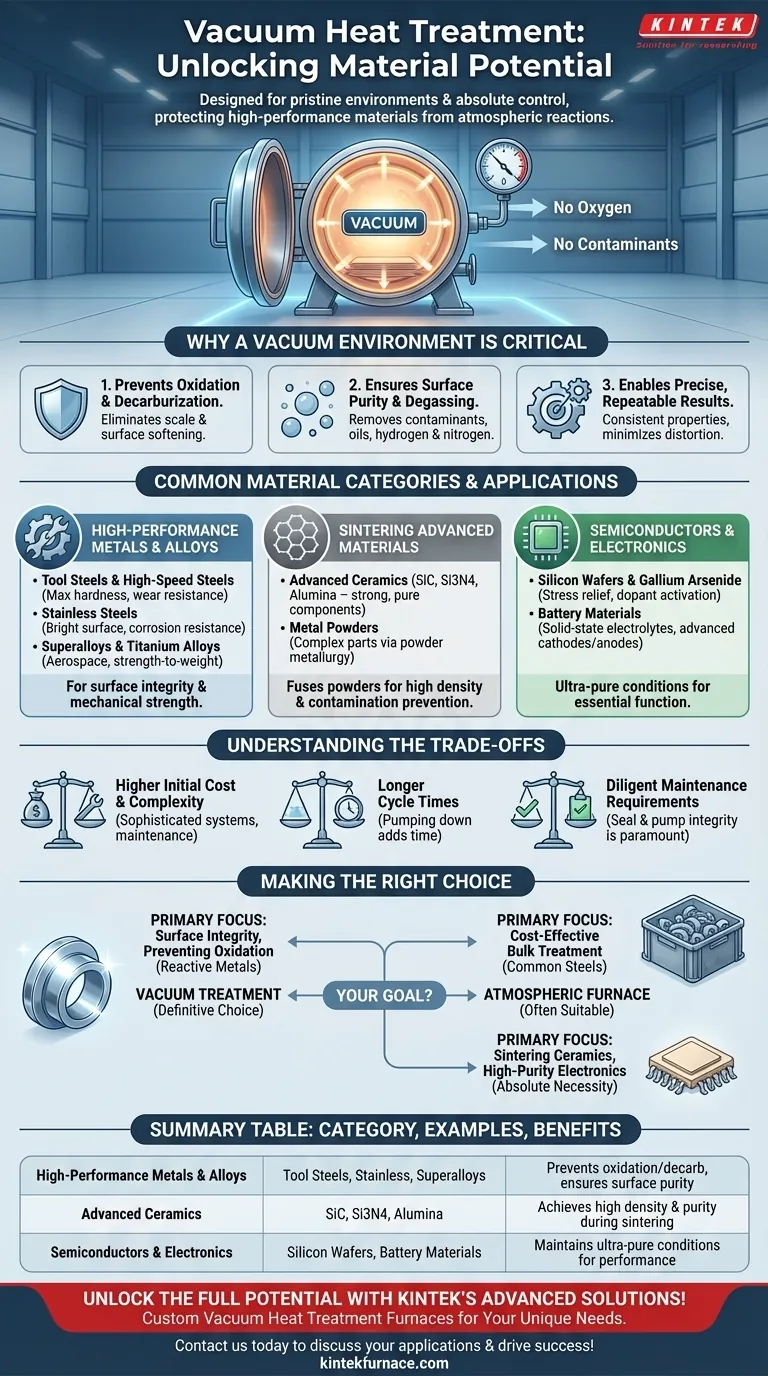
At its core, a vacuum heat treatment furnace is designed for materials that demand a pristine, controlled environment to achieve their highest potential. The process is used for a wide range of high-performance metals, alloys, advanced ceramics, and electronic components where any reaction with atmospheric gases during heating would be detrimental to the final product's integrity and performance.
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need for absolute environmental control. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, the process prevents surface defects like oxidation and decarburization, ensuring materials achieve their precise, intended metallurgical and physical properties.

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
The primary function of a vacuum furnace is not just to heat a material, but to protect it while it is hot and metallurgically reactive. This controlled atmosphere provides several distinct advantages over traditional furnaces.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
At high temperatures, most metals readily react with oxygen in the air, forming a layer of scale or oxide on the surface. This can ruin surface finish and alter dimensions. Similarly, the carbon content in steels can react with the atmosphere, a process called decarburization, which softens the surface and reduces fatigue life. A vacuum eliminates these destructive reactions.
Ensuring Surface Purity and Degassing
The vacuum environment actively purifies the material's surface. It can pull contaminants, oils, and unwanted dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen out of the metal, a process known as degassing. This is especially critical for preventing hydrogen embrittlement in certain alloys.
Enabling Precise, Repeatable Results
By removing the variable of atmospheric interaction, a vacuum furnace allows for exceptionally precise control over the heating and cooling cycle. This ensures that every part in a batch, and every batch over time, achieves the exact same specified properties, minimizing deformation and thermal stress.
Common Material Categories and Applications
The unique benefits of vacuum treatment make it the ideal choice for a specific set of demanding material classes.
High-Performance Metals and Alloys
This is the most common category. The process is essential for materials where surface integrity and mechanical strength are paramount.
- Tool Steels & High-Speed Steels: Achieve maximum hardness and wear resistance without a soft, decarburized surface layer.
- Stainless Steels: Maintain a bright, clean surface and preserve their corrosion-resistant properties.
- Superalloys & Titanium Alloys: Used heavily in the aerospace industry, these materials are highly reactive at temperature and require a vacuum to prevent embrittlement and preserve their strength-to-weight ratio.
Sintering of Advanced Materials
Sintering is a process that fuses powders into a solid mass using heat. A vacuum is critical to prevent contamination and achieve high density.
- Advanced Ceramics: Materials like silicon carbide, silicon nitride, and alumina are sintered in a vacuum to produce strong, pure components.
- Metal Powders: Used in powder metallurgy to create complex parts from titanium, superalloys, and other metals.
Semiconductors and Electronics
The electronics industry relies on ultra-pure materials, and any contamination can destroy a component's function.
- Silicon Wafers & Gallium Arsenide: Vacuum annealing is used to relieve stress and activate dopants without introducing impurities.
- Battery Materials: Emerging materials for solid-state electrolytes and advanced cathodes/anodes are processed in a vacuum to ensure purity and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not the solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are sophisticated machines with complex pumping systems, seals, and controls. This makes them significantly more expensive to purchase and install than conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping the chamber down to the required vacuum level adds time to the beginning of every cycle. For high-volume, low-margin parts, this can be a significant drawback compared to the speed of a continuous atmospheric furnace.
Diligent Maintenance Requirements
The integrity of the vacuum system is paramount. Seals, pumps, and the chamber itself require regular inspection and maintenance to prevent leaks and ensure consistent performance. This adds to the operational overhead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between vacuum and atmospheric treatment depends entirely on your material's sensitivity and the required quality of the final part.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and preventing oxidation: Vacuum treatment is the definitive choice, especially for reactive metals like titanium, tool steels, and superalloys.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bulk treatment of common steels: A traditional atmospheric furnace is often more suitable, as the protective benefits of a vacuum may not justify the added cost and cycle time.
- If your primary focus is sintering advanced ceramics or creating high-purity electronic components: A vacuum furnace is not just an option but an absolute necessity to prevent contamination.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize material integrity and peak performance above all other considerations.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Metals & Alloys | Tool Steels, Stainless Steels, Superalloys, Titanium Alloys | Prevents oxidation and decarburization, ensures surface purity and strength |
| Advanced Ceramics | Silicon Carbide, Silicon Nitride, Alumina | Achieves high density and purity during sintering |
| Semiconductors & Electronics | Silicon Wafers, Gallium Arsenide, Battery Materials | Maintains ultra-pure conditions for stress relief and performance |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced vacuum heat treatment solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing material integrity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















