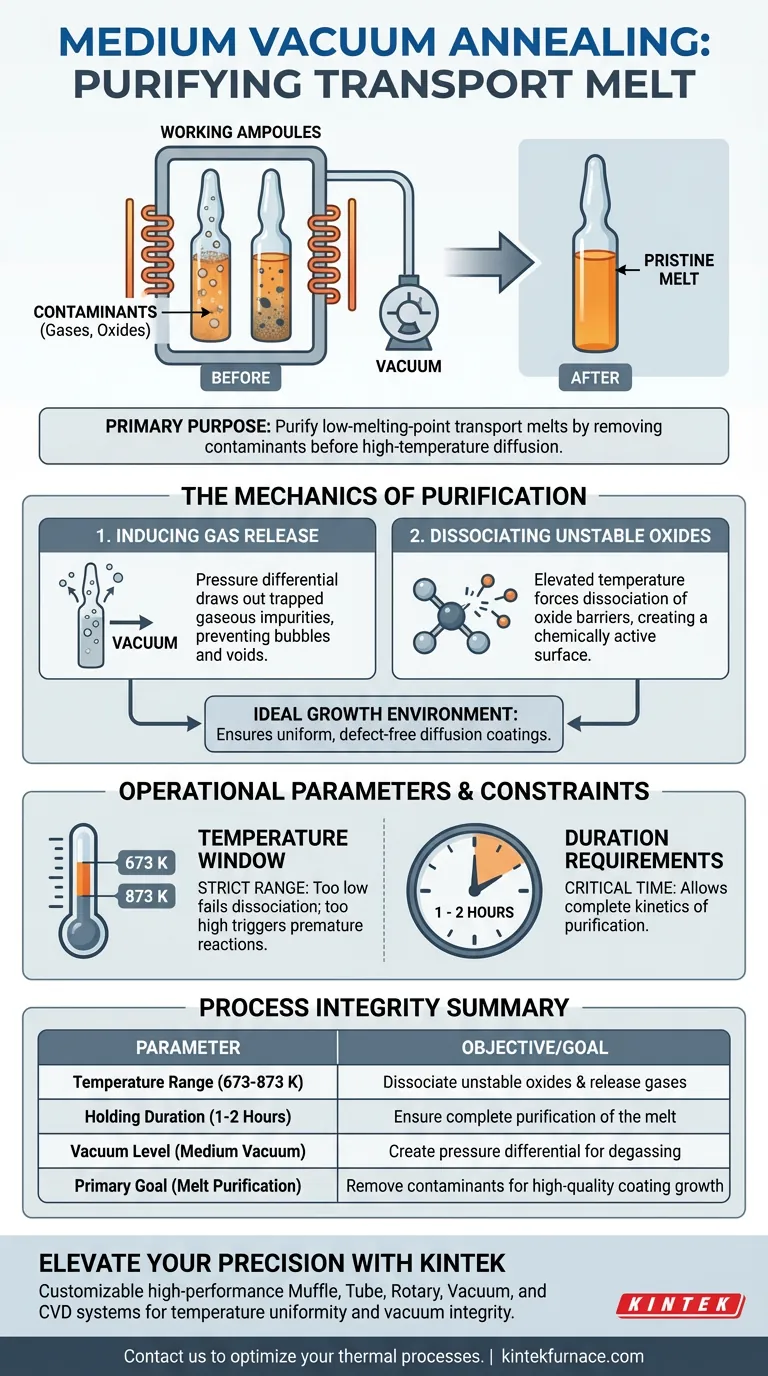
The primary purpose of medium vacuum annealing is to purify the transport melt. This pre-treatment step removes contaminants from working ampoules before high-temperature diffusion begins. By holding the ampoules at elevated temperatures in a vacuum, the process induces the release of gaseous impurities and forces the dissociation of unstable oxides.
The ultimate goal is to create a pristine chemical environment. By eliminating impurities and oxides from low-melting-point transport melts, you ensure that the subsequent growth of diffusion coatings is not compromised by contamination.
The Mechanics of Melt Purification
Inducing Gas Release
The presence of trapped gases within low-melting-point transport melts can be detrimental to the final product.
Vacuum annealing creates a pressure differential that draws these gaseous impurities out of the melt. This degassing step prevents gas bubbles or voids from forming during the critical high-temperature diffusion phase.
Dissociating Unstable Oxides
Oxides act as barriers to effective diffusion and coating growth.
The annealing process is specifically designed to facilitate the dissociation of unstable oxides. Breaking these chemical bonds prior to the main process ensures that the melt surface is chemically active and clean.
Creating the Ideal Growth Environment
The quality of a diffusion coating is directly dependent on the purity of the medium it grows in.
By removing these contaminants, the annealing step ensures a high-quality environment. This allows for uniform and defect-free growth of the diffusion coatings.
Operational Parameters and Constraints
The Temperature Window
Success relies on strict adherence to a specific temperature range.
The process must be conducted between 673 K and 873 K. Temperatures below this range may fail to dissociate oxides, while temperatures significantly above it could trigger premature diffusion reactions.
Duration Requirements
Time is a critical variable for ensuring complete purification.
The ampoules must be held at the target temperature for 1 to 2 hours. This duration provides sufficient time for the kinetics of gas release and oxide dissociation to reach completion.
Ensuring Process Integrity
Understanding the Trade-offs
While this step adds time to the overall production cycle, skipping it is a false economy.
Failing to perform this medium vacuum annealing often leads to poor coating adhesion or structural defects caused by inclusions. The time invested in this pre-treatment prevents the much higher cost of rejected parts after the high-temperature processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your diffusion processing, apply these guidelines:
- If your primary focus is coating purity: Prioritize the upper end of the time limit (2 hours) to ensure maximum dissociation of unstable oxides.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: Maintain strict temperature controls between 673 K and 873 K to stabilize the low-melting-point transport melts without triggering premature reactions.
A clean melt is the non-negotiable foundation for a high-performance diffusion coating.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Requirement | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 673 K - 873 K | Dissociate unstable oxides & release gases |
| Holding Duration | 1 - 2 Hours | Ensure complete purification of the melt |
| Vacuum Level | Medium Vacuum | Create pressure differential for degassing |
| Primary Goal | Melt Purification | Remove contaminants for high-quality coating growth |
Elevate Your Heat Treatment Precision with KINTEK
Don't let impurities compromise your diffusion coating quality. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory and industrial requirements.
Whether you are performing critical vacuum annealing or complex high-temperature diffusion, our systems provide the temperature uniformity and vacuum integrity your research demands.
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? Contact us today to consult with our specialists and find the perfect furnace solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Ismatov Jumaniez Faizullaevich. Mplementation Of The Process Of High Temperature Diffusion Treatment. DOI: 10.37547/ajast/volume05issue11-22
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are common heating elements used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- Why are vacuum-melted materials preferred for medical implants? Ensure Implant Purity and Longevity
- What is the core function of a vertical vacuum furnace in recycling waste magnesium alloys? Purify Magnesium via Vacuum Sublimation
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace? Unlock Boron Nitride Thermal Performance
- What role does a vacuum furnace play in the pre-treatment of UCF for magnesium matrix composites? Improve Bond Quality
- What role does a vacuum dryer play in the chemical modification of supraparticles? Master Vapor-Phase Hydrophobization
- What types of materials are commonly treated in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Enhance Performance with Pristine Heat Treatment
- How does vacuum carburizing improve surface quality? Achieve Clean, High-Strength Parts



















