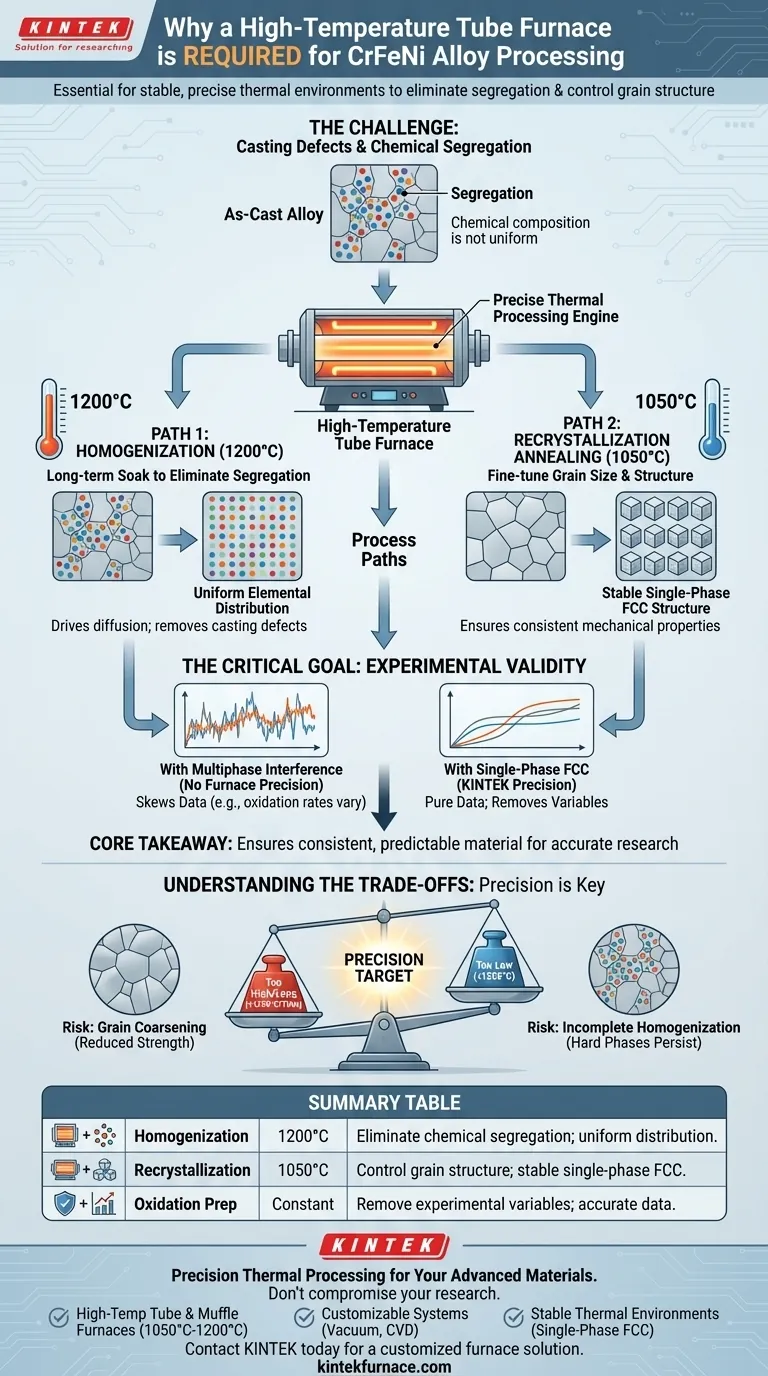
A high-temperature tube furnace is essential for processing CrFeNi medium-entropy alloys because it provides the stable, precise thermal environment required to eliminate chemical segregation and control grain structure. Specifically, it enables homogenization at 1200°C to remove casting defects and recrystallization annealing at 1050°C to achieve a uniform single-phase microstructure.
Core Takeaway The primary function of the furnace is to ensure the alloy achieves a stable single-phase face-centered cubic (FCC) structure. By eliminating chemical variation and multiphase structures, the treatment ensures that subsequent experiments, such as oxidation behavior analysis, are not skewed by microstructural inconsistencies.

Eliminating Chemical Composition Segregation
The Challenge of Casting
During the initial casting process of CrFeNi alloys, the chemical composition does not distribute perfectly evenly. This results in "segregation," where certain elements cluster together rather than mixing uniformly throughout the matrix.
The Solution: High-Temperature Homogenization
To correct this, the alloy requires a long-term "soaking" period at extremely high temperatures, specifically around 1200°C.
The Mechanism
The high-temperature tube furnace maintains this intense heat stably over long periods. This thermal energy drives diffusion, forcing the segregated elements to disperse until the material is chemically uniform.
Achieving Microstructural Stability
Recrystallization Annealing
After homogenization and processing, the alloy undergoes recrystallization annealing. The primary reference specifies a precise temperature of 1050°C for this stage.
Controlling Grain Size
This specific temperature allows researchers to fine-tune the grain size of the alloy. Proper grain size is critical for defining the material's mechanical and physical properties.
Establishing the Single-Phase Structure
The ultimate goal of this annealing step is to produce a stable, single-phase face-centered cubic (FCC) structure. This transforms the alloy into a consistent, predictable material.
The Critical Role of Experimental Validity
Removing Variables
For scientific accuracy, particularly in comparative experiments like oxidation studies, the material must be uniform.
Eliminating Multiphase Interference
If the alloy contains multiphase structures (mixtures of different crystal structures), these phases will oxidize at different rates. This creates "noise" in the data.
Ensuring Pure Data
By using the furnace to guarantee a single-phase FCC structure, researchers eliminate the interference of multiphase structures. This ensures that observed behaviors are due to the alloy's intrinsic properties, not inconsistent processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
While high heat is necessary, precision is non-negotiable. As seen in similar alloy systems (like TiAl), minor temperature deviations can lead to drastic, unintended changes in phase content.
Risk of Grain Coarsening
If the temperature is too high or the holding time is uncontrolled, the grain size may grow excessively (coarsening). While this dissolves second phases, it can negatively impact yield strength.
Risk of Incomplete Homogenization
Conversely, if the temperature fluctuates below the target 1200°C, chemical segregation may remain. This results in "hard" phases or skeleton structures persisting in the matrix, compromising the alloy's plasticity and validity for testing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is oxidation research: Prioritize the 1050°C annealing step to ensure a single-phase FCC structure, eliminating multiphase interference in your data.
- If your primary focus is mechanical uniformity: Prioritize the 1200°C homogenization soak to fully eliminate chemical segregation and casting defects.
Success depends on utilizing the furnace's precision to balance the dissolution of defects against the risk of microstructural coarsening.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Temperature | Primary Objective | Microstructural Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homogenization | 1200°C | Eliminate chemical segregation | Uniform elemental distribution; removes casting defects |
| Recrystallization | 1050°C | Control grain structure | Stable single-phase FCC structure; consistent mechanical properties |
| Oxidation Prep | Constant Heat | Remove experimental variables | Prevents multiphase interference for accurate data analysis |
Precision Thermal Processing for Your Advanced Materials
Don't let chemical segregation or inconsistent grain structures compromise your research data. KINTEK provides high-performance high-temperature furnaces engineered for the rigorous demands of medium-entropy alloy processing.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer:
- High-Temp Tube & Muffle Furnaces: Perfect for precise 1050°C-1200°C annealing and homogenization.
- Customizable Systems: Tailored Vacuum, CVD, and Rotary systems to meet your unique material specs.
- Stable Thermal Environments: Eliminate multiphase interference and ensure a uniform single-phase FCC structure every time.
Ready to elevate your material science experiments? Contact KINTEK today for a customized furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Anna M. Manzoni, Christiane Stephan‐Scherb. High‐Temperature Oxidation of the CrFeNi Medium‐Entropy Alloy. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202500400
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the accuracy of microplastic thermal decomposition? Ensure Pyrolysis Precision
- Why is an industrial-grade high-temperature tube furnace used for TiO2NW? Optimize Nanowire Annealing
- What are the roles of a vacuum tube furnace and a CCD camera in high-temperature wettability testing? Key Insights
- What are the specifications for large volume single zone tube furnaces? Find Your Ideal High-Temp Solution
- What is the purpose of using an industrial-grade vertical tube furnace in phosphorus recovery? High-Fidelity Simulation
- What role does an Electrically Heated Drop Tube Furnace (DTF) play in iron powder experiments? Boost Your Research Now!
- What are the benefits of using an alumina tube furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temp Material Processing
- How does a laboratory tube furnace facilitate the sulfidation of Co3O4@CNT? Advanced Synthesis Secrets



















