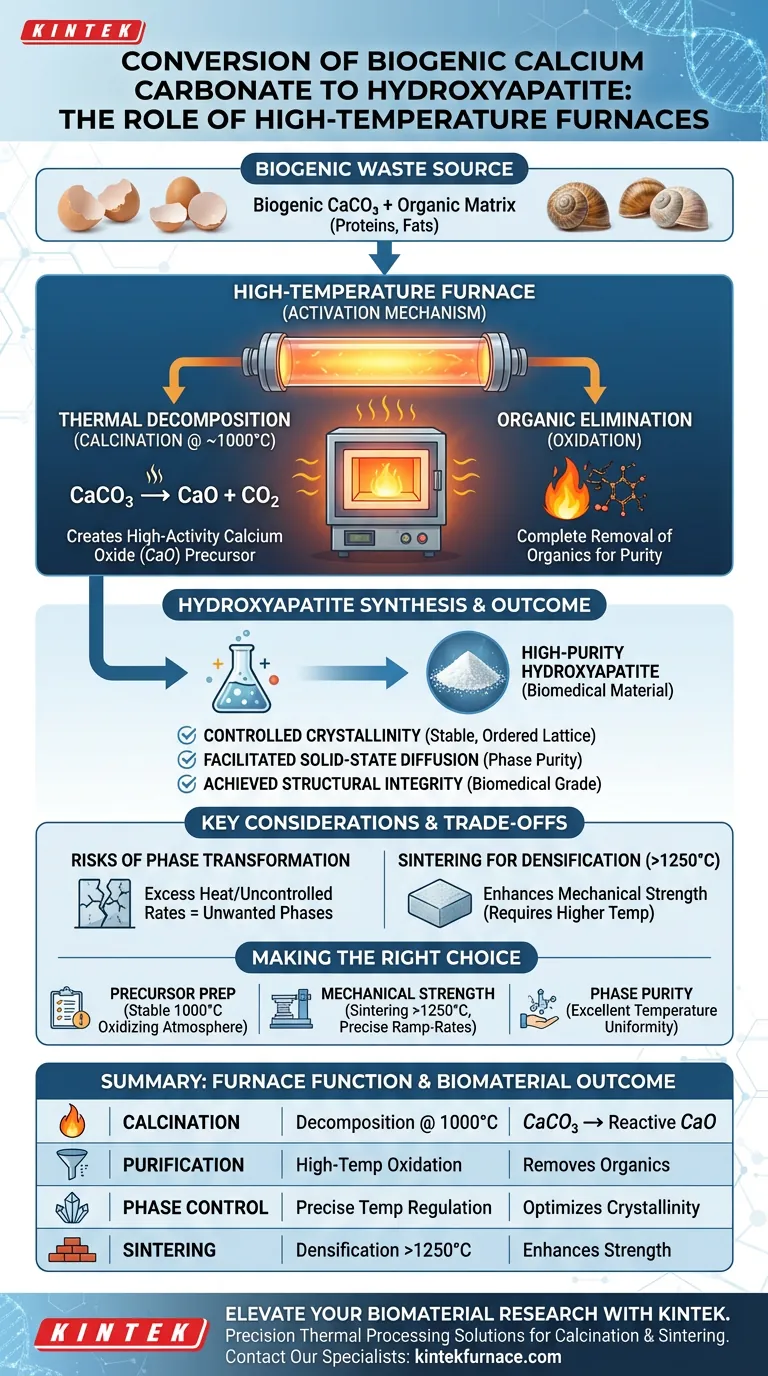
High-temperature tube or muffle furnaces serve as the primary activation mechanism in the conversion of biogenic calcium carbonate into hydroxyapatite.
Specifically, these furnaces facilitate calcination, a process that involves heating materials like eggshells or snail shells to approximately 1000°C. This high-heat environment performs two critical functions simultaneously: it obliterates organic contaminants (like proteins) and thermally decomposes calcium carbonate ($CaCO_3$) into high-activity calcium oxide ($CaO$), which is the essential precursor required for the chemical synthesis of hydroxyapatite.
The transformation from biological waste to biomedical material relies on precise thermal decomposition. By converting stable, organic-laden calcium carbonate into reactive calcium oxide, these furnaces create the chemical foundation necessary to synthesize high-purity hydroxyapatite.

The Mechanics of Thermal Conversion
Decomposing the Mineral Structure
The primary reference indicates that the core function of the furnace is to drive the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate ($CaCO_3$).
When biogenic materials are subjected to temperatures around 1000°C, the $CaCO_3$ structure breaks down. This reaction releases carbon dioxide and leaves behind calcium oxide ($CaO$). This oxide is a highly active chemical precursor, unlike the stable carbonate, making it chemically receptive to the phosphorus sources introduced later to form hydroxyapatite.
Eliminating Organic Matrices
Biogenic sources are rarely pure minerals; they are composite structures containing organic matrices such as collagen, fats, or proteins.
The furnace acts as an oxidation chamber. By maintaining a high-temperature oxidizing environment, it ensures the complete removal of these organic components. This step is non-negotiable for biomedical applications, where residual organics could trigger immune responses or weaken the final ceramic structure.
Achieving Structural Integrity and Purity
Controlling Crystallinity
Beyond simple decomposition, the furnace environment dictates the atomic arrangement of the resulting material.
Supplementary data suggests that precise temperature control allows for the optimization of crystallinity. A consistent thermal environment ensures that the atoms arrange themselves in a stable, ordered lattice, which directly correlates to the material's thermal stability and biological performance.
Facilitating Solid-State Diffusion
In methods involving solid-state synthesis, the furnace provides the energy required for diffusion.
Heat mobilizes atoms, allowing calcium and phosphorus reactants to diffuse across particle boundaries. This facilitates the chemical reactions necessary to form the hydroxyapatite phase without melting the material, ensuring high phase purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Phase Transformation
While high heat is necessary for conversion, excessive heat or uncontrolled heating rates can be detrimental.
If the temperature exceeds specific thresholds or fluctuates wildly, the hydroxyapatite can decompose into unwanted phases (such as tricalcium phosphate), altering its biological solubility. Precise heating curves are essential to maintain the specific crystal structure required for bioactivity.
Calcination vs. Sintering Requirements
It is vital to distinguish between preparing the precursor and densifying the final product.
While calcination (making $CaO$ from shells) typically occurs around 1000°C, sintering (densifying the final hydroxyapatite scaffold) may require temperatures exceeding 1250°C. A furnace selected for calcination must have the thermal headroom to handle sintering if you intend to perform both steps in the same equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your thermal processing equipment, align the furnace capabilities with your specific processing stage.
- If your primary focus is precursor preparation: Prioritize a furnace capable of maintaining a stable oxidizing atmosphere at 1000°C to ensure complete conversion of $CaCO_3$ to active $CaO$.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Ensure your furnace can reach sintering temperatures (>1250°C) with precise ramp-rate controls to achieve densification without decomposing the hydroxyapatite phase.
- If your primary focus is phase purity: Utilize a furnace with excellent temperature uniformity to prevent "hot spots" that could cause local phase transformations or incomplete calcination.
The furnace is not merely a heater; it is a precision reactor that defines the chemical purity and structural viability of your final biomaterial.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Furnace Function | Outcome for Biomaterial |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermal decomposition at ~1000°C | Converts $CaCO_3$ to highly reactive $CaO$ |
| Purification | High-temperature oxidation | Complete removal of organic proteins and fats |
| Phase Control | Precise temperature regulation | Optimizes crystallinity and prevents unwanted phases |
| Sintering | Densification at >1250°C | Enhances mechanical strength and structural integrity |
Elevate Your Biomaterial Research with KINTEK
Precision thermal processing is the difference between biological waste and high-performance hydroxyapatite. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the rigorous demands of calcination and sintering.
Our customizable lab furnaces ensure superior temperature uniformity and precise ramp-rate control, allowing you to achieve maximum phase purity and structural integrity for your biomedical applications.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process?
Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace solution for your unique laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Sara Piras, Carlo Santulli. Biomimetic Use of Food-Waste Sources of Calcium Carbonate and Phosphate for Sustainable Materials—A Review. DOI: 10.3390/ma17040843
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the muffle furnace optimize the processing workflow? Achieve Faster, Purer, and More Precise Results
- What scientific processes can a muffle furnace assist with? Unlock Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- How is a muffle furnace utilized in ash testing? Achieve Accurate Mineral Analysis for Your Lab
- What materials can be processed in a muffle furnace? Explore Versatile High-Temp Solutions
- What are some common applications of muffle furnaces? Unlock Clean, High-Temperature Solutions for Your Lab
- What makes muffle furnaces suitable for heat treatment processes? Achieve Precise, Uniform Heating for Your Materials
- What controls the temperature regulation in a muffle furnace? Master Precision with Advanced PID Controllers
- Why is a high-precision muffle furnace required for BCZT xerogel pre-calcination? Ensure Pure Phase and Reactivity



















