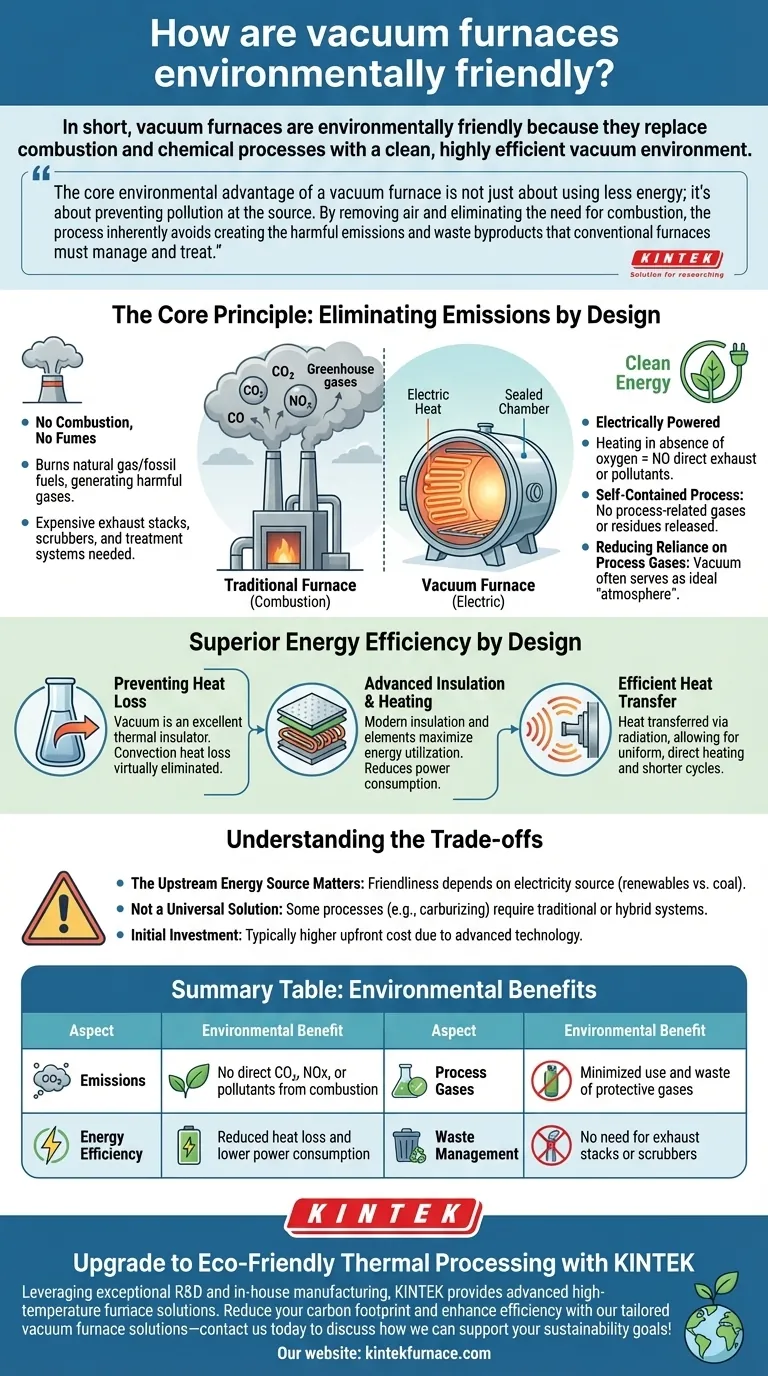
In short, vacuum furnaces are environmentally friendly because they replace combustion and chemical processes with a clean, highly efficient vacuum environment. By using electricity to heat parts inside a sealed, airless chamber, they fundamentally eliminate the direct production of harmful emissions like CO2, waste gases, and other pollutants associated with traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
The core environmental advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just about using less energy; it's about preventing pollution at the source. By removing air and eliminating the need for combustion, the process inherently avoids creating the harmful emissions and waste byproducts that conventional furnaces must manage and treat.
The Core Principle: Eliminating Emissions by Design
The most significant environmental benefit of a vacuum furnace comes from its fundamental operating principle. Unlike a traditional furnace that burns fuel, a vacuum furnace creates heat electrically within a controlled, sealed environment.
No Combustion, No Fumes
Traditional furnaces burn natural gas or other fossil fuels, which generates CO, CO₂, NOx, and other greenhouse gases that are released into the atmosphere.
Vacuum furnaces are electrically powered. Heating occurs in the absence of oxygen, so there is no combustion and, therefore, no direct creation of exhaust fumes or pollutants.
A Self-Contained Process
The sealed vacuum chamber ensures that the entire thermal process is self-contained. This prevents the release of any process-related gases or residues into the workplace or the external environment.
This design eliminates the need for costly and complex exhaust stacks, scrubbers, or wastewater treatment systems that are often required for atmosphere furnaces.
Reducing Reliance on Process Gases
For many applications like annealing and hardening, the vacuum itself serves as the ideal "atmosphere." It prevents oxidation and other surface reactions without the need for flammable or protective gases.
This reduces the environmental footprint associated with producing, transporting, and venting process gases like nitrogen, argon, or endothermic gas.
Superior Energy Efficiency by Design
Beyond eliminating direct emissions, vacuum furnaces are engineered for exceptional energy efficiency, which further lowers their overall carbon footprint.
Preventing Heat Loss
A vacuum is an excellent thermal insulator. By removing most of the air molecules from the chamber, heat loss through convection is virtually eliminated.
This means that more of the energy consumed is directed at the workload itself, rather than being lost to the surrounding environment.
Advanced Insulation and Heating
Modern vacuum furnaces utilize multi-layered, high-performance insulation materials and advanced heating elements that maximize energy utilization.
This efficient design significantly reduces overall power consumption compared to older or less-insulated furnace types, lowering both operating costs and the indirect environmental impact from electricity generation.
Efficient Heat Transfer
In a vacuum, heat is transferred primarily through radiation. This allows for uniform, direct, and highly effective heating of the parts without interference from gas molecules, contributing to shorter cycle times and less wasted energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, it is important to view vacuum furnaces within the complete operational context. No technology is without its considerations.
The Upstream Energy Source Matters
A vacuum furnace's environmental friendliness is tied to its electricity source. While the furnace itself produces no direct emissions, its carbon footprint depends on how the electricity is generated. A furnace powered by a coal-fired grid will have a larger indirect footprint than one powered by renewables.
Not a Universal Solution
Some metallurgical processes require specific chemical interactions with active gas atmospheres (e.g., carburizing). While hybrid vacuum furnaces exist, a traditional atmosphere furnace may be more suitable for these specific, chemistry-dependent applications.
Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. Their advanced technology, controls, and vacuum pumping systems typically result in a higher upfront cost compared to conventional atmosphere furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology requires aligning its capabilities with your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is reducing direct emissions and improving workplace safety: A vacuum furnace is the definitive solution, as its sealed, combustion-free process eliminates pollutants at the source.
- If your primary focus is lowering long-term operational costs: The superior energy efficiency and reduced need for consumables often offset the higher initial investment through lower utility bills.
- If your process demands specific gas-based surface chemistry: A traditional atmosphere furnace or a specialized hybrid system designed for that reaction may be a more practical fit.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic move towards cleaner, more efficient, and more precise thermal processing.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Emissions | No direct CO2, NOx, or pollutants from combustion |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduced heat loss and lower power consumption |
| Process Gases | Minimized use and waste of protective gases |
| Waste Management | No need for exhaust stacks or scrubbers |
Upgrade to Eco-Friendly Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Reduce your carbon footprint and enhance efficiency with our tailored vacuum furnace solutions—contact us today to discuss how we can support your sustainability goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals



















