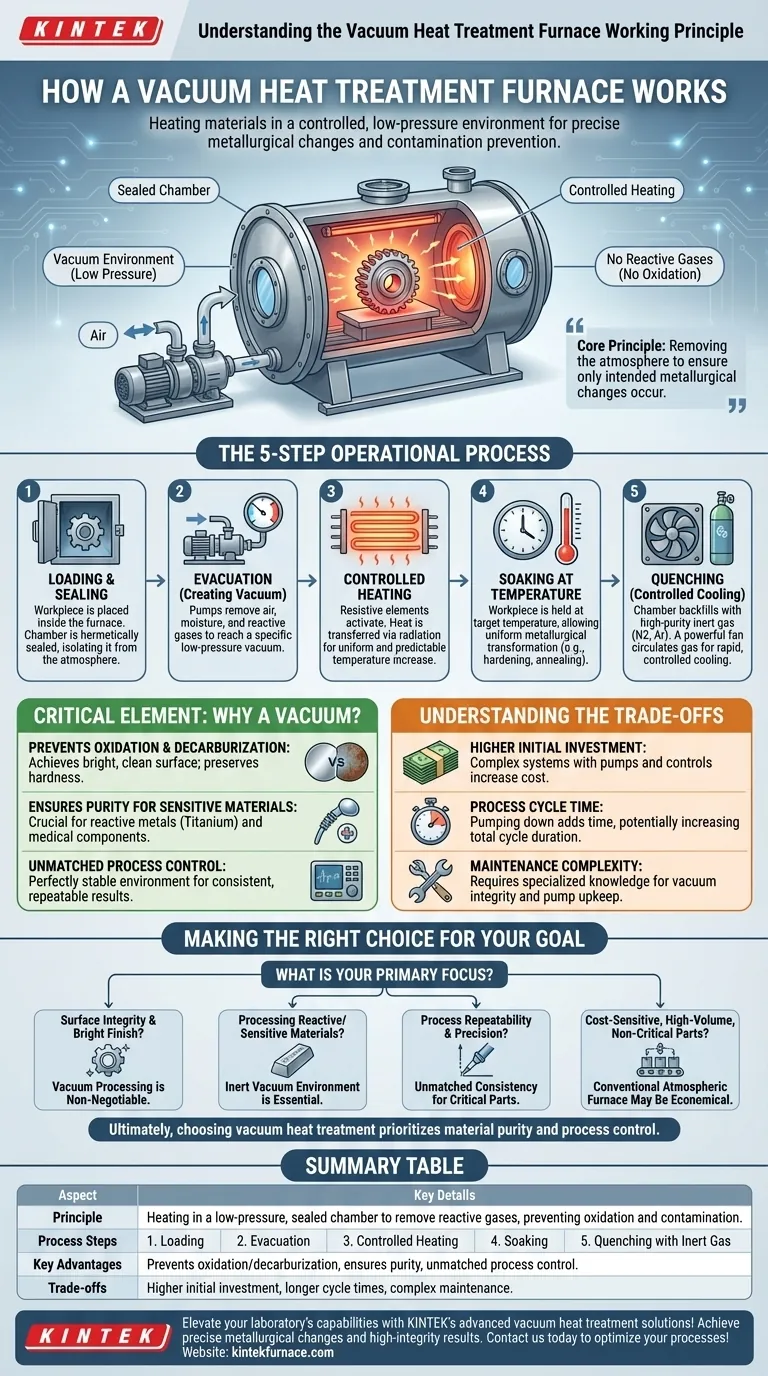
At its core, a vacuum heat treatment furnace operates by heating materials within a controlled, low-pressure environment. By using pumps to remove air and other reactive gases from a sealed chamber, the furnace prevents oxidation and contamination during the heating and cooling cycles. This allows for extremely precise metallurgical changes, resulting in clean, high-integrity parts without the surface damage common in conventional atmospheric heating.
The fundamental principle isn't just about reaching a target temperature; it's about removing the atmosphere. By evacuating reactive gases, a vacuum furnace ensures that the only changes to the material are the ones you intentionally introduce through controlled heating and cooling cycles.
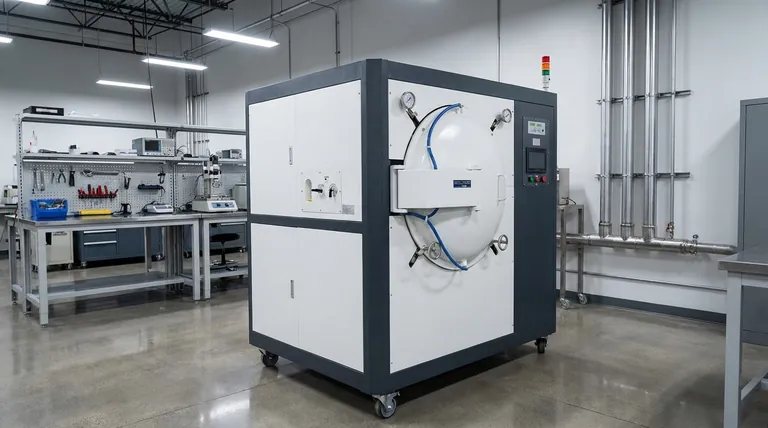

The Step-by-Step Working Process
Understanding the operational sequence reveals how a vacuum furnace achieves its superior results. The entire process, from heating to quenching, occurs within a single, sealed vessel.
Step 1: Loading and Sealing
The material to be treated, known as the workpiece, is placed inside the furnace chamber. The chamber is then hermetically sealed to create a closed system, isolating it from the outside atmosphere.
Step 2: Evacuation (Creating the Vacuum)
A system of pumps, typically a combination of mechanical and diffusion pumps, begins to evacuate the chamber. Air, moisture, and any other gases are removed until a specific, low-pressure level (the vacuum) is reached.
Step 3: Controlled Heating
Once the vacuum is established, resistive heating elements made of materials like graphite or molybdenum are activated. Heat is transferred to the workpiece primarily through radiation, which provides highly uniform and predictable temperature increases without the unevenness of air convection.
Step 4: Soaking at Temperature
The workpiece is held at the precise target temperature for a specified duration. This soaking period allows the desired metallurgical transformation, such as hardening, annealing, or tempering, to occur completely and evenly throughout the material.
Step 5: Quenching (Controlled Cooling)
After soaking, the material must be cooled at a specific rate. The furnace backfills the chamber with a high-purity, inert gas like nitrogen or argon. A powerful fan circulates this gas to cool the workpiece rapidly and controllably, a process known as gas quenching.
Why a Vacuum is the Critical Element
The use of a vacuum is what distinguishes this technology. It is not merely an incidental feature but the primary enabler of its key advantages.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
By removing oxygen, the furnace completely prevents oxidation, the process that creates scale and discoloration on a material's surface. This results in a bright, clean finish that often requires no secondary cleaning. It also prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of steel—which preserves hardness and wear resistance.
Ensuring Purity for Sensitive Materials
The clean, inert environment is crucial for processing reactive metals like titanium and superalloys used in aerospace. It is also essential for medical implants and semiconductor components, where even microscopic surface contamination can lead to component failure.
Achieving Unmatched Process Control
A vacuum provides a perfectly stable and predictable environment. Heat transfer is consistent, and process variables can be tightly controlled and repeated with digital accuracy. This all-in-one system eliminates the variability of moving parts between separate heating and quenching stations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnace technology is not a universal solution. Its benefits must be weighed against practical considerations.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces are complex systems involving sealed chambers, high-performance pumps, and sophisticated controls. This makes their initial acquisition and installation costs significantly higher than conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Process Cycle Time
The need to pump down the chamber to a deep vacuum adds time to the beginning of every cycle. While heating and cooling can be rapid, the total cycle time may be longer than some conventional processes, impacting overall throughput.
Maintenance Complexity
High-vacuum systems require specialized knowledge. Maintaining vacuum integrity, servicing pumps, and ensuring the cleanliness of the chamber are more demanding tasks than the upkeep of simpler atmospheric equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on the requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and a bright finish: Vacuum processing is non-negotiable, as it eliminates the oxidation that causes scaling and discoloration.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or sensitive materials: The inert vacuum environment is essential for materials like titanium or specific tool steels that would be damaged by air at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and precision: The highly controlled nature of a vacuum furnace offers unmatched consistency for critical components in the aerospace, medical, or high-end tooling industries.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, high-volume production of non-critical parts: A conventional atmospheric furnace may be a more economical solution, provided some surface oxidation is acceptable.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum heat treatment is a decision to prioritize material purity and process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Principle | Heating in a low-pressure, sealed chamber to remove reactive gases, preventing oxidation and contamination. |
| Process Steps | 1. Loading and Sealing 2. Evacuation 3. Controlled Heating 4. Soaking at Temperature 5. Quenching with Inert Gas |
| Key Advantages | Prevents oxidation and decarburization, ensures purity for sensitive materials, provides unmatched process control. |
| Trade-offs | Higher initial investment, longer process cycle times, more complex maintenance. |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced vacuum heat treatment solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization to meet unique experimental requirements. Achieve precise metallurgical changes, prevent contamination, and ensure high-integrity results for materials like titanium and superalloys. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your heat treatment processes and deliver superior outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















