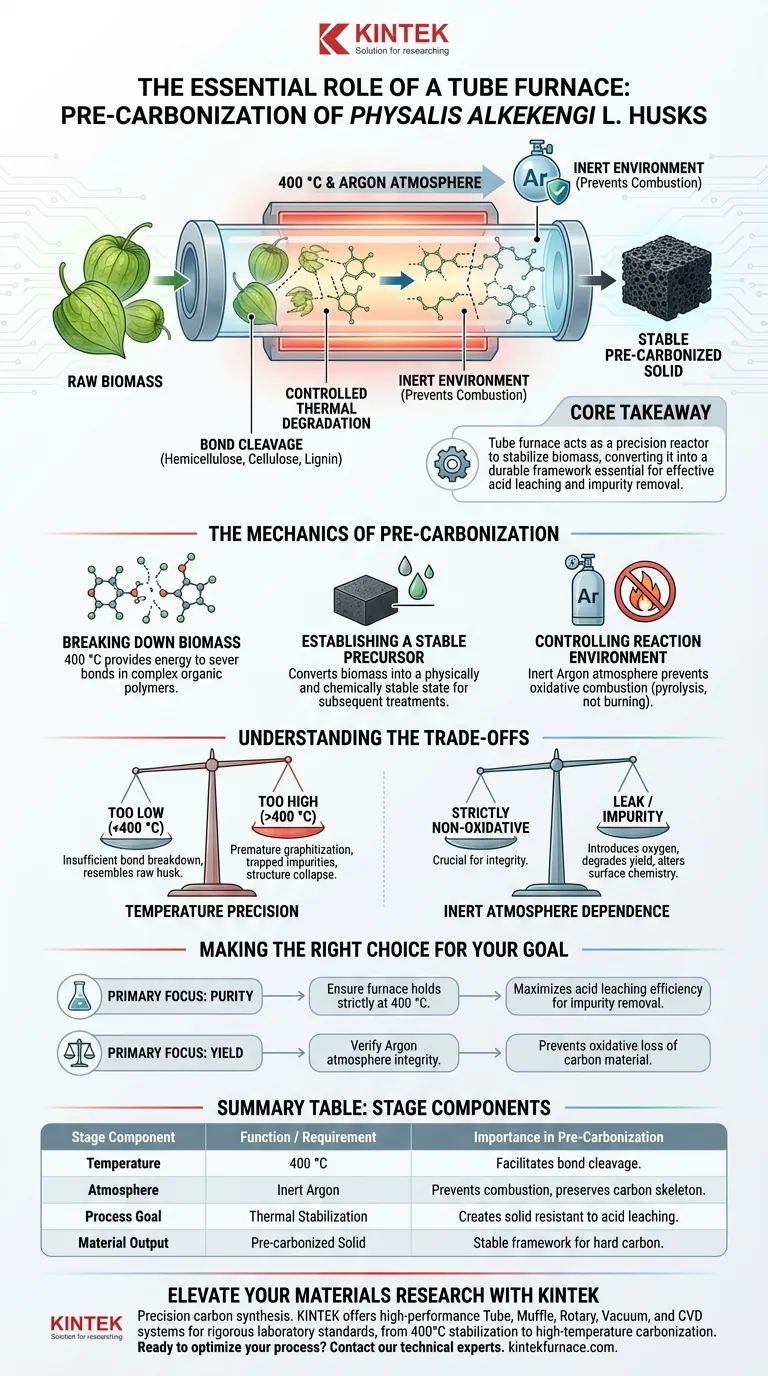
The primary function of the tube furnace during the pre-carbonization of Physalis alkekengi L. husks is to facilitate the thermal breakdown of the raw biomass's chemical structure. Operating at 400 °C under an argon atmosphere, the furnace fractures the internal chemical bonds of the husk's main components—hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin—transforming the raw material into a stable solid precursor suitable for subsequent chemical processing.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace acts as a precision reactor that stabilizes raw biomass before full carbonization. By breaking specific chemical bonds in an inert environment, it converts organic material into a durable solid framework, which is the essential prerequisite for effective acid leaching and impurity removal.

The Mechanics of Pre-Carbonization
Breaking Down Biomass Components
The fundamental role of the tube furnace in this specific stage is bond cleavage. The raw Physalis alkekengi L. husks are composed of complex organic polymers.
By maintaining a steady temperature of 400 °C, the furnace provides the thermal energy required to sever the chemical bonds within hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. This is not a total incineration, but a controlled degradation that alters the material's chemical identity.
Establishing a Stable Precursor
The output of this process is not the final hard carbon product, but rather a pre-carbonized material.
The tube furnace ensures that the biomass is converted into a solid state that is physically and chemically stable. This stability is critical because the material must withstand subsequent aggressive treatments, specifically acid leaching, which is used to remove impurities. Without this thermal stabilization, the raw biomass would not react predictably to chemical purification.
Controlling the Reaction Environment
A critical function of the tube furnace is the maintenance of a specific atmosphere. The process requires an inert argon environment to prevent combustion.
If the biomass were heated to 400 °C in the presence of oxygen, it would burn into ash. The tube furnace seals the environment, ensuring the material undergoes thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) rather than oxidative combustion. This preserves the carbon skeleton necessary for energy storage applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Precision vs. Material Integrity
While the tube furnace is powerful, the specific temperature setting of 400 °C is a calculated trade-off.
If the temperature is too low, the chemical bonds in the lignin and cellulose will not break down sufficiently, leaving the precursor chemically similar to the raw husk and unsuitable for acid leaching.
Conversely, if the temperature is ramped too high (e.g., toward the 1000 °C range used in later stages), the material may undergo premature graphitization or pore structure collapse. This would lock in impurities before they can be removed, reducing the final quality of the hard carbon.
Inert Atmosphere Dependence
The reliance on a tube furnace creates a dependency on the integrity of the inert gas flow.
The process is strictly non-oxidative. Any leak in the system or impurity in the argon gas supply can lead to the introduction of oxygen-containing functional groups or partial combustion. This degrades the carbon yield and alters the surface chemistry unpredictably, ruining the precursor before it reaches the carbonization stage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the pre-carbonization stage for Physalis alkekengi L. husks, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Purity: Ensure the furnace holds strictly at 400 °C to fully stabilize the solid precursor, as this maximizes the efficiency of the subsequent acid leaching step for impurity removal.
- If your primary focus is Yield: Verify the integrity of the argon atmosphere to prevent any oxidative loss of carbon material during the heating process.
Mastering this pre-carbonization step ensures you build a robust foundation for high-performance hard carbon materials.
Summary Table:
| Stage Component | Function / Requirement | Importance in Pre-Carbonization |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 400 °C | Facilitates bond cleavage of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. |
| Atmosphere | Inert Argon | Prevents oxidative combustion and preserves the carbon skeleton. |
| Process Goal | Thermal Stabilization | Creates a solid precursor resistant to subsequent acid leaching. |
| Material Output | Pre-carbonized Solid | Provides a stable framework for high-performance hard carbon production. |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of high-performance carbon synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the most rigorous laboratory standards. Whether you are stabilizing biomass precursors at 400°C or performing high-temperature carbonization, our customizable furnaces ensure the thermal accuracy and atmospheric integrity your research demands.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your unique laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Liying Liu, Yang Xu. Hard carbon derived from <i>Physalis alkekengi</i> L. husks as a stable anode for sodium-ion batteries. DOI: 10.1039/d4me00007b
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are corundum boats and tube furnaces utilized for biomass pre-carbonization? Optimize Your 500°C Pyrolysis
- What environmental conditions must a high-temperature tube furnace provide for MAX phase sintering? Expert Guidelines
- What is the significance of a rapid quenching device at the bottom of a lab tube furnace? Capture High-Temp Snapshot
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the pre-carbonization of biomass? Optimize Carbon Yield Today
- Why is a high-vacuum sealed quartz tube used in CVT? Ensuring High-Purity Fe4GeTe2 Single Crystal Growth
- What role does a tube furnace play in Se/NC composite synthesis? Mastering the Melt-Diffusion Method
- What is the role of a benchtop tube furnace in the preparation of corn stover biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis Precision
- How does a tube furnace achieve precise control over product components? Master Cottonseed Pyrolysis with Precision



















