In short, a muffle furnace can process an incredibly wide range of materials, including most metals, ceramics, glass, and certain plastics or organic compounds. Its primary function is to heat materials to very high temperatures in a controlled environment, making it a versatile tool for applications ranging from metallurgical heat treatment and ceramic firing to analytical chemistry.
The specific materials a muffle furnace can handle depend critically on the furnace's type. A standard furnace operating in air is suitable for many common processes, but materials that react with oxygen at high temperatures require a specialized vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace.

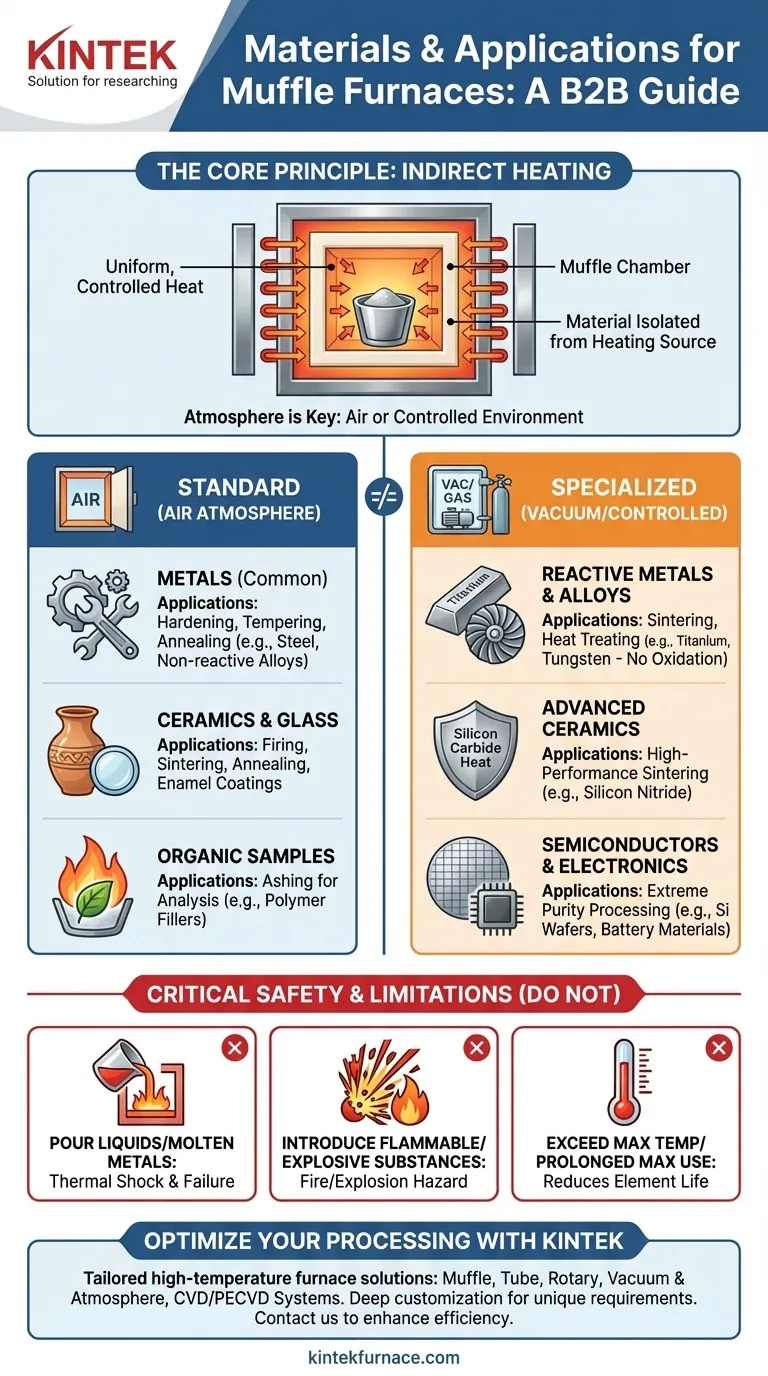
The Core Principle: What Is a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace operates on the principle of indirect heating. The material being processed is placed inside a chamber, or "muffle," which is then heated from the outside by heating elements.
The Benefit of Indirect Heating
This design isolates the material from direct contact with the heating source and any contaminants from combustion (in fuel-fired models). It provides excellent temperature uniformity and control, which is critical for sensitive processes.
The Role of Atmosphere
The default atmosphere inside a standard muffle furnace is air. This is perfectly suitable for many applications, such as annealing common metals or firing clay. However, this oxygen-rich environment is detrimental to other materials, which leads to a critical distinction.
Common Materials by Furnace Type
The most important factor in determining material compatibility is whether the process requires an air atmosphere or a controlled (inert or vacuum) atmosphere.
Standard (Air Atmosphere) Muffle Furnaces
These are the most common and versatile types of furnaces. They are ideal for processes that are stable in air or that intentionally use oxygen.
- Metals: Used for hardening, tempering, and annealing steel and other non-reactive alloys.
- Ceramics & Glass: Essential for firing pottery, sintering non-reactive ceramics, creating enamel coatings, and annealing glass to remove internal stresses.
- Organic Samples: Used in analytical chemistry for ashing, where a sample is burned to determine its inorganic, non-combustible content (e.g., filler in a polymer).
Specialized (Vacuum or Controlled Atmosphere) Furnaces
When a material cannot be exposed to air at high temperatures, a specialized furnace is required. These are often still muffle-style furnaces but with added capabilities for atmosphere control.
- Reactive Metals & Alloys: Sintering or heat-treating materials like titanium, tungsten, molybdenum, and superalloys requires a vacuum or inert gas to prevent rapid oxidation.
- Advanced Ceramics: Manufacturing high-performance ceramics like silicon nitride or silicon carbide often involves sintering processes that must be free of oxygen.
- Semiconductors & Electronics: Processing silicon wafers, gallium arsenide, and various battery materials requires extreme purity and a controlled atmosphere to achieve the desired electronic properties.
Understanding Critical Limitations and Safety
To ensure safe and effective operation, you must respect the furnace's design limitations. Misuse can lead to equipment damage or hazardous situations.
Prohibited Material States
It is strictly forbidden to pour liquids or molten metals directly into the furnace chamber. The extreme thermal shock can crack the ceramic muffle, leading to catastrophic failure and destroying the heating elements. Materials must be in a solid state and placed in a suitable crucible or container.
Prohibited Chemical Properties
Never place flammable, volatile, or explosive substances in a muffle furnace. The high temperatures will cause them to combust or expand rapidly, creating a severe fire or explosion hazard.
Operational Temperature Limits
Every furnace has a maximum rated temperature that should never be exceeded. Furthermore, running the furnace at its maximum temperature for extended periods can significantly shorten the life of the heating elements and insulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace is about matching the tool to the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment, ashing, or firing non-reactive materials: A standard air-atmosphere muffle furnace is the correct and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is sintering oxygen-sensitive metals, purifying materials, or processing advanced ceramics: You must use a furnace with vacuum or controlled inert gas capabilities.
- If your primary focus is material analysis: The specific test dictates the furnace; ashing requires a standard furnace, while tests on high-purity alloys may require a vacuum furnace.
Ultimately, understanding the interaction between your material and the furnace's atmosphere at high temperatures is the key to achieving successful results.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Compatible Furnace Type | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metals (e.g., steel) | Standard (Air) | Hardening, annealing, tempering |
| Ceramics & Glass | Standard (Air) | Firing, sintering, annealing |
| Organic Samples | Standard (Air) | Ashing for analysis |
| Reactive Metals (e.g., titanium) | Specialized (Vacuum/Controlled) | Sintering, heat treatment |
| Advanced Ceramics (e.g., silicon nitride) | Specialized (Vacuum/Controlled) | High-performance sintering |
| Semiconductors (e.g., silicon wafers) | Specialized (Vacuum/Controlled) | Processing for electronics |
Ready to optimize your material processing with the right furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















