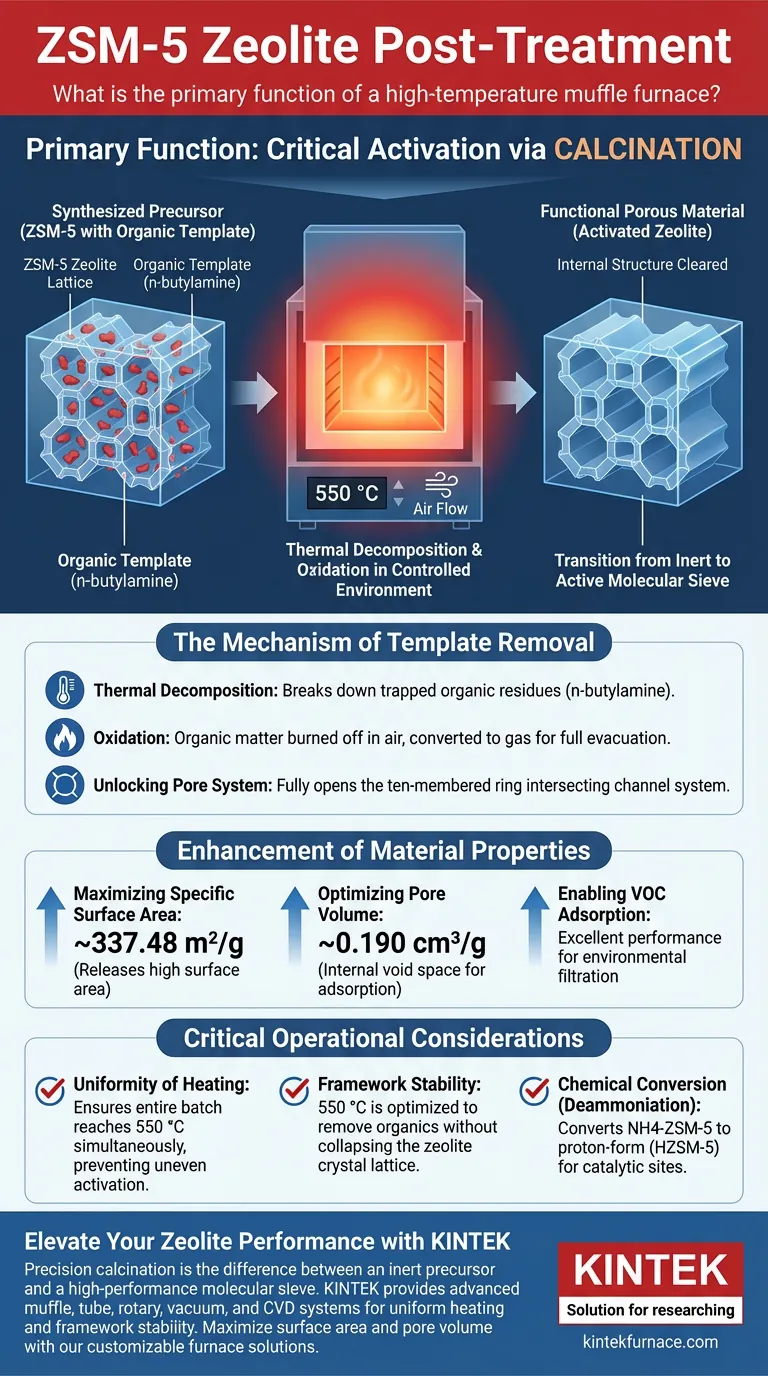
The primary function involves a critical activation step known as calcination. In the post-treatment of ZSM-5 zeolite, a high-temperature muffle furnace operating at 550 °C is utilized to completely decompose and oxidize the organic template agent (n-butylamine). This thermal process is the definitive step that clears the zeolite’s internal structure, transforming it from a synthesized precursor into a functional porous material.
The muffle furnace facilitates the transition from an inert solid to an active molecular sieve by removing pore-blocking agents. This process unlocks the zeolite's ten-membered ring channel system, unlocking the high surface area and pore volume necessary for high-performance applications like VOC adsorption.

The Mechanism of Template Removal
Thermal Decomposition
The ZSM-5 synthesis process typically leaves organic residues, specifically n-butylamine, trapped within the crystal lattice. The muffle furnace provides the sustained thermal energy required to break down these organic molecules.
Oxidation in a Controlled Environment
Beyond simple heating, the furnace acts as an oxidation chamber. At 550 °C, the organic template is burned off in the presence of air. This ensures that the organic matter is converted into gases and fully evacuated from the material.
Unlocking the Pore System
The removal of the template is not merely a cleaning step; it is a structural unveiling. This process fully opens the ten-membered ring intersecting channel system of the ZSM-5 zeolite. Without this step, the pores remain occupied and physically inaccessible to other molecules.
Enhancement of Material Properties
Maximizing Specific Surface Area
Once the pores are cleared, the material exhibits a dramatic increase in available surface area. The calcination process releases a high specific surface area, reaching up to 337.48 m²/g.
Optimizing Pore Volume
The effective removal of the template directly correlates to the internal void space available for adsorption. Post-treatment results in a significant pore volume of approximately 0.190 cm³/g, which is critical for the material's capacity to hold target molecules.
Enabling VOC Adsorption
The combination of high surface area and accessible pore volume directly dictates the zeolite's performance. This activation endows the ZSM-5 with excellent Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) adsorption performance, making it suitable for environmental filtration applications.
Critical Operational Considerations
Uniformity of Heating
A key advantage of using a muffle furnace over other heating methods is the ability to provide a uniform thermal field. The refractory lining protects the sample from direct contact with heating elements, ensuring that the entire batch reaches 550 °C simultaneously. This prevents uneven activation or localized structural damage.
Framework Stability
While the goal is to remove organics, the process must preserve the zeolite's crystalline structure. The operating temperature of 550 °C is carefully selected to be high enough to oxidize the n-butylamine but low enough to maintain the stability of the zeolite framework, ensuring the crystal lattice does not collapse.
Chemical Conversion (Deammoniation)
In cases where the precursor is in the ammonium form (NH4-ZSM-5), this high-temperature treatment performs a dual function. In addition to removing organics, it converts the material into the proton-form (HZSM-5) via deammoniation. This step creates the Bronsted acid sites required for catalytic applications, such as gas oil cracking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your ZSM-5 post-treatment, tailor your focus based on the end application:
- If your primary focus is Adsorption (VOCs): Prioritize complete oxidation of the n-butylamine template to maximize the specific surface area (aiming for ~337 m²/g) and pore accessibility.
- If your primary focus is Catalysis: Ensure the temperature profile is sufficient to facilitate deammoniation, converting the zeolite to its active protonic form (HZSM-5) while stabilizing the framework.
Ultimately, the high-temperature muffle furnace is the tool that operationalizes the zeolite, converting potential structural properties into actual performance capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Mechanism | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermal treatment at 550°C | Decomposes organic template (n-butylamine) |
| Oxidation | Controlled heating in air | Converts organic matter to gas for full removal |
| Activation | Unlocking 10-membered rings | Achieves high surface area (~337.48 m²/g) |
| Deammoniation | Conversion to H-form | Creates Bronsted acid sites for catalytic use |
Elevate Your Zeolite Performance with KINTEK
Precision calcination is the difference between an inert precursor and a high-performance molecular sieve. KINTEK provides the advanced high-temperature muffle furnaces required to achieve uniform heating and stable framework activation for your ZSM-5 zeolite applications.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique lab or industrial requirements. Whether you are optimizing VOC adsorption or refining catalytic cracking, our furnaces deliver the thermal accuracy your research demands.
Ready to maximize your material's surface area and pore volume?
Contact our specialists today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhenhua Sun, Zhaohui Huang. A Hydrothermal Synthesis Process of ZSM-5 Zeolite for VOCs Adsorption Using Desilication Solution. DOI: 10.3390/separations11020039
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a muffle furnace differ from a normal furnace? Discover Precision Heating Solutions
- What is a batch furnace? Maximize Flexibility and Precision for Your Heat Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in TiO2 sol-gel transformation? Achieve High-Performance Photocatalytic Coatings
- How does the performance of a high-temperature sintering furnace affect xPYNT–PINT ceramics? Key to Peak Properties
- What is the function of a Muffle Furnace in date stone carbonization? Optimize Your Bio-Activated Carbon Production
- What role do box type resistance furnaces play in new energy and environmental protection? Powering Sustainable Innovations
- Why is a muffle furnace required for sodium-ion cathode heat treatment? Engineering P2/P3 Crystal Phase Structures
- What are the standard features included with Box Furnaces? A Guide to Core Capabilities & Performance



















