In ash testing, a muffle furnace serves as a high-temperature oven designed to completely burn away all organic material from a sample. This process, known as incineration or ashing, leaves behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue (ash). The mass of this resulting ash is then measured to determine the precise ash content of the original substance, which is a critical quality metric in fields ranging from food science to materials engineering.
The core purpose of using a muffle furnace for ashing is to achieve complete combustion in a highly controlled and contaminant-free environment. This allows for the precise isolation and quantification of a material's inorganic mineral content.

The Fundamental Principle: Combustion and Isolation
Ash testing is a method of gravimetric analysis, meaning it relies on measuring mass. The muffle furnace is the instrument that enables the controlled decomposition required for this measurement.
What is "Ash"?
In this context, ash is the inorganic residue that remains after a sample is heated to a very high temperature. It primarily consists of minerals like calcium, potassium, magnesium, and other metallic and non-metallic elements that do not burn.
How the Furnace Achieves This
A muffle furnace operates at temperatures typically between 500°C and 1000°C. By placing a pre-weighed sample into the furnace for a set period, the intense heat causes all organic compounds (those based on carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) to combust and turn into gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, which then leave the system.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's enclosed chamber, which separates the sample from the heating elements. This design is critical because it prevents contamination from the combustion byproducts of the heating source itself, ensuring the resulting ash is purely from the sample. Heating occurs indirectly through thermal radiation and convection.
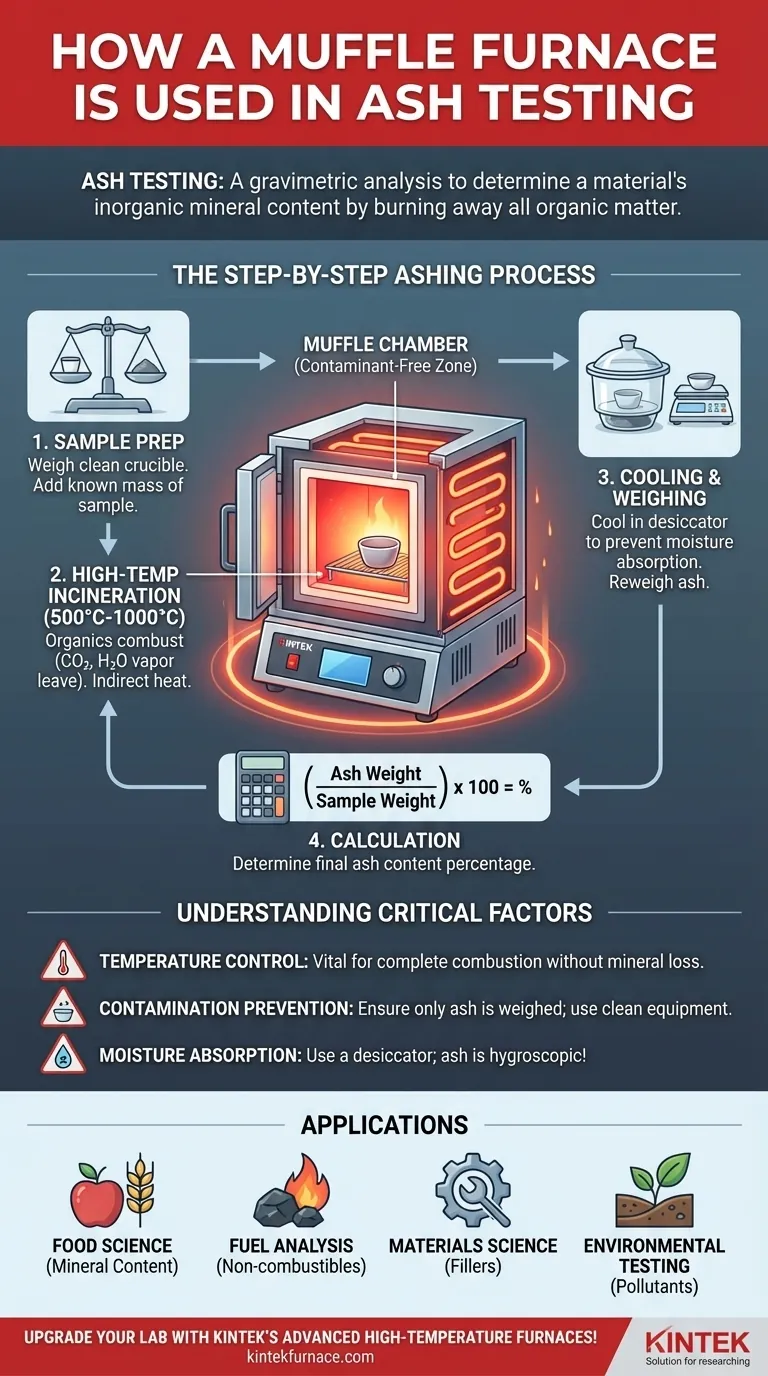
The Step-by-Step Ashing Process
While specific protocols vary by material, the general procedure for determining ash content is universal and methodical.
Step 1: Sample Preparation
A clean, empty container, typically a ceramic crucible, is heated to a high temperature, cooled, and weighed precisely. A known mass of the sample material is then added to this crucible.
Step 2: High-Temperature Incineration
The crucible containing the sample is placed inside the muffle furnace. The furnace is programmed to a specific temperature (e.g., 550°C for many food products) and held there for several hours until the sample is completely reduced to a light gray or white ash.
Step 3: Cooling and Weighing
The crucible is carefully removed from the furnace and placed in a desiccator. A desiccator is a sealed container with a drying agent that prevents the hot, dry ash from absorbing moisture from the air, which would compromise the final weight measurement.
Step 4: Calculation
Once cooled to room temperature, the crucible containing the ash is weighed again. The ash content is calculated as a percentage of the original sample's weight.
Understanding the Critical Factors
Achieving accurate and repeatable results depends on careful control over several variables. Deviating from established protocols can easily lead to incorrect conclusions.
Temperature Control is Paramount
Using a temperature that is too low will result in incomplete combustion, leaving behind charred organic material and artificially inflating the ash value. Conversely, a temperature that is too high can cause some volatile minerals to vaporize and escape, artificially lowering the ash value.
Preventing Sample Contamination
The integrity of the result depends on ensuring the only material being weighed is the ash from the sample. This requires using scrupulously clean crucibles and leveraging the muffle furnace's design to shield the sample from external contaminants.
The Risk of Moisture Absorption
Ash is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Failing to use a desiccator for cooling will cause the ash to gain weight, leading to a significant overestimation of the ash content.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The analysis of ash content provides fundamental information about a material's composition, and its interpretation is specific to the industry.
- If your primary focus is food science: Ash content is a direct measure of the total mineral content, which is a key component of nutritional analysis and a marker for quality and authenticity.
- If your primary focus is fuel analysis (e.g., coal): Ash represents the non-combustible portion of the fuel, which reduces energy efficiency and can cause fouling and slagging in boilers.
- If your primary focus is materials science (e.g., polymers or paper): Ash content often relates to the amount of inorganic fillers or additives used to modify properties like strength, stiffness, or fire resistance.
- If your primary focus is environmental testing: Ashing can be a preparatory step to isolate and analyze inorganic pollutants or heavy metals in samples like soil, sludge, or filters.
Mastering this technique provides a foundational insight into the non-combustible backbone of virtually any material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Burn organic material to isolate inorganic ash for gravimetric analysis |
| Temperature Range | Typically 500°C to 1000°C |
| Key Steps | Sample preparation, incineration, cooling in desiccator, weighing |
| Critical Factors | Precise temperature control, contamination prevention, moisture avoidance |
| Applications | Food science (mineral content), fuel analysis (efficiency), materials science (fillers), environmental testing (pollutants) |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing accuracy in ash testing and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and quality control goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















