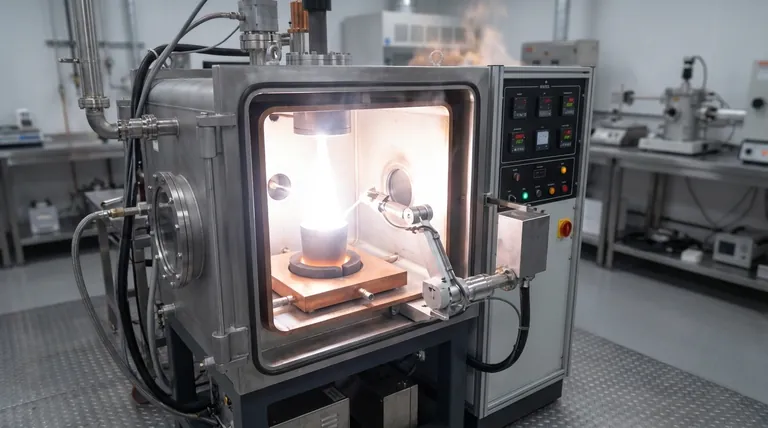
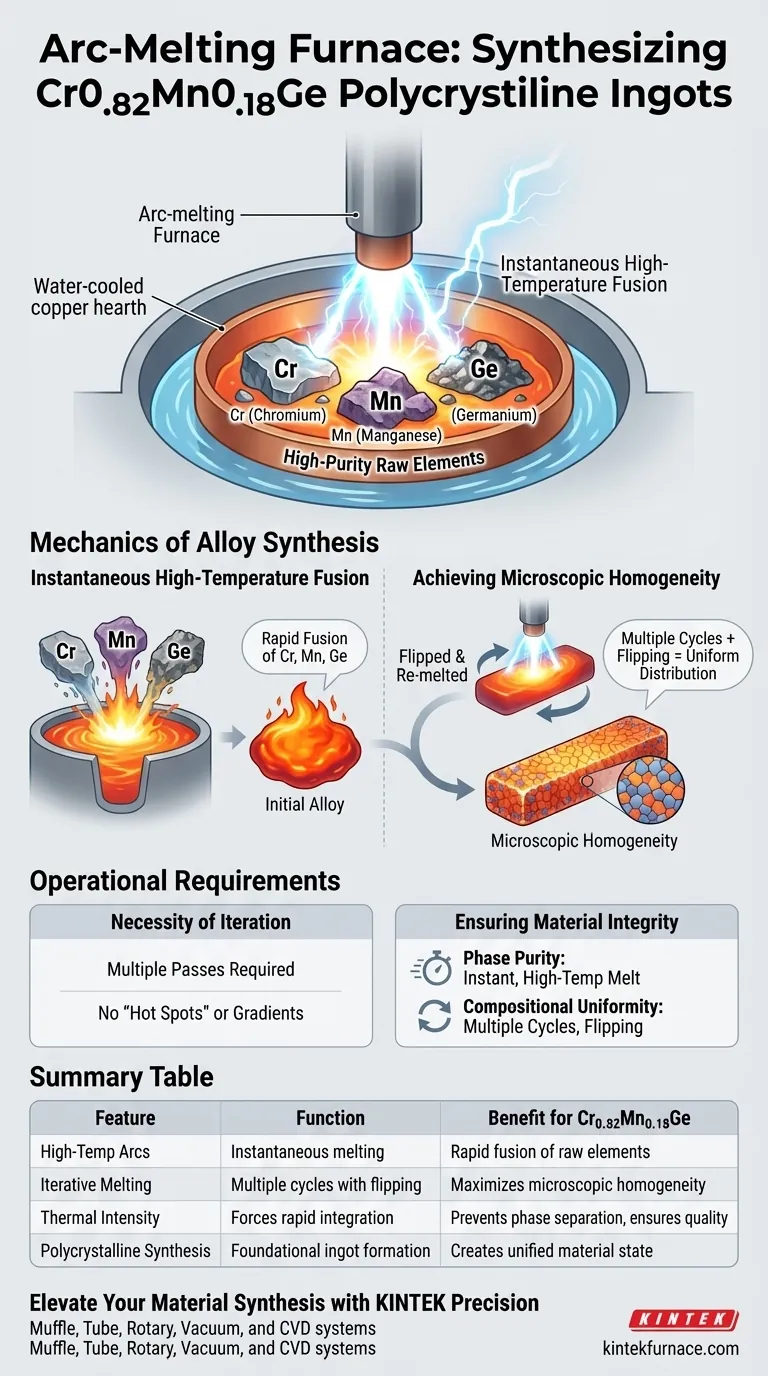
The primary function of an arc-melting furnace in the synthesis of Cr0.82Mn0.18Ge is to generate extremely high-temperature arcs that instantaneously melt high-purity raw elements. This intense thermal environment forces the Chromium (Cr), Manganese (Mn), and Germanium (Ge) to fuse rapidly, creating the initial polycrystalline alloy ingot.
The arc-melting furnace does more than simply liquefy metal; it employs high-intensity heat and iterative processing to ensure rapid component fusion and maximize the microscopic homogeneity of the alloy composition.

The Mechanics of Alloy Synthesis
Instantaneous High-Temperature Fusion
The synthesis process begins with raw, high-purity elements. The furnace utilizes high-temperature arcs to subject these materials to intense thermal energy.
This results in the instantaneous melting of the Cr, Mn, and Ge components. The speed of this transition is critical, as it ensures the immediate and rapid fusion of the separate elements into a singular alloy state.
Achieving Microscopic Homogeneity
Simply melting the elements together is often insufficient for advanced material applications. The distribution of elements within the ingot must be uniform at a microscopic level.
To achieve this, the furnace is used to perform multiple melting cycles. Between these cycles, the ingot is flipped to ensure that every part of the material is subjected to equal heat and mixing, thereby maximizing the microscopic homogeneity of the final composition.
Operational Requirements and Trade-offs
The Necessity of Iteration
A key operational reality of using an arc-melting furnace for this specific alloy is that a single melting pass is inadequate.
To prevent compositional gradients or "hot spots" where elements might not be perfectly mixed, the process demands repetition. The requirement to flip and re-melt the ingot multiple times adds time to the synthesis process but is non-negotiable for ensuring quality.
Ensuring Material Integrity
To replicate the successful synthesis of Cr0.82Mn0.18Ge ingots, consider the following processing priorities:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the initial melt is instantaneous and high-temperature to force rapid fusion of the raw elements.
- If your primary focus is Compositional Uniformity: You must prioritize multiple melting cycles with flipping to eliminate localized inhomogeneities.
The arc-melting furnace acts as the foundational tool for material consistency, turning distinct raw elements into a unified, homogeneous polycrystalline ingot.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Synthesis | Benefit for Cr0.82Mn0.18Ge |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Arcs | Instantaneous melting of Cr, Mn, and Ge | Rapid fusion of raw high-purity elements |
| Iterative Melting | Multiple melting cycles with flipping | Maximizes microscopic homogeneity of the alloy |
| Thermal Intensity | Forces rapid component integration | Prevents phase separation and ensures alloy quality |
| Polycrystalline Synthesis | Foundational ingot formation | Creates a unified material state for advanced applications |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving perfect microscopic homogeneity in complex alloys like Cr0.82Mn0.18Ge requires more than just heat—it requires precision and reliability. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces customizable for your unique research needs.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and material integrity? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your synthesis projects.
Visual Guide
References
- Victor Ukleev, L. Caron. Observation of magnetic skyrmion lattice in Cr0.82Mn0.18Ge by small-angle neutron scattering. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-86652-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the critical role of a Vacuum Induction Melting furnace in FeAl alloy prep? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Alloys
- How does the selection of an industrial EAF influence carbon steel purity? Optimize Your Melt Quality
- What are the key application requirements for the vacuum induction furnace? Ensure Safe, High-Purity Metal Processing
- How does a directional solidification furnace contribute to the manufacturing of high-purity Cu-Fe-Zn alloy ingots?
- What are the main advantages of vacuum melting furnaces? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metals for High-Performance Applications
- How does high thermal efficiency benefit induction furnaces? Unlock Major Cost Savings & Quality
- What are the key benefits of using an IGBT Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- Why is a vacuum electric arc furnace essential for Ti-Al alloys? Achieve Superior Metal Purity & Homogeneity



















