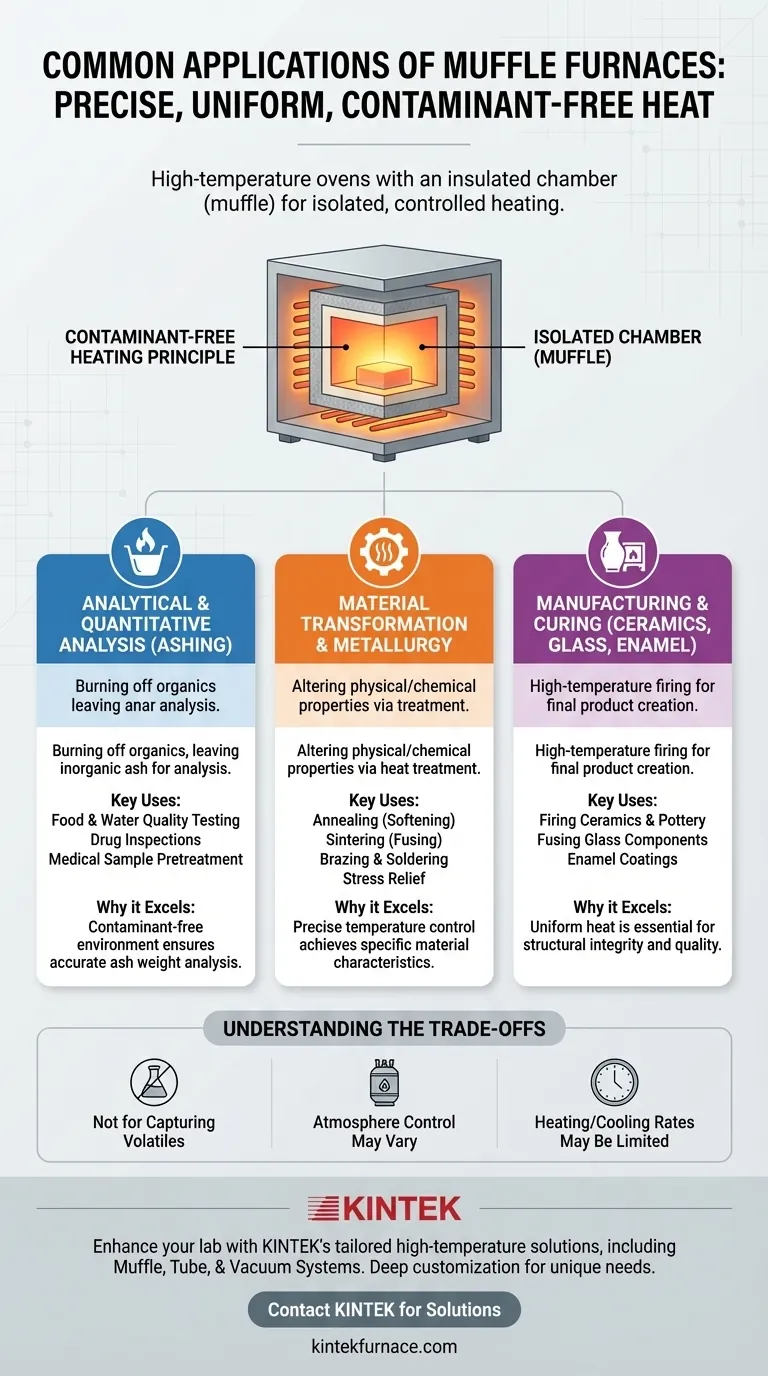
In essence, muffle furnaces are high-temperature ovens used for three primary purposes: analytical testing like ashing, altering the properties of materials through heat treatment, and manufacturing processes for ceramics and glass. Their defining feature is an insulated chamber (the "muffle") that isolates the material being heated from the direct heat source and any contaminants, ensuring a clean and controlled environment.
The core value of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its ability to provide precise, uniform, and contaminant-free heat. This makes it an indispensable tool for processes where the chemical and physical integrity of the sample is paramount.

The Core Principle: Contaminant-Free Heating
A muffle furnace is fundamentally a chamber furnace. Its key design element is the "muffle"—an insulated inner chamber that separates the material being processed from the heating elements.
Modern electrical models heat this chamber through conduction, convection, and blackbody radiation. This design is critical because it eliminates the byproducts of combustion (like gas or soot) that would be present in a fuel-fired furnace, preventing them from contaminating the sample.
This principle of clean, isolated heating is the reason muffle furnaces are trusted in sensitive laboratory and industrial applications.
Key Application Domains
The applications of muffle furnaces can be organized into three main categories, each leveraging the furnace's ability to provide a clean, high-temperature environment.
Analytical and Quantitative Analysis (Ashing)
Ashing is the process of using high temperatures to burn off all organic substances in a sample, leaving only the inorganic, non-combustible ash behind. This is a common method of sample preparation for further analysis.
The contaminant-free environment of a muffle furnace is essential for this work. It ensures that the final ash weight is accurate and not skewed by residue from the heating process itself.
Common uses include determining the ash content in food, analyzing pollutants in water quality tests, drug inspections, and the pretreatment of medical or biological samples.
Material Transformation and Metallurgy
In materials science and metallurgy, heat is used to intentionally alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. This is known as heat treatment.
Muffle furnaces are used for processes like annealing (softening metal), stress relief, sintering (fusing powders together), brazing, and soldering.
The ability to maintain a precise temperature in a controlled atmosphere is vital. It allows metallurgists to achieve specific material characteristics without introducing impurities that could cause weakness or failure.
Manufacturing and Curing (Ceramics, Glass, Enamel)
Many manufacturing processes require high-temperature firing to create a final product. Muffle furnaces provide the uniform and consistent heat needed for these applications.
This includes firing ceramics and pottery, fusing glass components together, and creating hard enamel coatings on metal.
In these processes, any temperature fluctuation or contamination can ruin the final product's structural integrity or aesthetic finish, making the stability of a muffle furnace essential for quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every high-temperature task. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not for Capturing Volatile Compounds
Muffle furnaces are designed to incinerate and vent organic materials. If your goal is to capture and analyze the volatile compounds released during heating, a pyrolysis system or a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) would be more appropriate.
Atmosphere Control is a Key Factor
A standard muffle furnace operates in an ambient air atmosphere. While this is suitable for many applications, some metallurgical processes require an inert (e.g., argon) or reactive atmosphere. For these tasks, you need a specialized furnace designed for atmosphere control.
Heating and Cooling Rates
While their temperature control is precise, standard muffle furnaces may not offer the extremely rapid heating or cooling rates required for certain specialized research, such as creating metallic glasses or performing thermal shock tests.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of furnace and process parameters depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (ashing): Prioritize a furnace with certified temperature uniformity and accuracy to ensure complete and repeatable combustion of your samples.
- If your primary focus is material property alteration (heat treating): You must consider temperature range, ramp-rate control, and whether your process requires a specialized furnace with a controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing (ceramics or glass): Look for a furnace with the appropriate chamber size for your throughput, robust construction for production cycles, and exceptional temperature uniformity for consistent product quality.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is a powerful instrument for any process that demands pure, high-intensity heat.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Key Uses | Why Muffle Furnaces Excel |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Testing | Ashing for food, water, drugs | Contaminant-free environment ensures accurate ash analysis |
| Material Transformation | Annealing, sintering, brazing | Precise temperature control for altering material properties |
| Manufacturing | Ceramics firing, glass fusing | Uniform heating for consistent product quality and integrity |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for ashing, heat treatment, or manufacturing. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















