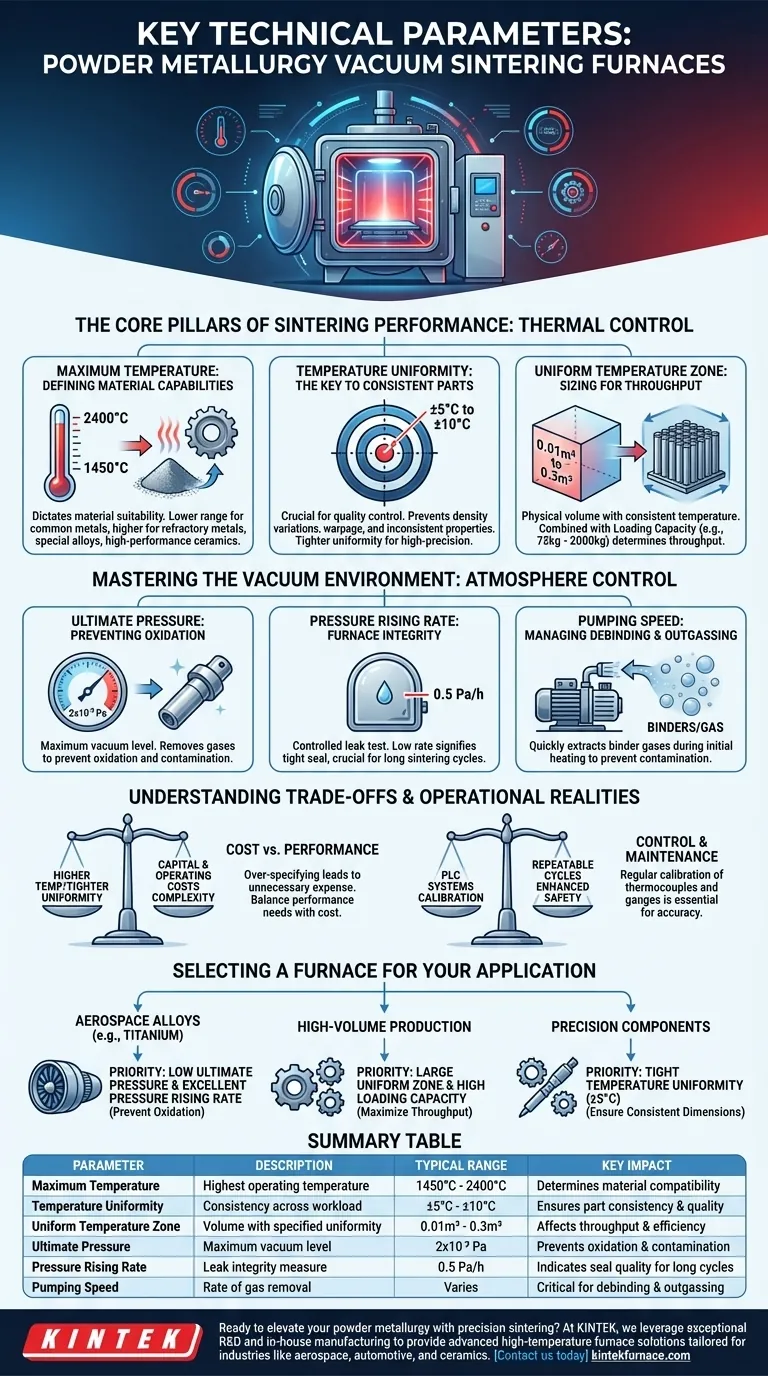
To properly evaluate a powder metallurgy vacuum sintering furnace, you must look beyond the marketing and focus on a core set of technical parameters. The most critical specifications are the maximum operating temperature, the ultimate pressure (vacuum level), the temperature uniformity across the working zone, and the pressure rising rate, which indicates the furnace's seal integrity. These figures directly dictate the types of materials you can process and the quality of the final product.
The technical specifications of a vacuum furnace are not just a list of capabilities; they are the levers that control the final metallurgical properties of your components. Understanding how temperature, vacuum, and uniformity interact is the key to achieving consistent, high-density, and high-performance parts.
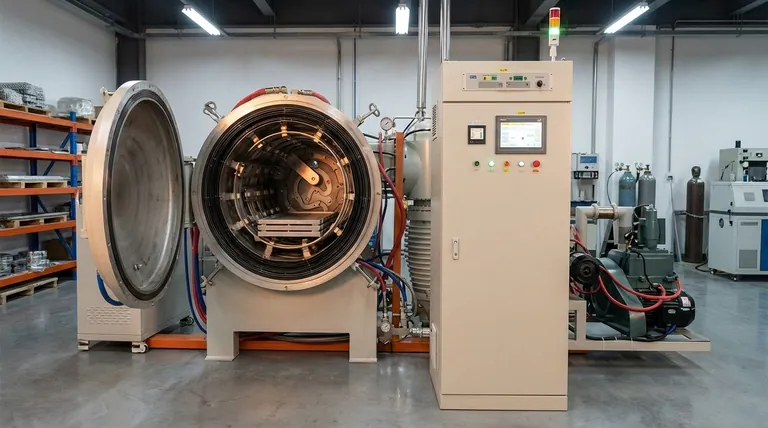

The Core Pillars of Sintering Performance
The primary goal of sintering is to create a dense, strong component from powder. The furnace's thermal performance parameters are the most direct controls you have over this transformation.
Maximum Temperature: Defining Material Capabilities
The maximum achievable temperature dictates which materials you can successfully sinter. A furnace's temperature range, often between 1450°C and 2400°C, determines its suitability for different alloy systems.
Lower-range furnaces are sufficient for many common metals, while those reaching 2000°C or higher are necessary for refractory metals, special alloys, and high-performance ceramics.
Temperature Uniformity: The Key to Consistent Parts
This parameter, typically specified as ±5°C or ±10°C, measures the temperature consistency across the entire workload. It is arguably the most critical factor for quality control.
Poor uniformity results in parts sintering at different rates, leading to variations in density, warpage, and inconsistent mechanical properties across a single batch. A tighter uniformity of ±5°C is essential for high-precision or aerospace applications.
Uniform Temperature Zone: Sizing for Throughput
This defines the physical volume within the furnace where the specified temperature uniformity is maintained. It is often measured in cubic meters (e.g., 0.01m³ to 0.3m³).
Combined with the loading capacity (e.g., 75 kg to 2000 kg), this parameter determines the furnace's throughput. A larger uniform zone allows you to process more parts per cycle, directly impacting production efficiency.
Mastering the Vacuum Environment
The "vacuum" in vacuum sintering is not an absence of everything; it's a highly controlled atmosphere designed to prevent contamination and unwanted chemical reactions.
Ultimate Pressure: Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Ultimate pressure, or the maximum vacuum level, is a measure of how effectively air and other gases are removed from the chamber. A typical high-vacuum specification is 2x10⁻³ Pa.
This extremely low-pressure environment is critical for preventing the oxidation of reactive materials like titanium and ensuring the purity of the final alloy.
Pressure Rising Rate: A Measure of Furnace Integrity
This specification, often around 0.5 Pa/h, is essentially a controlled leak test. It measures how quickly pressure increases in the sealed, evacuated chamber over one hour.
A low pressure rising rate signifies a tight seal and a high-integrity chamber. This is crucial for long sintering cycles, as it ensures the controlled atmosphere remains pure from start to finish.
Pumping Speed: Managing Debinding and Outgassing
Pumping speed is about more than just how fast the furnace reaches its ultimate pressure. It is a critical factor during the debinding phase.
During this initial heating stage, binders mixed with the metal powder evaporate, creating a large volume of gas. A robust vacuum system with a high pumping speed is required to extract these binder substances quickly and reliably, preventing them from contaminating the parts or the furnace interior.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Realities
Selecting the right furnace involves balancing performance specifications against cost and operational complexity.
Higher Temperature vs. Cost and Complexity
A furnace capable of 2400°C requires more advanced (and expensive) heating elements, insulation, and power systems than a furnace rated for 1600°C. Over-specifying the temperature range leads to unnecessary capital expenditure and higher operating costs.
Tighter Uniformity vs. Furnace Design
Achieving a tight temperature uniformity of ±5°C demands a more sophisticated heating element configuration and a more advanced PLC control system. While this increases the initial cost, it reduces part rejection rates and is non-negotiable for applications where consistency is paramount.
The Importance of Control and Maintenance
Modern furnaces rely on PLC control systems for automated, repeatable cycles and enhanced safety. However, the listed specifications are only meaningful if the equipment is properly maintained.
Regular calibration of thermocouples and vacuum gauges is essential to ensure the furnace is actually delivering the performance shown on the spec sheet.
Selecting a Furnace for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by the specific demands of your materials and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-performance aerospace alloys (e.g., titanium): Prioritize a low ultimate pressure (high vacuum) and an excellent pressure rising rate to eliminate any risk of oxidation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard parts: Emphasize a large uniform temperature zone and a high loading capacity to maximize throughput and reduce cost-per-part.
- If your primary focus is precision components with tight tolerances: Your most critical parameter is temperature uniformity (demand ±5°C) to ensure consistent shrinkage and final part dimensions.
By understanding how each parameter influences the final material properties, you can select a furnace that serves not just as a tool, but as a guarantee of quality.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Highest operating temperature | 1450°C to 2400°C | Determines material compatibility |
| Temperature Uniformity | Consistency across workload | ±5°C to ±10°C | Ensures part consistency and quality |
| Uniform Temperature Zone | Volume with specified uniformity | 0.01m³ to 0.3m³ | Affects throughput and efficiency |
| Ultimate Pressure | Maximum vacuum level | 2x10⁻³ Pa | Prevents oxidation and contamination |
| Pressure Rising Rate | Leak integrity measure | 0.5 Pa/h | Indicates seal quality for long cycles |
| Pumping Speed | Rate of gas removal | Varies | Critical for debinding and outgassing |
Ready to elevate your powder metallurgy with precision sintering? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, automotive, and ceramics. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your part quality and production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















