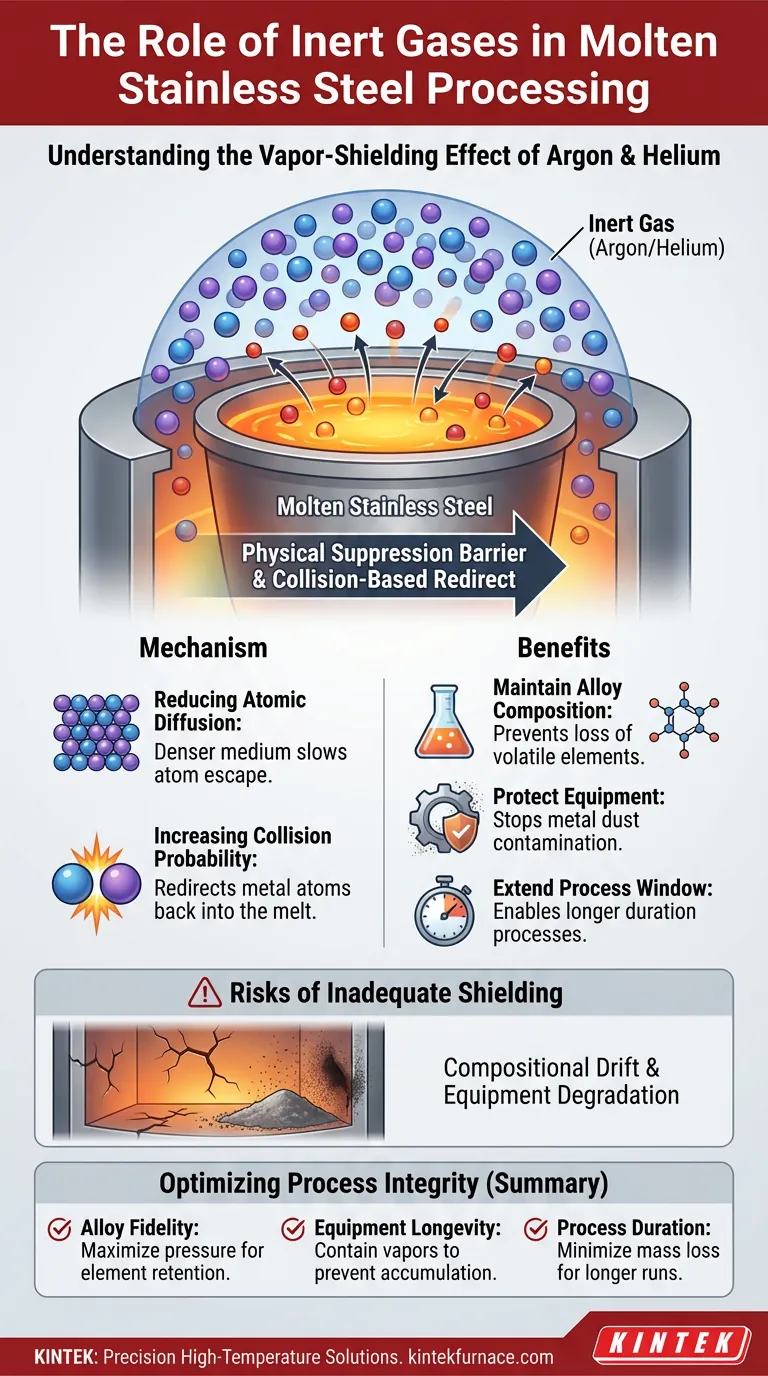
Inert gases like argon or helium act primarily as a physical suppression barrier when processing molten stainless steel at high temperatures. By introducing these gases into the processing environment, you create a "vapor-shielding effect" that significantly inhibits the evaporation of volatile alloy elements, ensuring the material retains its intended chemical properties.
The presence of inert gas molecules creates a high-collision environment that physically blocks metal atoms from escaping the melt. This suppression mechanism is critical for maintaining precise alloy composition and protecting the furnace interior from contamination.
The Mechanism of Vapor Shielding
Reducing Atomic Diffusion
In a high-temperature vacuum, metal atoms can easily escape the molten surface. Introducing an inert gas drastically reduces the diffusion rate of these atoms.
The gas creates a denser medium above the melt, making it difficult for metal vapors to disperse away from the surface.
Increasing Collision Probability
The fundamental physics behind this protection involves atomic collisions. When metal atoms attempt to leave the melt, the presence of inert gas molecules increases the probability of collisions.
Instead of escaping freely, the metal atoms strike the gas molecules. This interaction often redirects the metal atoms back into the melt, effectively capping the evaporation process.
Critical Process Benefits
Maintaining Alloy Composition
Stainless steel relies on a specific balance of elements to maintain its properties. Excessive evaporation can lead to the preferential loss of volatile elements.
By inhibiting this evaporation, inert gases help maintain the sample composition, ensuring the final product meets metallurgical specifications.
Protecting Internal Components
When metal atoms escape the melt, they eventually condense on cooler surfaces. This results in "metal dust" contamination on internal furnace components, such as heating elements or observation windows.
The vapor-shielding effect prevents this contamination, reducing maintenance needs and preserving the integrity of the equipment.
Extending the Experimental Window
High evaporation rates can rapidly deplete a sample, limiting the time available for processing or analysis.
By suppressing material loss, inert gases extend the viable experimental window, allowing for longer duration processes without degrading the sample volume.
The Risks of Inadequate Shielding
Compositional Drift
Without a sufficient vapor shield, the melt suffers from uncontrolled evaporation. This leads to compositional drift, where the ratio of alloy elements shifts unpredictably, potentially rendering the steel unusable for its intended application.
Equipment Degradation
The lack of a gaseous barrier allows metal vapor to coat the furnace interior unrestricted. This buildup of conductive metal dust can cause short circuits in heating elements or obscure optical paths required for temperature monitoring.
Optimizing Process Integrity
To ensure consistent results in high-temperature stainless steel processing, the application of inert gas is not optional; it is a control variable.
- If your primary focus is Alloy Fidelity: Ensure sufficient gas pressure to maximize collision probability and suppress the loss of volatile elements.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Utilize the gas shield to contain metal vapors at the source, preventing costly dust accumulation on sensitive furnace internals.
- If your primary focus is Process Duration: Rely on the vapor-shielding effect to minimize mass loss, enabling longer processing times without compromising the sample.
Effective use of inert gases transforms the processing environment from a vacuum of loss into a stabilized system of control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Inert Gas (Argon/Helium) | Benefit to Stainless Steel Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporation Control | Acts as a physical suppression barrier | Inhibits loss of volatile alloy elements |
| Atomic Physics | Increases collision probability | Redirects metal atoms back into the melt |
| Alloy Integrity | Prevents compositional drift | Ensures final product meets metallurgical specs |
| Maintenance | Reduces metal dust condensation | Protects heating elements and furnace windows |
| Process Duration | Minimizes material mass loss | Extends the viable experimental and analysis window |
Precision High-Temperature Solutions for Your Laboratory
Maintaining alloy fidelity requires absolute control over your thermal environment. At KINTEK, we understand that the right atmosphere is as critical as the right temperature. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific inert gas and vapor-shielding requirements.
Our specialized laboratory high-temp furnaces are designed to protect your samples from compositional drift while safeguarding your equipment from contamination.
Ready to elevate your metallurgical research? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our customizable furnace solutions can optimize your high-temperature processes.
Visual Guide
References
- Jannatun Nawer, Douglas M. Matson. Thermodynamic assessment of evaporation during molten steel testing onboard the International Space Station. DOI: 10.1038/s41526-024-00416-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are inert gases like nitrogen and argon used in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- Why compare air and nitrogen atmospheres in CZTS post-annealing? Isolate Oxygen's Impact for Higher Efficiency
- Why is high-temperature annealing in an Air Atmosphere Furnace necessary for YAG ceramics after vacuum sintering? Achieve Optical Clarity and Mechanical Stability
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What is the role of a laboratory annealing furnace in memristor fabrication? Enhance Interface & Stability
- How are atmosphere furnaces used in material processing? Master Precise Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What are the environmental benefits of using furnace atmospheres? Reduce Emissions and Waste with Advanced Control
- What protective role does a constant flow of inert gas play in dynamic atmosphere sintering? Enhance Material Integrity



















