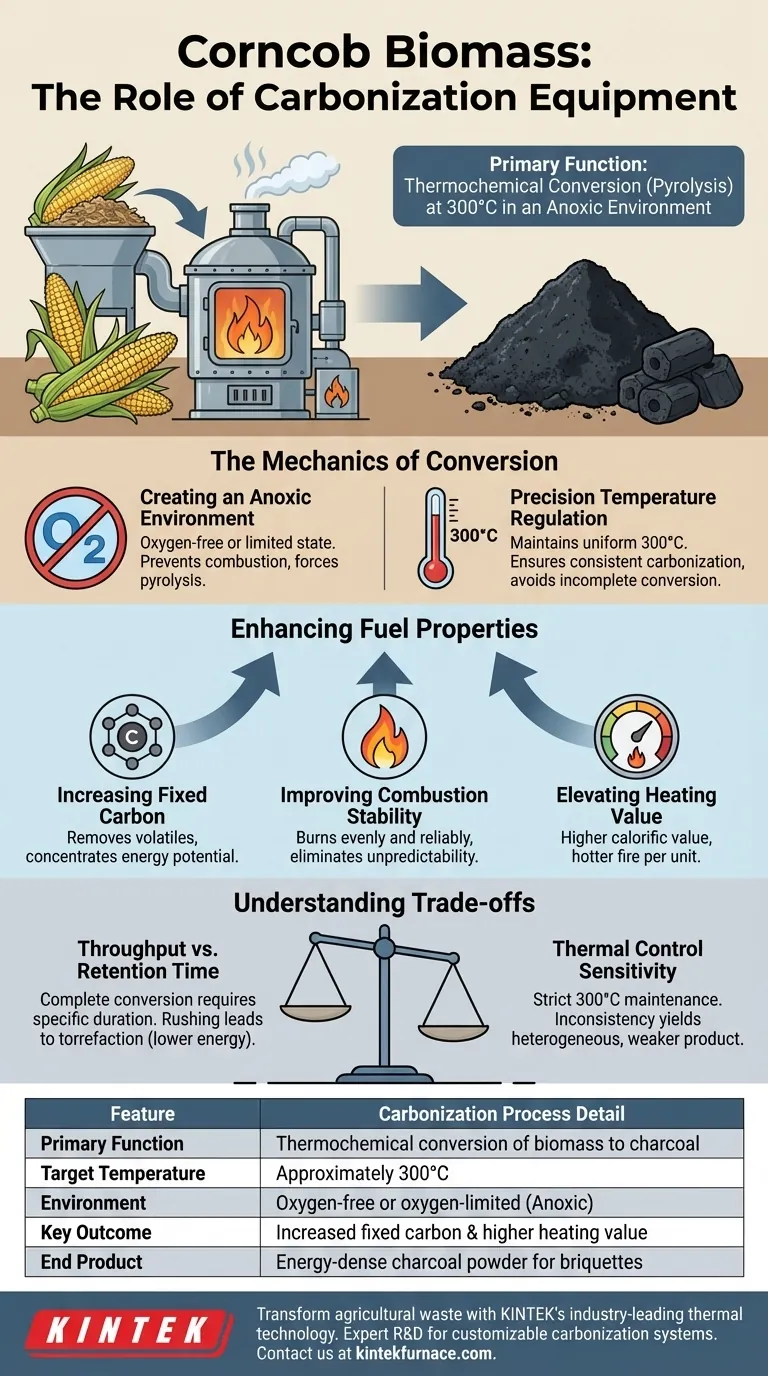
The primary function of carbonization equipment is to subject raw corncob biomass to a controlled, high-temperature environment to induce thermochemical conversion. Specifically, this machinery maintains a temperature of approximately 300°C within an oxygen-free or oxygen-limited chamber to execute pyrolysis. This process transforms the raw organic material into charcoal powder with a significantly higher fixed carbon content, serving as a superior precursor for biomass briquettes.
Core Takeaway: Carbonization equipment is the critical "refining" stage that turns low-grade agricultural waste into high-grade fuel by stripping away volatiles and concentrating carbon, thereby ensuring the final fuel source is stable and energy-dense.

The Mechanics of Conversion
To understand the value of this equipment, you must look beyond simple heating and understand the specific environment it creates.
Creating an Anoxic Environment
The equipment’s most vital role is atmospheric control. It ensures that the heating process occurs in an oxygen-free or oxygen-limited state.
If oxygen were present at these temperatures, the corncobs would simply combust and turn to ash. By excluding oxygen, the equipment forces pyrolysis, causing the material to decompose chemically without burning.
Precision Temperature Regulation
The reference specifies a target temperature of around 300°C. The equipment must maintain this thermal consistency to ensure uniform carbonization.
At this specific temperature range, the volatile components of the corncob are driven off, leaving behind the carbon structure. Fluctuations below this range result in incomplete conversion, while excessive heat could degrade the material structure unnecessarily.
Enhancing Fuel Properties
The ultimate goal of using this equipment is to alter the physical and chemical properties of the biomass to make it a viable fuel.
Increasing Fixed Carbon
Raw corncobs have relatively low energy density. The carbonization equipment concentrates the energy potential by removing moisture and volatile gases.
This results in a charcoal powder with high fixed carbon content. This "fixed carbon" is the fuel that provides sustained heat during combustion.
Improving Combustion Stability
Raw biomass tends to burn unpredictably, often producing smoke and fluctuating heat.
By converting the material into charcoal powder first, the equipment ensures the resulting biomass briquettes possess improved combustion stability. This creates a fuel source that burns evenly and reliably.
Elevating Heating Value
The process directly improves the heating value (calorific value) of the fuel. The output creates a hotter fire per unit of weight compared to the raw agricultural waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While carbonization is essential for high-quality fuel, it introduces specific operational constraints that must be managed.
Throughput vs. Retention Time
Achieving a complete thermochemical conversion requires the biomass to remain in the 300°C zone for a specific duration.
Rushing the material through the equipment to increase production speed will lead to "torrefaction" (light roasting) rather than true carbonization, resulting in a lower energy product.
Thermal Control Sensitivity
The process is highly sensitive to the 300°C benchmark.
If the equipment fails to maintain this temperature uniformly, you will produce a heterogeneous mix of raw cob and charcoal. This inconsistency weakens the structural integrity and burn quality of the final briquettes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of carbonization equipment dictates the quality tier of your final biomass product.
- If your primary focus is High-Energy Industrial Fuel: Ensure your equipment can strictly maintain the 300°C threshold to maximize fixed carbon content and heating value.
- If your primary focus is Production Consistency: Prioritize equipment with precise atmospheric controls to prevent oxygen leakage, ensuring stable combustion in the final product.
Carbonization is not just a heating step; it is the fundamental chemical upgrade that turns waste into a valuable energy commodity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Carbonization Process Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermochemical conversion of biomass to charcoal |
| Target Temperature | Approximately 300°C |
| Environment | Oxygen-free or oxygen-limited (Anoxic) |
| Key Outcome | Increased fixed carbon & higher heating value |
| End Product | Energy-dense charcoal powder for briquettes |
Transform agricultural waste into high-value energy with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal technology. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet your precise carbonization requirements. Whether you are optimizing industrial fuel production or researching biomass conversion, our team delivers the consistency and thermal control you need to succeed. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom laboratory or production furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Adam Yonanda, Elvianto Dwi Daryono. Optimization of Natural Adhesive Type and Concentration on Characteristics of Corn Cob Biobriquettes. DOI: 10.70609/gtech.v9i1.6194
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is high-purity argon gas used to purge the furnace? Ensure Precision in TGA Oxidation Kinetic Tests
- Why are carbon nanotubes considered superior adsorbents? Efficient Removal of Harmful Organic Gases
- What is the importance of dental restorations? Restore Function and Prevent Oral Health Decline
- How can high-temperature furnace systems be used to evaluate and prevent slagging? Optimize Boiler Performance
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven utilized for ZnO-FL drying? Preserving Delicate Nanoparticle Morphologies
- What is the purpose of the two-step heat treatment process? Optimize Zirconolite-Based Glass-Ceramic Matrices
- How does precise temperature control affect MoS2/rGO hybrids? Mastering Nanowall Morphology
- How does the introduction of SiO2 as an additive improve the sintering process of solid electrolytes? Boost Densification



















