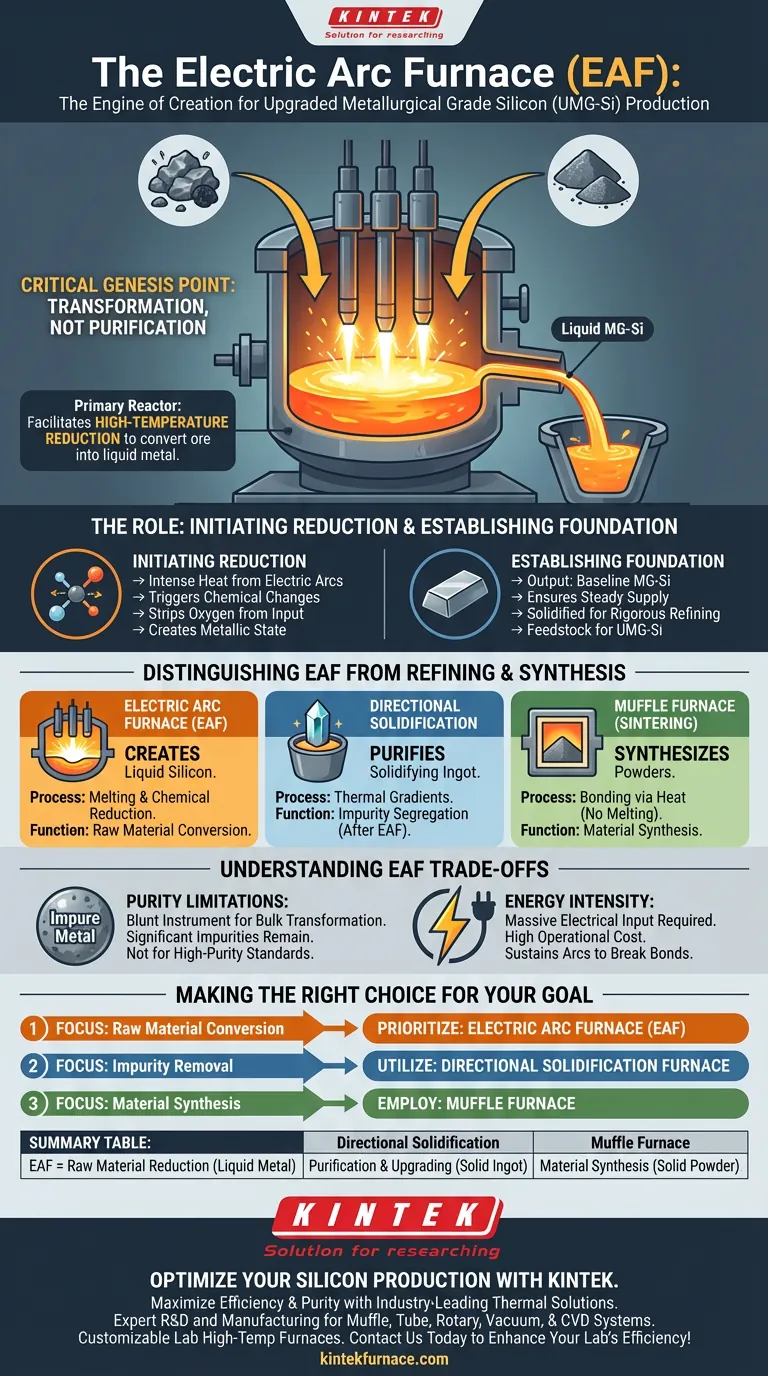
The electric arc furnace (EAF) serves as the critical genesis point in the production of upgraded metallurgical grade silicon (UMG-Si). It functions as the primary reactor where raw materials undergo a high-temperature reduction process to transform from ore into liquid metal. This initial step creates the foundational metallurgical grade silicon that serves as the necessary feedstock for all subsequent purification and upgrading stages.
The electric arc furnace is not primarily a tool for purification, but for transformation. Its core function is to facilitate the reduction reaction that turns raw ingredients into the initial silicon metal required to begin the Upgraded Metallurgical Grade Silicon (UMG-Si) value chain.
The Role of the EAF in the Production Chain
Initiating the Reduction Process
The primary technical function of the electric arc furnace is to facilitate a reduction reaction.
Inside the furnace, intense heat generated by electric arcs triggers chemical changes in the raw materials.
This process strips oxygen from the input material, effectively converting it into a metallic state known as metallurgical grade silicon.
Establishing the Material Foundation
The output of the electric arc furnace is the baseline material for the entire industry.
While the goal is "upgraded" silicon, the process must start with standard metallurgical grade silicon (MG-Si).
The EAF ensures there is a steady supply of this liquid silicon foundation, which is then solidified and prepared for the rigorous refining steps that follow.
Distinguishing the EAF from Refining Technologies
EAF vs. Directional Solidification
It is vital to distinguish between the creation of silicon and the purification of silicon.
The electric arc furnace creates the liquid silicon metal.
In contrast, a directional solidification furnace is used later in the process to remove metallic impurities.
As noted in advanced processing, directional solidification controls temperature gradients to push impurities to the top of the ingot, a step that is only possible after the EAF has done its work.
EAF vs. Sintering Processes
The EAF should also not be confused with muffle furnaces used in material synthesis.
Muffle furnaces are typically utilized for sintering, where powdered materials are heated to form a solid mass without melting.
The EAF acts conversely; it relies on fully melting and chemically reducing materials rather than bonding powders via heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Purity Limitations
The electric arc furnace is a blunt instrument compared to downstream equipment.
It is designed for bulk transformation and volume, not for achieving high-purity semiconductor standards immediately.
The silicon produced here contains significant impurities that must be removed later; expecting high-purity output directly from the EAF is technically infeasible.
Energy Intensity
The reduction process within an EAF is highly energy-intensive.
It requires massive electrical input to sustain the arcs necessary for breaking chemical bonds.
This makes the EAF stage one of the most costly operational steps in terms of power consumption within the silicon production lifecycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your production line, you must align the equipment function with your specific processing stage.
- If your primary focus is raw material conversion: Prioritize the electric arc furnace to efficiently reduce ore into liquid metallurgical grade silicon.
- If your primary focus is impurity removal: Utilize a directional solidification furnace to segregate metallic impurities and upgrade the silicon quality.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis: Employ a muffle furnace for sintering powders into solids without melting the base material.
Success in silicon production requires recognizing that the electric arc furnace is the engine of creation, while subsequent furnaces are the engines of refinement.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Function | State of Material | Core Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Arc (EAF) | Raw Material Reduction | Liquid Metal | Chemical reduction of ore to MG-Si |
| Directional Solidification | Purification & Upgrading | Solidifying Ingot | Impurity segregation via thermal gradients |
| Muffle Furnace | Material Synthesis | Solid Powder | Sintering and bonding without melting |
Optimize Your Silicon Production with KINTEK
Maximize your metallurgical efficiency and material purity with industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique production needs.
Whether you are refining silicon or synthesizing advanced materials, our team ensures you have the precision equipment to succeed. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
References
- Production of upgraded metallurgical-grade silicon for a low-cost, high-efficiency, and reliable PV technology. DOI: 10.3389/fphot.2024.1331030
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum desiccator used for the preservation of extracted fruit peel extracts? Protect Bioactive Compounds
- Why is a laboratory blast drying oven necessary for preparing Reduced Graphene Oxide precursors? Ensure Powder Quality
- What is the significance of using a laboratory electric furnace for the quenching and tempering of hull steel? Achieve Precise Microstructure Control
- What is the purpose of setting an industrial drying oven to 70°C for sludge? Preserve Volatiles & Optimize Pre-treatment
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum drying oven? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Mortar Testing
- What role does an RTA system play in processing SiN thin films? Unlock High-Performance Quantum & Optical Materials
- What is the primary function of carbonization equipment? Master Biomass to Fuel Conversion with Precision
- What causes the increase in specific gravity of Moso Bamboo? Master Cellular Densification in Heat Treatment



















