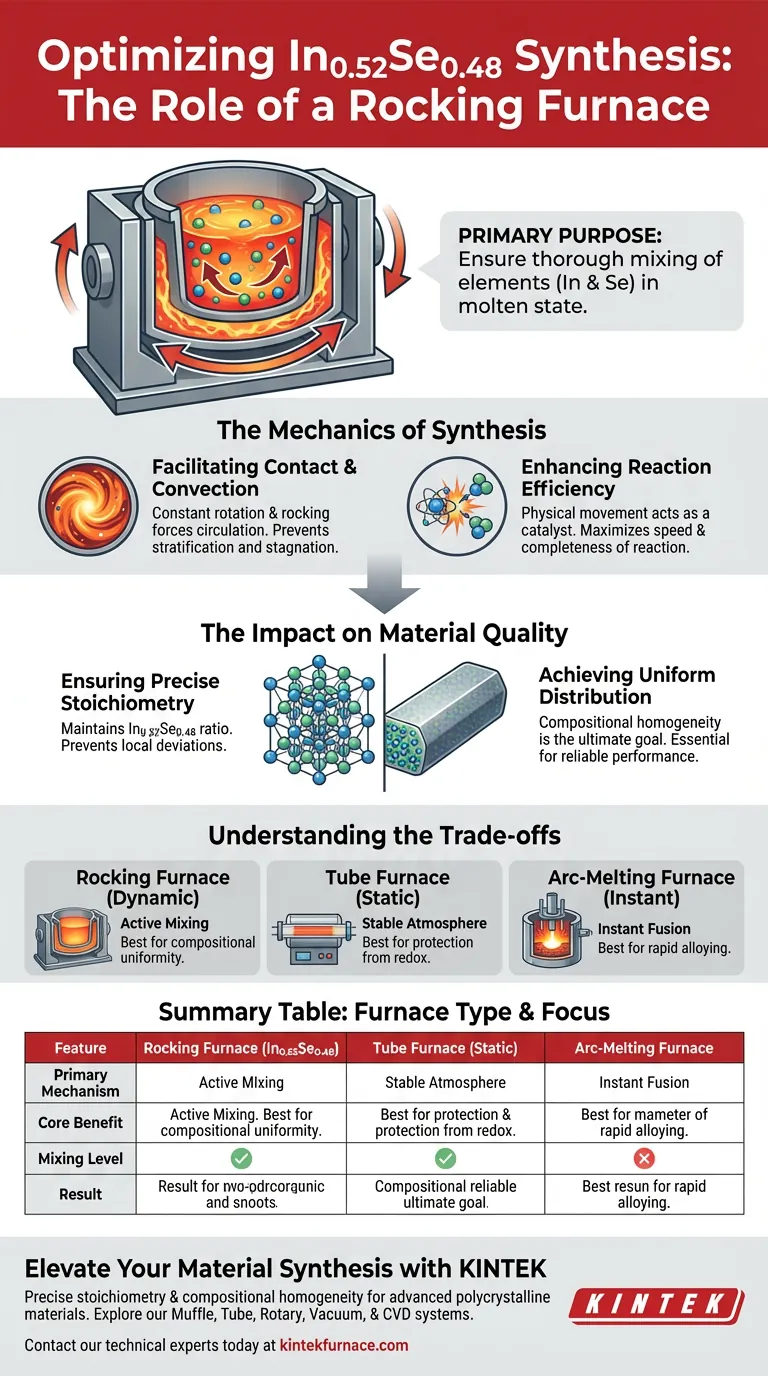
The primary purpose of using a rocking furnace in the synthesis of In0.52Se0.48 is to ensure the thorough mixing of elements while they are in a molten state. By applying constant rotation and rocking motions, the furnace creates mechanical convection between the high-purity Indium (In) and Selenium (Se). This forced movement is the key driver for reaction efficiency, ensuring the final material achieves precise stoichiometry and a uniform composition.
The core advantage of a rocking furnace is that it moves beyond simple heating to active mixing. This dynamic process is essential for preventing material segregation, ensuring that the In0.52Se0.48 polycrystalline material is chemically consistent throughout.

The Mechanics of Synthesis
Facilitating Contact and Convection
In standard heating, molten elements may stratify based on density or remain static. A rocking furnace eliminates this issue by introducing constant rotation and rocking.
This mechanical action forces the molten Indium and Selenium to circulate. It ensures that the reactants are in a state of continuous, thorough contact rather than sitting stagnant.
Enhancing Reaction Efficiency
The physical movement within the furnace acts as a catalyst for the physical reaction. By promoting convection, the furnace ensures that unreacted portions of the melt are constantly brought together.
This maximizes the speed and completeness of the reaction. It prevents pockets of unreacted material from remaining in the final ingot.
The Impact on Material Quality
Ensuring Precise Stoichiometry
For materials like In0.52Se0.48, adhering to the specific chemical ratio is critical. Variations in the ratio can drastically alter the material's properties.
The rocking furnace prevents local deviations in the mixture. It ensures that the ratio of Indium to Selenium is maintained precisely throughout the entire volume of the material.
Achieving Uniform Distribution
The ultimate goal of using this apparatus is compositional homogeneity.
Without the rocking motion, the final polycrystalline material could suffer from uneven compositional distribution. The furnace ensures that the pre-synthesized material is uniform, which is a prerequisite for reliable performance in subsequent applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Dynamic vs. Static Environments
While a rocking furnace excels at mixing, it differs fundamentally from static methods. For example, a standard tube furnace (often used for NaRu2O4) prioritizes a stable, sealed environment for atmosphere control over physical mixing.
If the reaction requires a delicate balance of volatile gases or extreme protection from redox reactions, the dynamic motion of a rocking furnace might introduce unnecessary variables compared to a static setup.
Mixing Speed vs. Instant Fusion
The rocking furnace relies on sustained motion to achieve homogeneity over time. This contrasts with methods like arc-melting (used for Cr-Mn-Ge alloys), which utilizes high-temperature arcs for instantaneous fusion.
While arc-melting is faster for rapid alloying, it may not provide the gentle, sustained mixing required for the precise stoichiometric balance of In0.52Se0.48.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct synthesis method, you must align the furnace capabilities with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is compositional uniformity in the melt: Use a rocking furnace to induce convection and ensure precise stoichiometry, as required for In0.52Se0.48.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature fusion: Consider an arc-melting furnace to instantaneously melt and alloy raw elements.
- If your primary focus is atmosphere stability: Utilize a sealed tube furnace to maintain a protective inert environment and prevent unwanted redox reactions.
Success in synthesis depends not just on reaching the right temperature, but on controlling how the elements interact once they get there.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rocking Furnace (In0.52Se0.48) | Tube Furnace (Static) | Arc-Melting Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Mechanical convection & rocking | Stable atmosphere control | High-temperature electric arc |
| Core Benefit | Eliminates material segregation | Prevents redox reactions | Instantaneous fusion |
| Mixing Level | High (Active circulation) | Low (Passive diffusion) | Moderate (Rapid alloying) |
| Result | Precise stoichiometry | Atmosphere purity | Fast cycle times |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise stoichiometry and compositional homogeneity are non-negotiable for advanced polycrystalline materials. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside specialized furnaces tailored for your unique research needs.
Whether you are synthesizing In0.52Se0.48 or developing next-generation alloys, our customizable high-temperature solutions ensure your lab achieves repeatable, high-quality results every time.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Min Jin, Xuechao LIU. Growth and Characterization of Large-size InSe Crystal from Non-stoichiometric Solution <i>via</i> a Zone Melting Method. DOI: 10.15541/jim20230524
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of rotary tube furnaces? Unlock Efficient Bulk Material Processing
- What makes rotary tube furnaces suitable for continuous processing? Unlock High-Volume Efficiency & Uniformity
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What role does the rotary kiln serve in coal-based DRI production? Unlock Cost-Effective Ironmaking Efficiency
- What factors should be considered when choosing between a batch-type and continuous-type rotary kiln? Optimize Your Production Strategy
- Why are rotary tube furnaces considered efficient? Achieve uniform heating and energy savings
- What distinguishes rotary furnaces from vacuum furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Process
- What is a rotary furnace and what is it used for? Achieve Uniform Heating for Industrial Materials



















