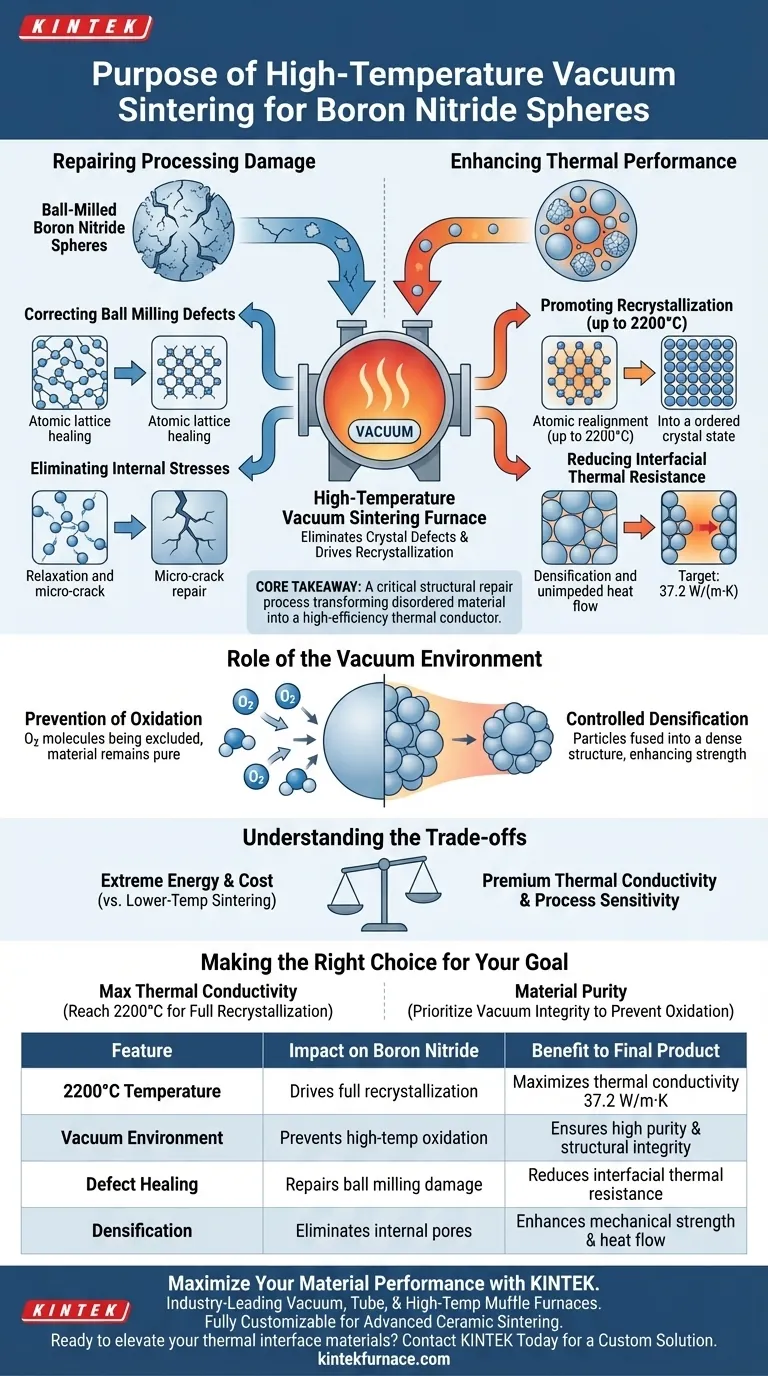
The purpose of using a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace for Boron Nitride Spheres is to repair atomic-level structural damage and maximize thermal performance. By subjecting the material to temperatures up to 2200°C, the process eliminates crystal defects introduced during ball milling and drives recrystallization, which is essential for reducing interfacial thermal resistance.
Core Takeaway This post-treatment step is not merely about heating; it is a critical structural repair process. It transforms the disordered, high-defect structure of ball-milled Boron Nitride into a highly crystalline, efficient thermal conductor capable of achieving conductivity values of 37.2 W/(m·K).
Repairing Processing Damage
Correcting Ball Milling Defects
The fabrication of Boron Nitride Spheres often involves ball milling, a mechanical process that physically shapes the material.
While effective for shaping, this mechanical force introduces significant crystal defects into the material's atomic structure.
The sintering furnace provides the thermal energy necessary to heal these defects, restoring the integrity of the crystal lattice.
Eliminating Internal Stresses
Mechanical processing creates residual internal stresses that can compromise the material's stability.
High-temperature treatment allows the material to relax. This eliminates residual stresses and heals micro-cracks, ensuring the final spheres are structurally sound.
Enhancing Thermal Performance
Promoting Recrystallization
The primary goal of reaching temperatures as high as 2200°C is to force recrystallization.
At these extreme temperatures, the atomic structure realigns into a more perfect, ordered state. High crystal quality is the fundamental requirement for efficient phonon transport (heat transfer).
Reducing Interfacial Thermal Resistance
Heat struggles to move across boundaries where defects or gaps exist.
By densifying the material and perfecting the crystal structure, sintering significantly reduces interfacial thermal resistance. This allows heat to flow unimpeded, directly enabling high thermal conductivity metrics.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
Prevention of Oxidation
While the primary reference focuses on heat, the "vacuum" aspect is equally critical for material purity.
Operating in a vacuum (often around $10^{-3}$ Pa in similar industrial applications) creates an oxygen-free environment. This prevents the Boron Nitride from oxidizing at high temperatures, which would degrade its properties and introduce impurities.
Controlled Densification
The furnace provides a stable environment for particle diffusion.
This drives the material to eliminate internal pores and increase relative density. A denser material translates directly to better mechanical strength and superior thermal properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Extreme Energy Requirements
Achieving and maintaining 2200°C requires significant energy input and specialized equipment.
This makes the process costly compared to lower-temperature sintering used for other ceramics (e.g., alumina often sinters at 1700°C). It is a high-cost step justified only by the need for premium thermal conductivity.
Process Sensitivity
The benefits of recrystallization are highly dependent on precise temperature control.
If the temperature profile is inconsistent, the material may retain metastable phases or fail to fully recrystallize. This results in products that look correct but fail to meet the targeted thermal conductivity of 37.2 W/(m·K).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your Boron Nitride post-treatment, consider these priorities:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Thermal Conductivity: You must ensure the furnace is capable of reaching and holding 2200°C to guarantee full recrystallization and defect elimination.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Prioritize the vacuum integrity of the furnace to prevent oxidation and surface contamination during the heating cycle.
Summary: The high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace is the defining tool that converts mechanically processed Boron Nitride into a high-grade thermal interface material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Boron Nitride | Benefit to Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| 2200°C Temperature | Drives full recrystallization | Maximizes thermal conductivity (37.2 W/m·K) |
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents high-temp oxidation | Ensures high purity and structural integrity |
| Defect Healing | Repairs ball milling damage | Reduces interfacial thermal resistance |
| Densification | Eliminates internal pores | Enhances mechanical strength and heat flow |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Achieving the extreme temperatures and vacuum precision required for Boron Nitride recrystallization demands world-class equipment. KINTEK provides industry-leading Vacuum, Tube, and High-Temp Muffle furnaces specifically engineered for advanced ceramic sintering.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique thermal profiles. Whether you need to eliminate crystal defects or achieve maximum densification, our expert team is ready to assist.
Ready to elevate your thermal interface materials?
Contact KINTEK Today for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Hongbo Jiang, Ying Chen. Unleashing the Potential of Boron Nitride Spheres for High‐Performance Thermal Management. DOI: 10.1002/cnma.202300601
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- Why is graphite commonly used as a heating element in vacuum furnaces? Unlock High-Temp Stability & Efficiency
- What are the key technical parameters of powder metallurgy vacuum sintering furnaces? Optimize Your Sintering Process
- What is the working principle of a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Achieve Clean, High-Integrity Metal Parts
- What is the specific function of the high vacuum in SiC/Cu-Al2O3 sintering? Achieve 1.5x10^-2 Pa for Peak Density
- How are vacuum furnaces environmentally friendly? Achieve Clean, Efficient Heat Treatment
- What factors are critical for the proper functioning of a vacuum furnace? Maximize Material Purity and Process Control
- What are the different types of vacuum furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Process



















