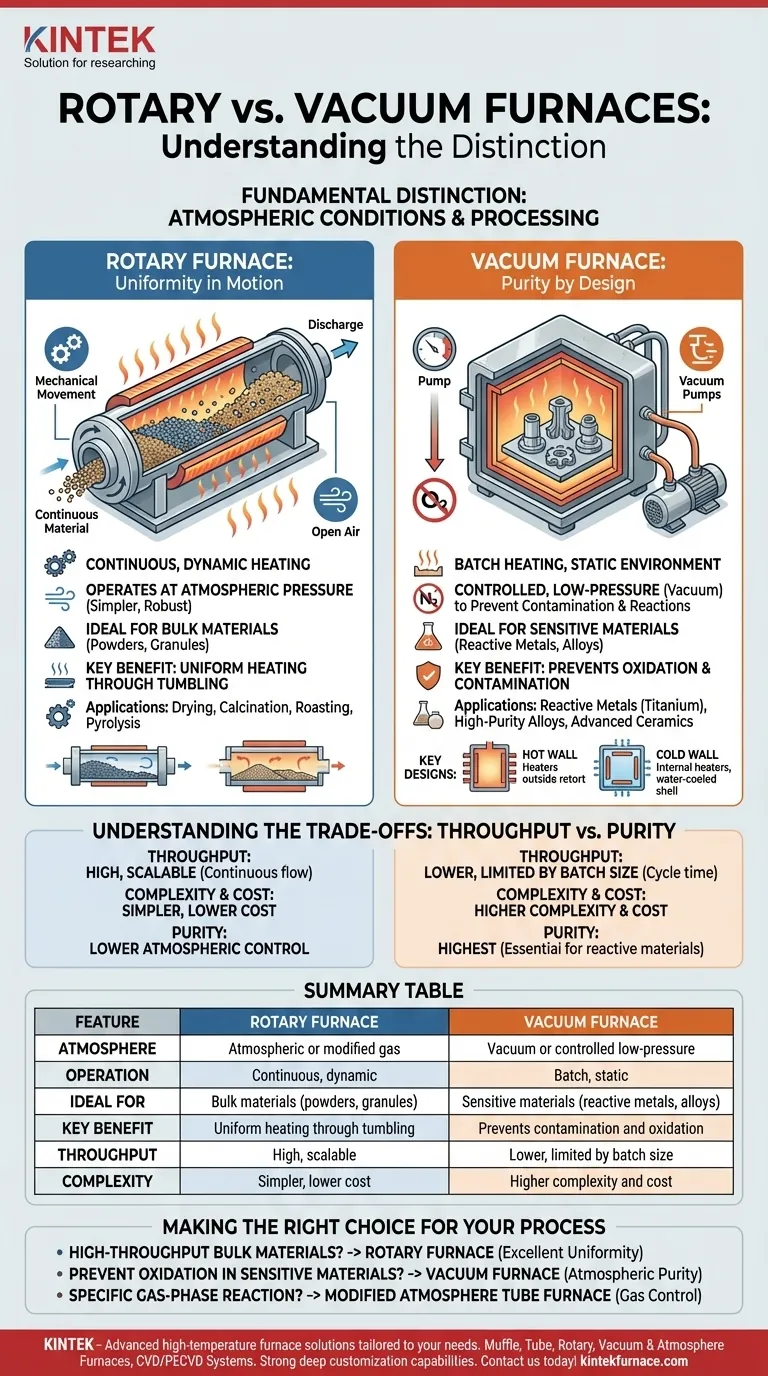
The fundamental distinction between a rotary furnace and a vacuum furnace lies in the atmospheric conditions they create. A rotary furnace is designed for continuous, dynamic heating of materials at atmospheric pressure, while a vacuum furnace is designed for batch heating in a controlled, low-pressure environment to prevent contamination and unwanted chemical reactions.
The choice is not simply about heat, but about the processing environment. Rotary furnaces excel at achieving uniform heating for bulk materials in motion, whereas vacuum furnaces prioritize atmospheric purity for sensitive, static materials.

Understanding the Rotary Furnace: Uniformity in Motion
A rotary furnace is a specific type of tube furnace designed for continuous processing and thermal consistency. Its defining feature is mechanical movement.
The Core Principle: Mechanical Tumbling
The "rotary" aspect refers to a cylindrical tube that slowly rotates during operation. This tumbling motion continuously exposes all surfaces of the material to the heat source.
This design is ideal for processing bulk materials like powders, granules, or small parts, ensuring every particle achieves a uniform temperature.
Operating at Atmospheric Pressure
Rotary furnaces almost always operate at or near standard atmospheric pressure. This makes them simpler and more robust for standard industrial processes like drying, calcination, roasting, and pyrolysis where atmospheric purity is not the primary concern.
Some models can be adapted to use a "modified atmosphere," where a specific gas like nitrogen or argon is introduced to displace ambient air, but this is distinct from creating a vacuum.
Configuration for Throughput
As a type of tube furnace, they are designed for material to pass through a long, cylindrical heating chamber.
They often feature multiple heating zones (e.g., three-zone configurations) to provide excellent temperature uniformity along the entire processing length, which is critical for consistent results in a continuous flow.
Understanding the Vacuum Furnace: Purity by Design
A vacuum furnace's primary purpose is to remove the atmosphere, creating a controlled environment where heat treatment can occur without external influence.
The Core Principle: Removing the Atmosphere
By using a system of vacuum pumps, these furnaces evacuate air and other gases from a sealed chamber. This prevents oxidation, contamination, and other reactions that would occur in the presence of oxygen or nitrogen at high temperatures.
This makes them essential for processing reactive metals (like titanium), high-purity alloys, and advanced ceramics used in aerospace, medical, and electronics applications.
Key Designs: Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall
Vacuum furnaces come in two main configurations. Hot wall furnaces have heating elements outside the vacuum retort, while cold wall furnaces have internal heaters and a water-cooled outer shell.
Cold wall designs are more common for high-performance applications, offering higher maximum temperatures, faster heating and cooling cycles, and superior temperature uniformity.
The Batch Process Nature
Unlike the continuous flow of a rotary furnace, vacuum furnaces are inherently batch-processing systems. Material is loaded, the chamber is sealed, a vacuum is pulled, the heating cycle is run, and the material cools before the chamber can be opened and unloaded.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Throughput vs. Purity
Choosing between these furnaces requires a clear understanding of your process priorities, as each involves significant trade-offs.
Throughput and Scalability
A rotary furnace is built for high throughput. Its ability to process material continuously makes it the clear choice for industrial-scale production where large volumes are required.
Vacuum furnaces are limited by their batch size and total cycle time (including pump-down and cooling). This makes them less suitable for high-volume, low-margin materials.
Material Purity and Reactivity
This is the vacuum furnace's domain. For materials where even trace amounts of oxygen would cause failure, the purity of a vacuum environment is non-negotiable.
A standard rotary furnace cannot provide this level of atmospheric control and is unsuited for processing highly reactive or sensitive materials.
System Complexity and Cost
Vacuum systems add significant complexity, cost, and maintenance requirements. The need for robust seals, high-performance pumps, and precise gauges makes a vacuum furnace a more complex and expensive piece of equipment than a comparable atmospheric rotary furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision must be guided by the specific requirements of your material and the desired outcome of the thermal treatment.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processing of bulk materials like powders or ores: A rotary furnace is your ideal choice for its continuous operation and excellent thermal uniformity.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation in sensitive materials like titanium or advanced alloys: A vacuum furnace is the only tool that can provide the necessary atmospheric purity.
- If your primary focus is a specific gas-phase reaction, such as nitriding or carburizing: A modified atmosphere tube furnace (which may or may not be rotary) is the correct choice, as it is designed to introduce and control specific process gases.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace begins with defining whether your process needs to control material movement or material purity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotary Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Atmospheric or modified gas | Vacuum or controlled low-pressure |
| Operation | Continuous, dynamic | Batch, static |
| Ideal For | Bulk materials (powders, granules) | Sensitive materials (reactive metals, alloys) |
| Key Benefit | Uniform heating through tumbling | Prevents contamination and oxidation |
| Throughput | High, scalable | Lower, limited by batch size |
| Complexity | Simpler, lower cost | Higher complexity and cost |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process efficiency and material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















