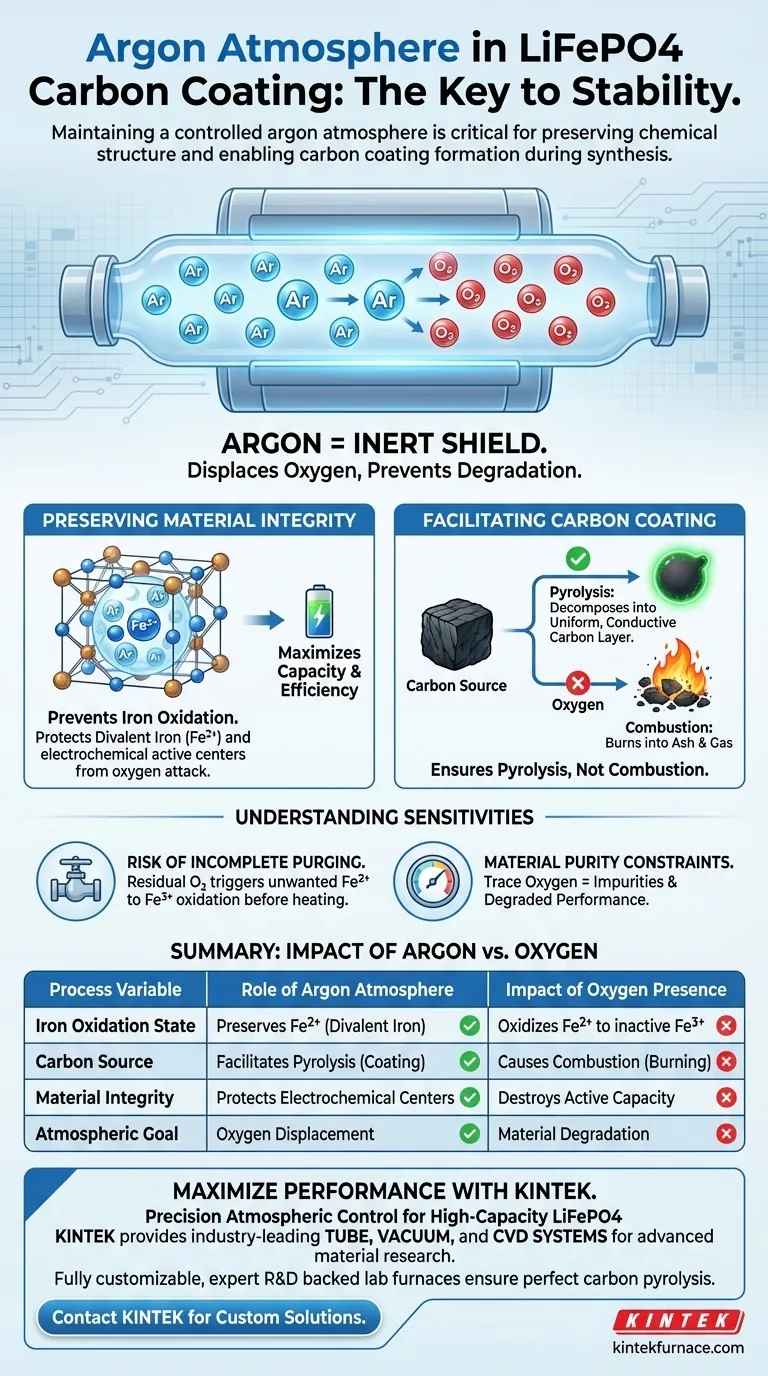
Maintaining a controlled argon atmosphere is the single most critical factor in preserving chemical stability during LiFePO4 synthesis. In the context of a quartz tube furnace, argon serves as an inert shield that displaces atmospheric oxygen. This prevents the degradation of the material’s chemical structure and allows the necessary carbon coating to form through thermal decomposition rather than burning away.
By eliminating oxygen, argon preserves the essential divalent iron (Fe2+) state required for electrochemical activity and ensures carbon sources undergo pyrolysis rather than combustion.

Preserving Material Integrity
Preventing Iron Oxidation
The primary threat to LiFePO4 at high temperatures is the presence of oxygen. An argon atmosphere effectively prevents the oxidation of divalent iron (Fe2+) into trivalent iron (Fe3+).
Protecting Active Centers
The performance of the battery material relies heavily on specific electrochemical active centers. If the iron oxidizes due to a lack of inert gas, these centers are compromised, significantly reducing the material's capacity and efficiency.
Facilitating the Carbon Coating
Pyrolysis vs. Combustion
The objective of the process is to decompose a carbon source to create a conductive coating. In the presence of oxygen, carbon sources would simply combust (burn), leaving behind ash or gas rather than a useful coating.
Ensuring Proper Decomposition
Argon ensures the carbon source undergoes pyrolysis. This process allows the organic material to chemically decompose in an oxygen-free environment, depositing a uniform, conductive carbon layer onto the LiFePO4 particles.
Understanding Process Sensitivities
The Risk of Incomplete Purging
It is not sufficient to simply introduce argon into the quartz tube; the system must be thoroughly purged. Any residual oxygen remaining in the tube before heating begins can trigger the unwanted oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+.
Material Purity Constraints
There is no middle ground regarding atmospheric control in this synthesis. Even trace amounts of oxygen can lead to impurities that degrade the electronic conductivity and overall performance of the final battery cathode.
Ensuring Synthesis Success
To achieve high-quality LiFePO4, you must treat the atmospheric control as a precision variable rather than a passive setting.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Prioritize the complete displacement of oxygen to strictly maintain the Fe2+ oxidation state.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity: Maintain a continuous, positive pressure of argon to ensure the carbon source undergoes pyrolysis without combustion.
A strictly controlled argon atmosphere is the foundational requirement for converting raw precursors into high-performance, electrochemically active battery materials.
Summary Table:
| Process Variable | Role of Argon Atmosphere | Impact of Oxygen Presence |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Oxidation State | Preserves Fe2+ (Divalent Iron) | Oxidizes Fe2+ to inactive Fe3+ |
| Carbon Source | Facilitates Pyrolysis (Coating) | Causes Combustion (Burning) |
| Material Integrity | Protects Electrochemical Centers | Destroys Active Capacity |
| Atmospheric Goal | Oxygen Displacement | Material Degradation |
Maximize Your Battery Material Performance with KINTEK
Precision atmospheric control is the difference between high-capacity LiFePO4 and failed synthesis. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically engineered to maintain the rigorous inert environments required for advanced material research.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your unique processing needs—ensuring complete oxygen displacement and perfect carbon pyrolysis every time.
Ready to elevate your material purity? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Da Eun Kim, Yong Joon Park. Improving the Electrochemical Properties of LiFePO4 by Mixed-source-derived Carbon Layer. DOI: 10.33961/jecst.2025.00213
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory tube furnace in BiFeO3 nanopowder production? Master the Calcination Stage
- Why is heat treatment in a tube furnace or muffle furnace required after synthesizing magnesium hydroxide nano-precursors via electrochemical methods? Unlock the Full Potential of Your MgO Nanomaterials
- Why must air inlets be equipped with HEPA filters? Preventing Fiber Backflow in Split Tube Furnace Enclosures
- What factors should be considered when selecting a horizontal electric furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency for Your Lab
- How do horizontal furnaces support the ceramics industry? Boost Performance with Precision Heat Treatment
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for CrFeNi alloy treatment? Ensure Single-Phase Microstructural Stability
- What are the handling and placement precautions for a vacuum tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace in Ti3AlC2 synthesis? Achieve Pure MAX Phase Precursor Powders



















