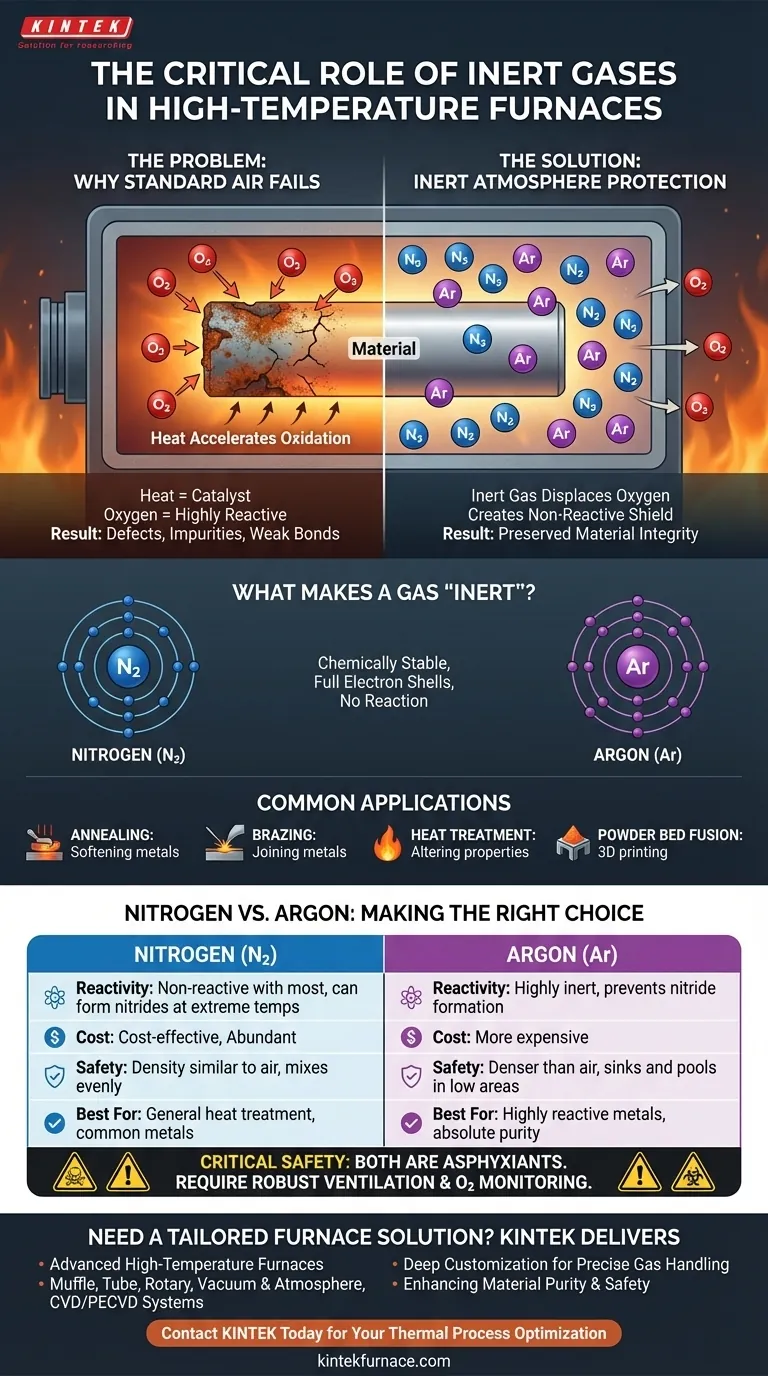
Inert gases are used in high-temperature furnaces to create a protective, non-reactive atmosphere around the material being processed. This gaseous shield displaces oxygen and other reactive elements from the air, which would otherwise cause damaging oxidation, contamination, and unwanted chemical changes at elevated temperatures.
The fundamental challenge in high-temperature processing is that heat accelerates unwanted chemical reactions, primarily with oxygen. Using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is not about adding something to the process, but about removing the reactive element—oxygen—to preserve the material's integrity.
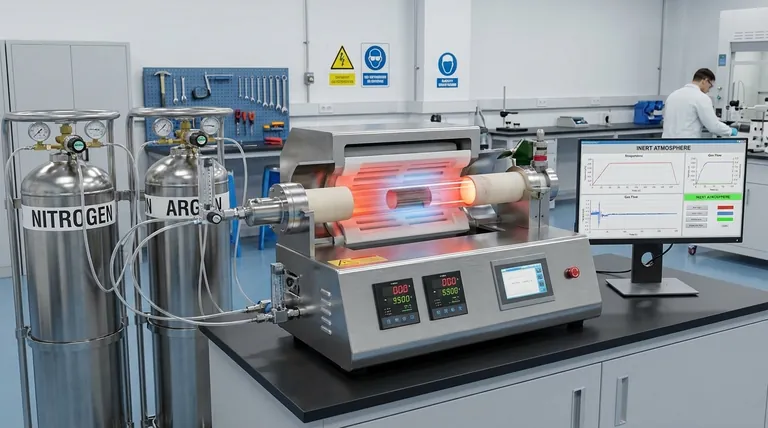

The Problem: Why a Standard Atmosphere Fails
When materials are heated in normal air, the process itself can become the source of defects. This is a critical issue in industries like aerospace and manufacturing where material properties must be precise.
Heat as an Unwanted Catalyst
High heat acts as a powerful catalyst for chemical reactions. At room temperature, many materials are stable in air, but once heated in a furnace, their atoms become energized and far more likely to bond with surrounding elements.
The Role of Oxygen in Oxidation
Oxygen is highly reactive, especially at high temperatures. When a hot metal or other material is exposed to oxygen, it rapidly forms oxides on the surface. This is the same basic process as rusting, but it occurs in minutes or seconds instead of years.
The Impact on Material Integrity
This oxidation compromises the material's quality. It can create a brittle surface layer, introduce impurities into the alloy, weaken structural bonds in processes like brazing, and ultimately cause the finished part to fail.
The Solution: Creating a Controlled, Inert Atmosphere
To prevent these destructive reactions, the furnace chamber is purged of air and filled with a gas that will not participate in any chemical reactions.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
Inert gases, like nitrogen and argon, are chemically stable because their outermost electron shells are full. They have no tendency to share, gain, or lose electrons, meaning they will not react with other elements, even under intense heat.
How Inert Gas Protects the Material
The inert gas is used to physically displace all the oxygen and moisture from the furnace chamber. By flooding the environment with a non-reactive gas, the heated material is effectively shielded. There is simply no oxygen left for it to react with.
Common Applications
This technique is essential for sensitive thermal processes where material purity is paramount. Key applications include:
- Annealing: Softening metals to improve ductility.
- Brazing: Joining two pieces of metal with a filler material.
- Heat Treatment: Altering the physical and chemical properties of a material.
- Powder Bed Fusion: 3D printing with metal powders.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Nitrogen vs. Argon
While both are inert, the choice between nitrogen and argon depends on material sensitivity, cost, and safety factors.
Nitrogen: The Cost-Effective Workhorse
Nitrogen (N₂) is the most common inert gas used in furnaces because it is abundant and relatively inexpensive. It effectively prevents oxidation for a wide range of common metals and processes.
Argon: The High-Purity Specialist
Argon (Ar) is significantly more inert than nitrogen. While nitrogen is non-reactive with most materials, it can react with certain highly sensitive metals at extreme temperatures to form nitrides. For materials like titanium or certain stainless steels, argon is required to ensure absolute purity.
Critical Safety Considerations
Both gases are non-toxic, but they are asphyxiants. They can kill by displacing oxygen in a confined space, and this hazard must be managed carefully.
Their physical properties create different risks. Argon is denser than air and will sink, creating invisible, oxygen-deficient pools in low-lying areas of a facility. Nitrogen has a density similar to air and will mix more evenly, reducing oxygen levels throughout a poorly ventilated room. Proper ventilation and continuous oxygen monitoring are non-negotiable safety requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice between nitrogen and argon depends entirely on your material requirements, budget, and safety protocols.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment and cost-efficiency: Nitrogen is typically the superior choice for preventing basic oxidation in most common metals.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals or ensuring absolute purity: Argon is necessary to prevent even minor nitride formation and guarantee the highest material integrity.
- If your primary focus is safety (which it must always be): You must implement robust ventilation and continuous oxygen monitoring, accounting for the different physical behaviors of nitrogen and argon.
By understanding these principles, you can ensure both the quality of your product and the safety of your team.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Nitrogen | Argon |
|---|---|---|
| Reactivity | Non-reactive with most materials | Highly inert, prevents nitride formation |
| Cost | Cost-effective and abundant | More expensive |
| Safety | Density similar to air, mixes evenly | Denser than air, sinks and pools |
| Best For | General heat treatment, common metals | Highly reactive metals, absolute purity |
Need a furnace solution tailored to your inert gas requirements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise handling of inert gases to meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing material purity and safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision



















