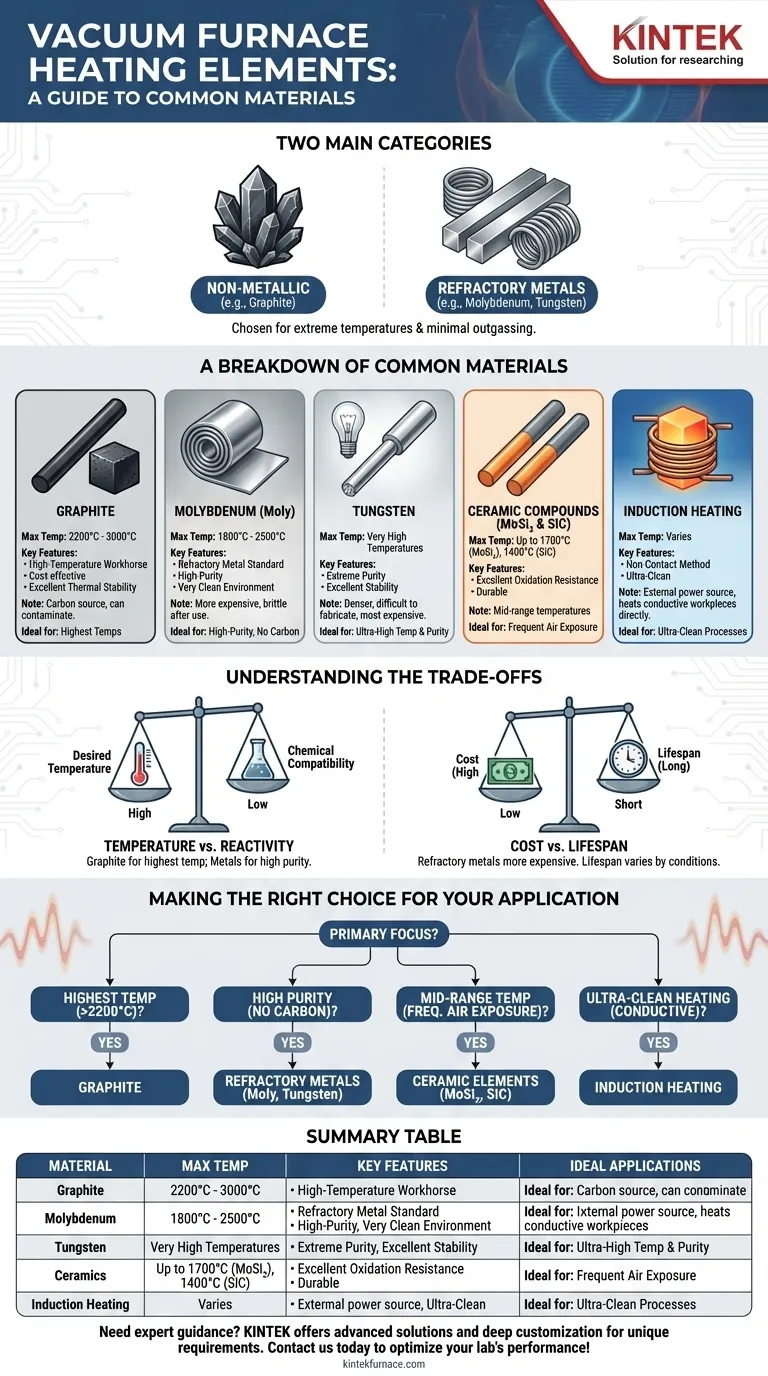
The most common heating elements in vacuum furnaces are chosen based on their ability to withstand extreme temperatures with minimal outgassing. These materials fall into two main categories: non-metallic elements like graphite, and refractory metals such as molybdenum and tungsten. Other specialized options include ceramic compounds like silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂), as well as induction heating systems.
The choice of a heating element is a critical design decision that balances maximum operating temperature against chemical compatibility with the workload. Graphite is the go-to for the highest temperatures, while refractory metals are essential for high-purity processes where carbon contamination is unacceptable.

A Breakdown of Common Heating Element Materials
The material of the heating element directly defines the furnace's capabilities, including its maximum temperature, the purity of the vacuum environment, and its suitability for different applications.
Graphite: The High-Temperature Workhorse
Graphite is the most common material for very high-temperature vacuum furnaces, capable of operating reliably up to 2200°C and even reaching 3000°C in some designs.
Its low cost, ease of machining into complex shapes, and excellent thermal stability make it a cost-effective choice. However, it is a source of carbon and can react with or contaminate certain materials.
Molybdenum (Moly): The Refractory Metal Standard
Molybdenum is a refractory metal used for high-purity applications where carbon from graphite elements would be a problem. It provides a very clean heating environment.
Moly elements are effective for temperatures up to approximately 1800°C, and in some specialized hot-zone designs, can reach as high as 2500°C. They are more expensive than graphite and become brittle after high-temperature use.
Tungsten: For Extreme Purity and Temperature
Tungsten is another refractory metal, often chosen when process temperatures exceed the normal operating limits of molybdenum. It offers excellent stability and purity at very high temperatures.
Because it is denser, more difficult to fabricate, and more expensive than molybdenum, tungsten is typically reserved for the most demanding high-purity and ultra-high-temperature applications.
Ceramic Compounds (MoSi₂ & SiC)
Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are ceramic-based heating elements primarily used for furnaces that operate at mid-range temperatures, typically up to 1700°C and 1400°C respectively.
Their primary advantage is excellent resistance to oxidation, making them extremely durable in furnaces that are frequently cycled or exposed to air.
Induction Heating: A Fundamentally Different Approach
Induction is not a heating element material but a method. An external copper coil, cooled by water, generates a powerful magnetic field that directly heats a conductive workpiece or a graphite susceptor inside the chamber.
Because the power source is outside the hot zone, this method is ideal for ultra-clean processes where any potential contamination from a resistive element must be avoided.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right heating element involves more than just looking at a temperature chart. You must consider the entire system and potential interactions within the vacuum environment.
Temperature vs. Reactivity
The most critical trade-off is between the desired temperature and chemical compatibility. Graphite can achieve the highest temperatures but will introduce carbon into the environment, which is unsuitable for processing certain alloys or ceramics. In these cases, a metallic element like molybdenum is required, even if it has a slightly lower temperature ceiling.
Cost vs. Lifespan
Graphite is generally the least expensive element material. Refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten are significantly more costly. Element lifespan is heavily influenced by operating temperature, the frequency of thermal cycles, and exposure to contaminants in the vacuum chamber.
System Integration and Power
Heating elements must be connected to a power supply, typically a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) or a Variable Reactance Transformer (VRT). These systems use multiple control zones to ensure temperature uniformity across the hot zone.
Mounting and Insulation
Elements are mounted using robust ceramic or quartz insulators. It is critical that these insulators remain clean, as an accumulation of carbon dust or condensed metal vapor can create a conductive path and cause a short circuit. Graphite elements are often connected to each other using large, bolted graphite bridges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific goals of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (>2200°C): Graphite is almost always the most cost-effective and capable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing without carbon contamination: Refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten are the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is mid-range temperatures with frequent air exposure: Ceramic elements like MoSi₂ offer a durable, oxidation-resistant solution.
- If your primary focus is ultra-clean heating of a conductive workpiece: An induction heating system provides a non-contact method that eliminates element contamination.
By matching the element's properties to your specific process temperature, atmosphere, and purity needs, you ensure reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Up to 3000°C | Cost-effective, easy to machine, carbon source | High-temperature processes (>2200°C) where carbon contamination is acceptable |
| Molybdenum | Up to 2500°C | High purity, brittle after use | High-purity processes avoiding carbon contamination |
| Tungsten | Very high temperatures | Extreme purity, expensive, hard to fabricate | Ultra-high-temperature and high-purity applications |
| Ceramics (MoSi₂, SiC) | Up to 1700°C | Oxidation-resistant, durable | Mid-range temperatures with frequent air exposure |
| Induction Heating | Varies | Non-contact, ultra-clean | Ultra-clean heating of conductive workpieces |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right heating element for your vacuum furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for high-temperature and high-purity processes. Contact us today to optimize your lab's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















