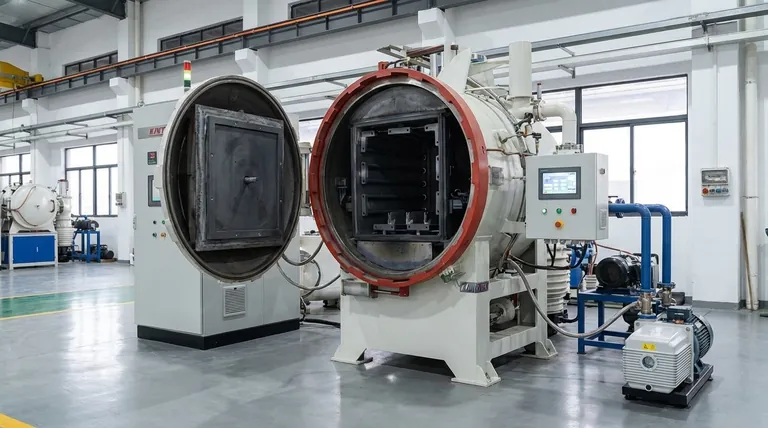
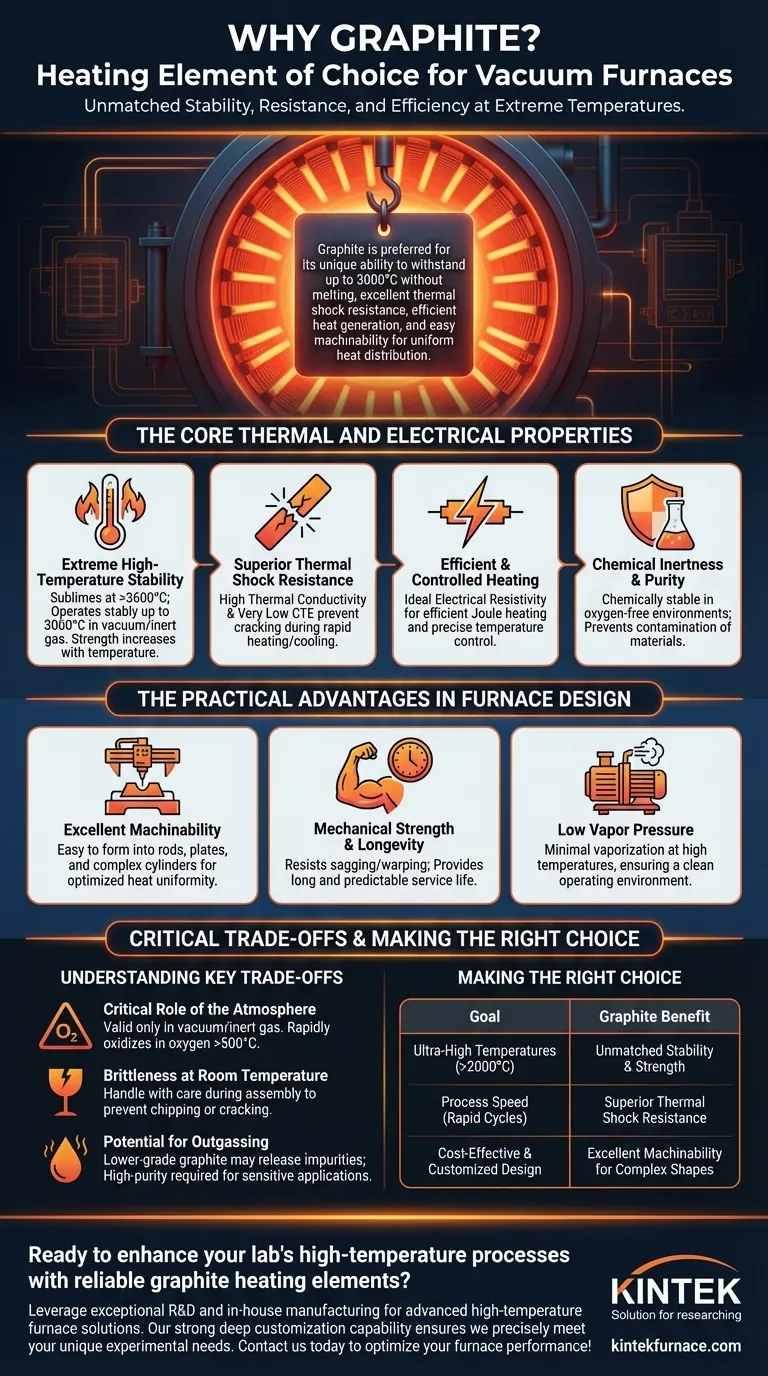
In short, graphite is the preferred material for vacuum furnace heating elements due to its unique ability to withstand extreme temperatures up to 3000°C without melting, combined with its excellent resistance to the thermal shock of rapid heating and cooling. Its electrical properties allow it to efficiently generate heat, and it can be easily machined into the complex shapes required for effective and uniform heat distribution.
Graphite's value lies in a rare combination of properties: it has an extremely high sublimation point, gets stronger as it gets hotter, and resists fracturing during rapid temperature changes, making it one of the few materials that can reliably perform in the harsh environment of a high-temperature vacuum furnace.

The Core Thermal and Electrical Properties
To understand why graphite is so dominant in this application, we must look at its fundamental material properties. It isn't just one attribute but the combination of several that makes it uniquely suitable.
Extreme High-Temperature Stability
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; instead, it sublimes (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at over 3600°C. This gives it an exceptionally high operational ceiling, allowing it to function stably in a vacuum or inert gas at temperatures up to 3000°C.
Unlike metals that soften and weaken when heated, graphite's mechanical strength actually increases with temperature, providing structural integrity when it's needed most.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnace elements undergo immense stress from rapid heating and cooling cycles. Graphite excels here due to two key properties: a high thermal conductivity and a very low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE).
High thermal conductivity ensures that heat spreads evenly throughout the element, preventing hot spots that could cause stress. The low CTE means the material expands and contracts very little when its temperature changes, drastically reducing internal stresses and preventing cracking.
Efficient and Controlled Heating
Graphite has an electrical resistivity that is ideal for Joule heating—the process of generating heat by passing an electrical current through a resistive material. It is conductive enough to carry the required current but resistive enough to dissipate that energy as heat efficiently and controllably.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
In the oxygen-free environment of a vacuum or inert gas (like argon), graphite is chemically stable and non-reactive. This is critical as it prevents the heating elements from contaminating the materials being heat-treated, ensuring the purity of the final product.
The Practical Advantages in Furnace Design
Beyond its core physics, graphite offers significant practical benefits that simplify the design, manufacturing, and operation of vacuum furnaces.
Excellent Machinability
Despite its strength at high temperatures, graphite is a relatively soft material that is easy to machine. It can be cut, milled, and drilled into complex shapes like rods, curved plates, and cylinders. This allows for the creation of optimized heating elements that provide excellent temperature uniformity across the furnace's hot zone.
Mechanical Strength and Longevity
The inherent strength and stability of graphite elements mean they resist sagging or warping over time, even after thousands of hours of operation. This structural integrity, combined with its resistance to thermal shock, results in a long and predictable service life.
Low Vapor Pressure
At high temperatures in a vacuum, materials can begin to vaporize, which can contaminate the furnace and the product. Graphite has a very low vapor pressure, meaning it remains a stable solid with minimal vaporization, contributing to a clean operating environment.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While graphite is an exceptional material, its use comes with critical constraints that every operator must understand. Its advantages are entirely dependent on the operating environment.
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere
Graphite's high-temperature capability is only valid in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere. When exposed to oxygen at temperatures above approximately 500°C, graphite will rapidly oxidize and burn away, leading to catastrophic failure of the element. This is the single most important limitation of using graphite.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
While strong when hot, graphite can be brittle and fragile at room temperature. It must be handled with care during furnace assembly, loading, and maintenance to prevent chipping or cracking, which can create points of failure when heated.
Potential for Outgassing
The purity of the graphite matters. Lower-grade graphite can contain moisture or other impurities that are released as gas ("outgassing") when first heated in a vacuum. This can compromise the vacuum level and potentially contaminate sensitive workloads, necessitating the use of higher-purity (and more expensive) graphite for demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting heating element material depends on your furnace's specific operational requirements.
- If your primary focus is reaching ultra-high temperatures (above 2000°C): Graphite is the default and often only practical choice due to its unmatched stability and strength at extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is process speed with rapid heating and cooling cycles: Graphite's superior thermal shock resistance makes it far more reliable than metallic elements like molybdenum or tungsten, which can become brittle.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective and customized furnace design: Graphite's excellent machinability allows for the creation of complex, high-performance heating elements at a reasonable cost.
Ultimately, graphite's unique synthesis of thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties makes it the benchmark material for reliable, high-performance heating in vacuum furnaces.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit in Vacuum Furnaces |
|---|---|
| High sublimation point (>3600°C) | Enables stable operation up to 3000°C without melting |
| Increased strength at high temperatures | Maintains structural integrity under extreme heat |
| Low thermal expansion & high conductivity | Resists thermal shock for rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| Ideal electrical resistivity | Facilitates efficient and controlled Joule heating |
| Chemical inertness in vacuum | Prevents contamination of heat-treated materials |
| Excellent machinability | Allows for custom shapes ensuring uniform heat distribution |
Ready to enhance your lab's high-temperature processes with reliable graphite heating elements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your furnace performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness



















