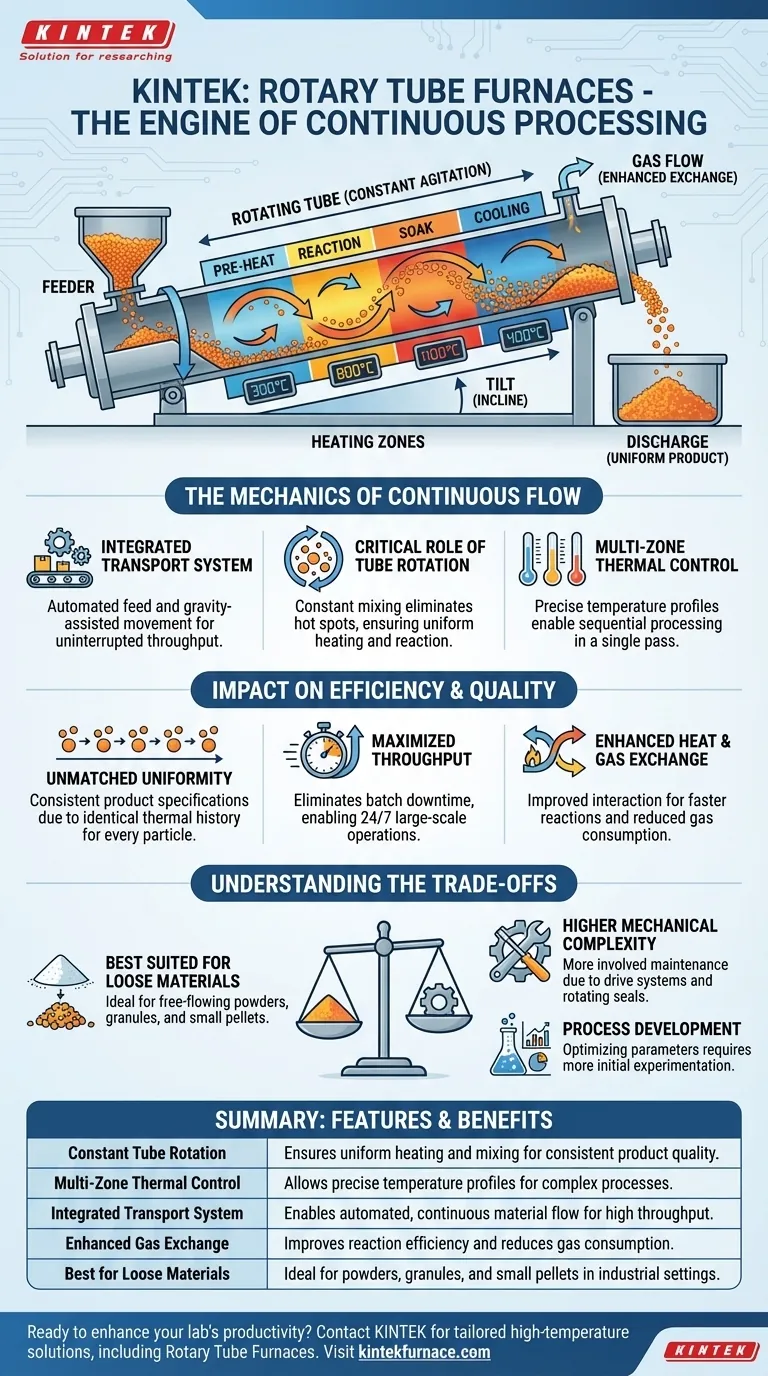
At their core, rotary tube furnaces are purpose-built for continuous processing because they combine material transport with thermal treatment in a single, dynamic operation. Their design allows for a constant, uninterrupted flow of loose material through a heated, rotating tube, ensuring every particle receives uniform exposure to heat and the processing atmosphere.
The key to their suitability is not merely the ability to move material from one end to the other. It is the constant agitation from the tube's rotation, which guarantees exceptionally uniform heating and atmospheric reaction for every particle in the mass flow, a level of consistency difficult to achieve in static batch processes.

The Mechanics of Continuous Flow
The suitability of a rotary tube furnace for continuous operation is not a single feature but the result of several integrated design principles working in concert.
The Integrated Transport System
A dedicated feeding system, often a screw feeder or hopper, introduces raw material into one end of the furnace tube. The slight incline of the tube, combined with its slow rotation, gently tumbles the material, conveying it steadily toward the discharge end where it is collected. This creates an automated, hands-off throughput.
The Critical Role of Tube Rotation
The rotation is the most important element for process quality. As the tube rotates, it continuously lifts and turns the material over on itself. This constant mixing prevents hot spots, eliminates unprocessed cores within the material bed, and ensures the entire surface area of every particle is exposed to the furnace's heat and atmosphere.
Multi-Zone Thermal Control
Industrial rotary furnaces are rarely a single temperature. They are typically divided into multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube. This allows you to create a precise temperature profile, enabling complex processes like drying, pre-heating, reacting, and cooling to occur sequentially in one continuous pass.
The Impact on Process Efficiency and Quality
The mechanical design directly translates into significant advantages for high-volume manufacturing and material processing.
Unmatched Product Uniformity
Because every particle follows a similar path and is subjected to the same tumbling action and temperature profile, the final product is exceptionally uniform. This consistency is critical for applications where material properties must fall within tight specifications.
Maximized Throughput and Productivity
By eliminating the stop-and-start nature of batch processing, rotary tube furnaces dramatically increase productivity. There is no downtime for loading, unloading, heating, or cooling the entire furnace chamber, making them the standard for large-scale, 24/7 industrial operations.
Enhanced Heat and Gas Exchange
The constant tumbling action breaks up the material bed, improving the efficiency of heat transfer into the particles. Furthermore, it significantly enhances gas diffusion, ensuring process gases (like oxygen for oxidation or inert gas for protection) can interact effectively with the material surface, often leading to reduced gas consumption and faster reaction times compared to static methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary tube furnaces are a specialized tool. Understanding their limitations is key to making a sound technical decision.
Best Suited for Loose Materials
These furnaces are specifically designed for free-flowing powders, granules, or small pellets. They are not suitable for processing large, solid parts, intricate components, or liquids.
Higher Mechanical Complexity
The inclusion of a drive motor, rotating seals, and a support structure makes a rotary furnace more mechanically complex than a simple static box or tube furnace. This translates to different and potentially more involved maintenance requirements over the furnace's lifetime.
Process Development Can Be More Involved
Optimizing a continuous process requires balancing feed rate, rotation speed, tube angle, and the temperature of each zone. While highly repeatable once established, finding the ideal parameters for a new material can require more initial experimentation than a simple batch process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this technology fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a uniform powder: A rotary tube furnace is purpose-built for this task, offering superior throughput and consistency.
- If your primary focus is efficient calcination, roasting, or oxidation: The enhanced heat and gas exchange created by the rotation makes this an exceptionally efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is processing small, diverse batches or large, solid objects: A static batch furnace is a simpler, more cost-effective, and appropriate solution.
By integrating material transport directly into the heating process, rotary tube furnaces offer an unparalleled solution for scaling up material processing efficiently and reliably.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Constant Tube Rotation | Ensures uniform heating and mixing for consistent product quality |
| Multi-Zone Thermal Control | Allows precise temperature profiles for complex processes |
| Integrated Transport System | Enables automated, continuous material flow for high throughput |
| Enhanced Gas Exchange | Improves reaction efficiency and reduces gas consumption |
| Best for Loose Materials | Ideal for powders, granules, and small pellets in industrial settings |
Ready to enhance your lab's productivity with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Rotary Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for superior efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your continuous processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















