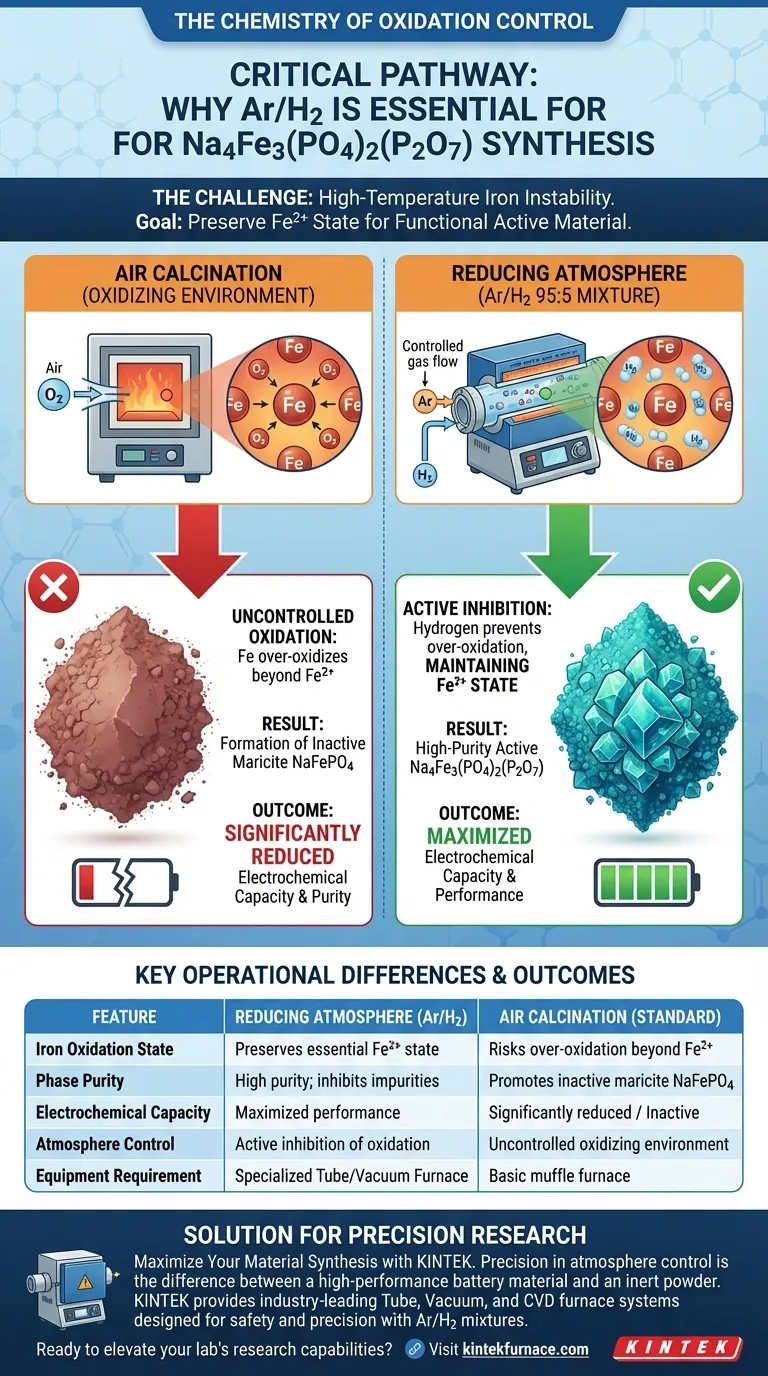
The use of a reducing atmosphere is not optional; it is chemically essential for this synthesis. When preparing Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7), a furnace utilizing a specific mixture of Argon and Hydrogen (Ar/H2) is required to prevent the iron from oxidizing beyond its functional state. Unlike air calcination, which exposes the material to excess oxygen, this reducing environment actively maintains iron in the Fe2+ state, ensuring the formation of the correct active material rather than inactive impurities.
Utilizing a 95:5 Ar/H2 reducing atmosphere creates a controlled environment that inhibits over-oxidation, ensuring the stability of Iron in the critical Fe2+ state. This step is the defining factor in preventing the formation of inactive maricite contaminants and maximizing the electrochemical capacity of the final product.

The Chemistry of Oxidation Control
Preserving the Fe2+ State
The fundamental challenge in synthesizing Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) is the chemical instability of iron at high temperatures.
To achieve the desired crystal lattice, iron must remain in the Fe2+ oxidation state.
If you attempt this process using air calcination, the oxygen present acts as a strong oxidizer. This causes "over-oxidation," pushing the iron away from the necessary Fe2+ state and destabilizing the target compound.
Preventing Impurity Formation
The most significant consequence of failing to use a reducing atmosphere is the creation of impurities.
Specifically, an oxidizing environment (like air) favors the formation of maricite NaFePO4.
The primary reference indicates that maricite is electrochemically inactive. Therefore, if maricite forms due to a lack of reducing gas, the resulting material will have significantly lower purity and poor performance.
The Role of the Ar/H2 Mixture
Active Inhibition
The standard protocol involves a gas mixture of 95% Argon and 5% Hydrogen.
While Argon provides an inert blanket, the Hydrogen component is the active agent. It creates a reducing environment that actively inhibits oxidation.
This effectively "protects" the iron during the high-temperature sintering stage, locking it into the crystal structure correctly.
Impact on Electrochemical Capacity
The physical environment of the furnace directly dictates the performance of the final battery material.
By ensuring the iron remains as Fe2+ and avoiding maricite formation, the reducing atmosphere maximizes the electrochemical capacity.
Air calcination, by contrast, would yield a product with compromised capacity due to the presence of inactive phases.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
Equipment Requirements
Using a reducing atmosphere requires more specialized equipment than air calcination.
You generally need a laboratory tube furnace capable of sealing the environment to manage gas flow precisely.
This setup allows for the efficient discharge of unwanted gases while maintaining the specific 95:5 Ar/H2 ratio required for success.
Complexity vs. Quality
The trade-off here is between process simplicity and material viability.
Air calcination is simpler and requires fewer safety controls than handling hydrogen gas.
However, in this specific context, simplicity comes at the cost of product failure. The complexity of managing a reducing atmosphere is the price of admission for obtaining a functional material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When setting up your synthesis protocol, the choice of atmosphere dictates whether you produce a high-performance battery material or an inert powder.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: You must use the 95:5 Ar/H2 mixture to prevent the formation of the inactive maricite NaFePO4 phase.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Performance: You must avoid air calcination to ensure Iron remains in the Fe2+ state, which is required for maximum capacity.
Success in this synthesis relies entirely on using a reducing atmosphere to chemically engineer the stability of the iron atoms.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Reducing Atmosphere (95:5 Ar/H2) | Air Calcination (Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Oxidation State | Preserves essential Fe2+ state | Risks over-oxidation beyond Fe2+ |
| Phase Purity | High purity; inhibits impurities | Promotes inactive maricite NaFePO4 |
| Electrochemical Capacity | Maximized performance | Significantly reduced / Inactive |
| Atmosphere Control | Active inhibition of oxidation | Uncontrolled oxidizing environment |
| Equipment Requirement | Specialized Tube/Vacuum Furnace | Basic muffle furnace |
Maximize Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in atmosphere control is the difference between a high-performance battery material and an inert powder. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems specifically designed to handle delicate Ar/H2 gas mixtures with absolute safety and precision.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our customizable high-temp furnaces ensure your Na4Fe3(PO4)2(P2O7) synthesis maintains the critical Fe2+ state while eliminating inactive maricite contaminants.
Ready to elevate your lab's research capabilities? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution
Visual Guide
References
- Yaprak Subaşı, Reza Younesi. Synthesis and characterization of a crystalline Na<sub>4</sub>Fe<sub>3</sub>(PO<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub>(P<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub>) cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. DOI: 10.1039/d4ta03554b
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of retort furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What roles do inert gases like argon or helium play when processing molten stainless steel? Enhance Alloy Composition
- What problems arise when ordinary metal materials are heated in an air furnace? Avoid Oxidation and Embrittlement
- What are the benefits of using an atmosphere furnace in the electronics industry? Enhance Component Reliability and Performance
- How does atmosphere control affect defect formation in graphitic carbon nitride? Master Atmosphere Engineering
- What role does a high-temperature activation furnace perform in magnetic catalyst synthesis? Optimize Your Fe3O4 Yield
- What high-temperature processes commonly use argon in furnaces? Essential Guide for Reactive Metals
- What is the purpose of sealing mechanisms in atmosphere furnaces? Ensure Process Purity and Safety



















