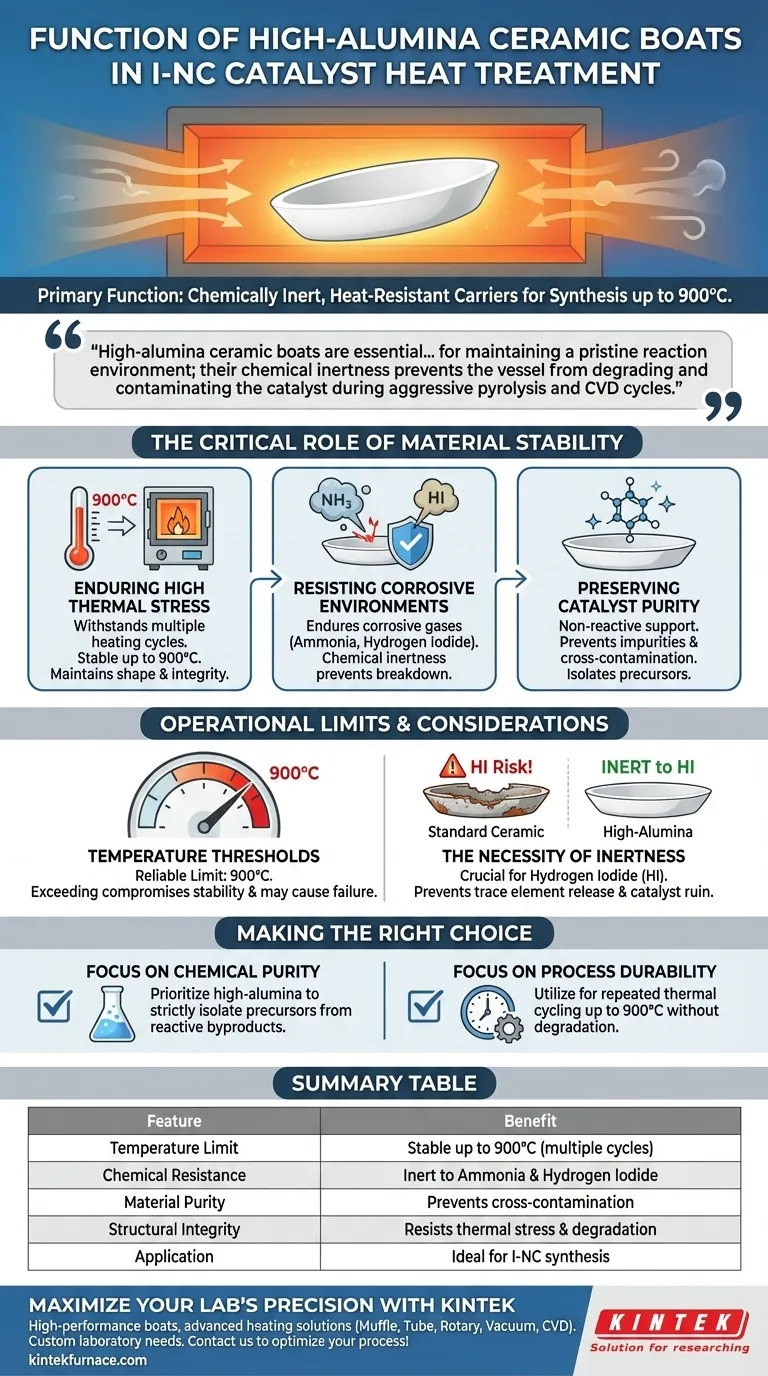
High-alumina ceramic boats function primarily as chemically inert, heat-resistant carriers designed to hold precursor materials during the synthesis of iodine-doped nitrogen-carbon (I-NC) catalysts. Their specific role is to provide a stable isolation platform that withstands temperatures up to 900°C without reacting with corrosive gases like ammonia or hydrogen iodide. By resisting these harsh conditions, they prevent contamination and ensure the structural integrity of the synthesis process.
High-alumina ceramic boats are essential not just for holding material, but for maintaining a pristine reaction environment; their chemical inertness prevents the vessel from degrading and contaminating the catalyst during aggressive pyrolysis and CVD cycles.

The Critical Role of Material Stability
Enduring High Thermal Stress
The synthesis of I-NC catalysts requires rigorous heat treatment, specifically involving pyrolysis and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
High-alumina boats are selected for their ability to withstand multiple heating cycles.
According to technical specifications, these components remain stable at temperatures up to 900°C. This thermal resilience ensures the boat maintains its shape and structural integrity throughout the heating and cooling phases.
Resisting Corrosive Environments
The doping process introduces highly reactive and corrosive agents into the heating chamber.
Specifically, the process involves gases such as ammonia and hydrogen iodide.
Standard ceramic or metallic carriers might degrade or corrode when exposed to these chemicals at high temperatures. High-alumina ceramic is distinct because of its chemical inertness, allowing it to endure exposure to these specific corrosive gases without breaking down.
Preserving Catalyst Purity
The ultimate goal of the heat treatment is to create a specific chemical structure in the catalyst.
Any reaction between the carrier boat and the precursors would introduce impurities, altering the iodine doping levels or the carbon structure.
By acting as a strictly non-reactive support, the high-alumina boat ensures that the final product remains pure. It isolates the precursors from the furnace environment, ensuring the chemical reaction is limited strictly to the intended synthesis materials.
Operational Limits and Considerations
Temperature Thresholds
While high-alumina boats offer excellent stability, they are not invincible.
The data indicates a reliable upper limit of 900°C for these specific applications.
Exceeding this temperature threshold during aggressive heat treatments could compromise the boat's stability, potentially leading to material failure or subtle reactivity that could impact the catalyst.
The Necessity of Inertness
It is a common pitfall to assume any ceramic vessel will suffice for pyrolysis.
However, the presence of hydrogen iodide makes standard ceramics risky.
Failure to use high-alumina specifically designed for this inertness can lead to cross-contamination, where the boat releases trace elements into the I-NC catalyst, effectively ruining the doping profile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
To ensure the successful production of iodine-doped nitrogen-carbon catalysts, consider the following regarding your choice of carrier:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize high-alumina boats to strictly isolate precursors from reactive byproducts like hydrogen iodide and ammonia.
- If your primary focus is Process Durability: Utilize these boats for their ability to withstand repeated thermal cycling up to 900°C without structural degradation.
By selecting the correct carrier material, you convert a potential variable—the reaction vessel—into a reliable constant.
Summary Table:
| Feature | High-Alumina Ceramic Boat Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Limit | Stable up to 900°C for multiple cycles |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to corrosive Ammonia and Hydrogen Iodide |
| Material Purity | Prevents cross-contamination during CVD/Pyrolysis |
| Structural Integrity | Resists thermal stress and degradation |
| Application | Ideal for Iodine-doped Nitrogen-Carbon (I-NC) synthesis |
Maximize Your Lab’s Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let material contamination compromise your research. KINTEK provides high-performance high-alumina ceramic boats and advanced heating solutions tailored for rigorous synthesis environments.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a full range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique high-temperature laboratory needs. Ensure your catalysts maintain their structural integrity and chemical purity with the industry standard in thermal equipment.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your heat treatment process!
Visual Guide
References
- Junjun Pei, Jinming Luo. Non-metallic iodine single-atom catalysts with optimized electronic structures for efficient Fenton-like reactions. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56246-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What roles do metal shielding disks and heat shields play in in-situ SEM? Ensure Precision & Protect Your Lab Equipment
- Why is a high-performance vacuum pumping system necessary for industrial alloys? Ensure Purity & Peak Performance
- What is the critical role of a mechanical vacuum pump in WS2 gas sensor prep? Ensure High Purity & Performance
- Why are silicon carbide crucibles selected for C95800 aluminum bronze? Ensure Purity & Efficiency
- What role does a high-temperature heating stage play in characterizing the thermal stability of piezoelectric ceramics?
- What are the functions of Silica Quartz Tubes and quartz glass wool in RDF pyrolysis? Enhancing Experimental Accuracy
- Why are evaporators and condensers required for zirconium tetrachloride purification? Mastering Nuclear-Grade Standards
- What is the function of a vacuum rotary vane pump in hydrogen measurement? Ensure High-Purity Gas Analysis Baseline
















