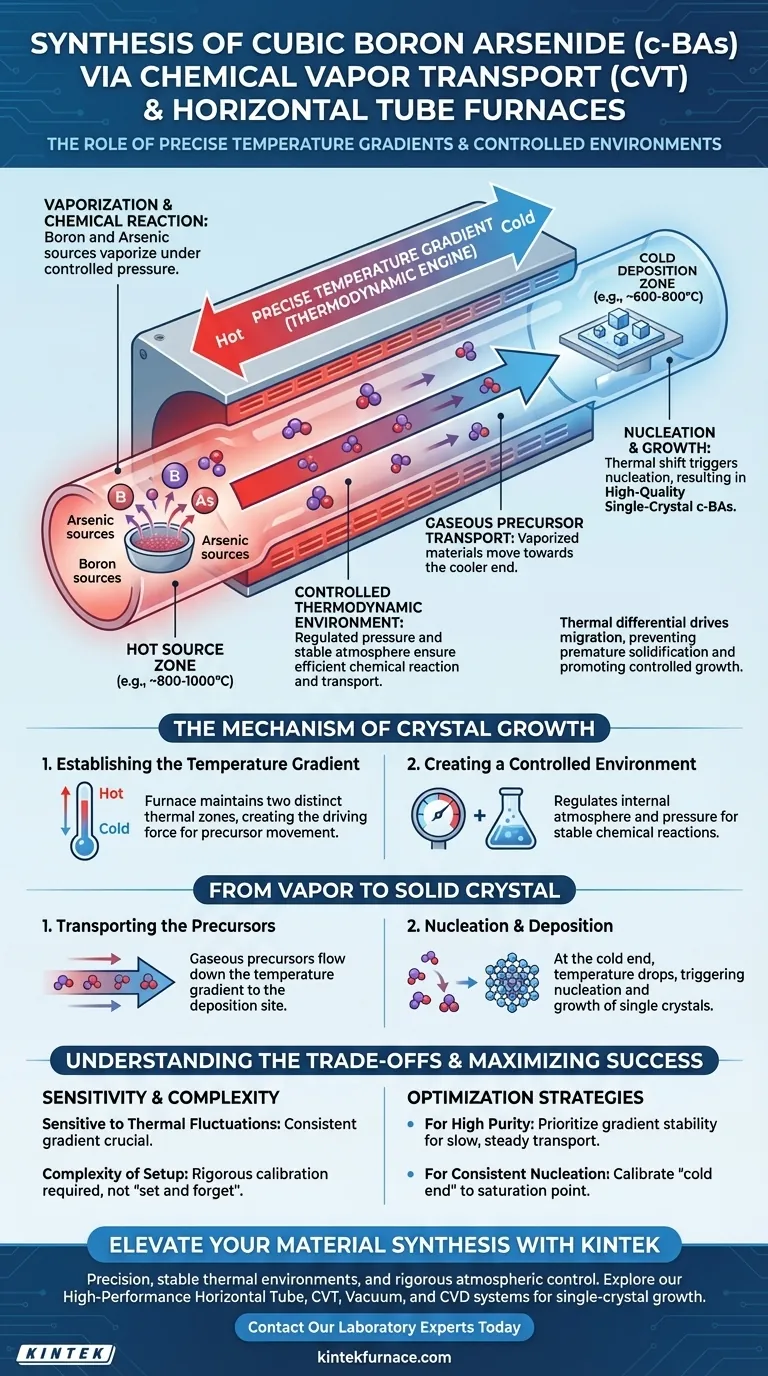
The primary role of Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) equipment and horizontal tube furnaces is to facilitate the synthesis of cubic boron arsenide (c-BAs) by establishing precise temperature gradients that drive the movement of gaseous precursors. This equipment creates a controlled thermodynamic environment where boron sources and arsenic vapor react under specific pressures, enabling the material to migrate from a hot source zone to a cooler deposition zone.
The horizontal tube furnace serves as the foundational vessel for the CVT process, creating the thermal differential necessary to transport vaporized materials. This controlled migration is the key mechanism for ensuring the nucleation and growth of high-quality single-crystal c-BAs.
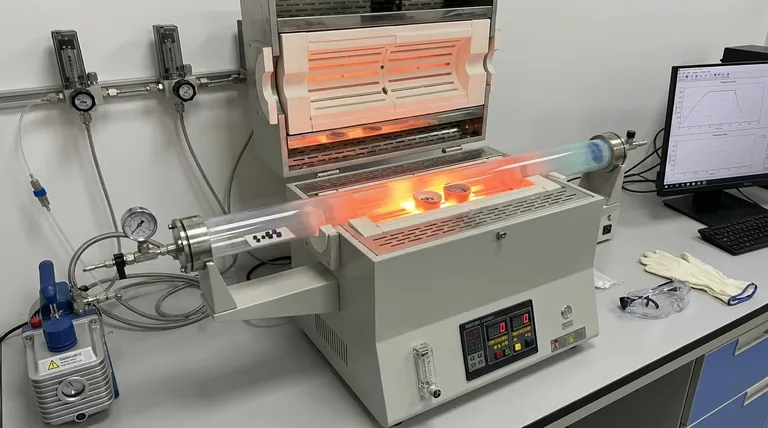

The Mechanism of Crystal Growth
Establishing the Temperature Gradient
The central function of the horizontal tube furnace is to create two distinct thermal zones. The equipment maintains a "hot end" where the raw source materials are located and vaporized.
Simultaneously, it maintains a "cold end" at the opposite side of the tube. This precise temperature gradient acts as the engine of the process, providing the thermodynamic force required to drive gaseous precursors from one end to the other.
Creating a Controlled Environment
Beyond simple heating, the furnace regulates the internal atmosphere of the reaction. It ensures the environment remains stable under specific pressures required for the synthesis.
This stability allows arsenic vapor to react chemically with boron sources efficiently. Without this controlled thermodynamic environment, the reaction would be unpredictable, leading to poor quality or failed synthesis.
From Vapor to Solid Crystal
Transporting the Precursors
Once the reaction initiates at the hot end, the gaseous precursors must move to the deposition site. The layout of the horizontal tube facilitates this flow down the temperature gradient.
The gas travels away from the source zone, carrying the necessary chemical components. This transport phase is critical for delivering material to the substrate without premature solidification.
Nucleation and Deposition
When the gaseous precursors reach the colder end of the furnace, the temperature drops below the saturation point. This thermal shift triggers nucleation, where the gas begins to organize into a solid structure.
This process results in the growth of c-BAs on substrates located in the cold zone. Because the delivery is slow and controlled, the resulting material forms high-quality single crystals rather than disordered polycrystals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Thermal Fluctuations
The reliance on a precise temperature gradient means the process is highly sensitive to thermal instability. If the furnace cannot maintain a consistent difference between the hot and cold ends, the transport rate may fluctuate.
Complexity of Setup
Achieving the correct "specific pressures" and thermodynamic conditions requires rigorous calibration. This is not a "set and forget" method; it demands careful monitoring to ensure the environment supports single-crystal growth throughout the entire duration.
Maximizing Synthesis Success
To achieve the best results when synthesizing cubic boron arsenide using CVT, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is high purity: Prioritize the stability of the temperature gradient to ensure a slow, steady transport of precursors, which minimizes defects in the crystal lattice.
- If your primary focus is consistent nucleation: Ensure the "cold end" temperature is precisely calibrated to the specific saturation point of the c-BAs vapor to promote controlled growth on the substrate.
Ultimately, the successful synthesis of cubic boron arsenide depends entirely on the equipment's ability to maintain a rigorous thermal environment that guides the material from vapor to high-quality solid.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in c-BAs Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Hot Source Zone | Facilitates vaporization of raw boron and arsenic sources |
| Cold Deposition Zone | Triggers nucleation and growth of high-quality single crystals |
| Temperature Gradient | Acts as the thermodynamic engine driving gaseous precursor movement |
| Atmospheric Control | Regulates specific pressures and stability for chemical reactions |
| Horizontal Tube Design | Enables the controlled flow and transport of vaporized materials |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing complex materials like cubic boron arsenide. At KINTEK, we understand that the success of your research depends on stable thermal environments and rigorous atmospheric control.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Horizontal Tube, CVT, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the exact temperature gradients required for single-crystal growth. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customizable high-temp furnace tailored to your unique lab requirements, KINTEK provides the reliability you need to minimize defects and maximize purity.
Ready to optimize your CVT process? Contact our laboratory experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your synthesis goals.
Visual Guide
References
- Jae‐Hoon Kim, Joon Sang Kang. Isotope‐Enriched Cubic Boron Arsenide with Ultrahigh Thermal Conductivity. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202502544
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What preparations are needed before starting a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Can a quartz tube furnace be used for controlled atmosphere experiments? Achieve Precise Heat and Gas Control
- What are the key application features of a fluidized bed vertical tube furnace? Boost Efficiency and Uniformity
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for long-term heat treatment of FeTeSe crystals? Achieve High Crystallinity & Uniformity
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace required during Fe-Mn catalyst synthesis? Control Morphology and CNF Quality
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate Fe-Nx-C electrocatalyst formation? Expert Synthesis Insights
- What are the key takeaways regarding tubular furnaces and materials science? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing for Advanced Materials



















